|
Pfeiffer Syndrome
Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis) which affects the shape of the head and face. In addition, the syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands (such as wide and deviated thumbs) and feet (such as wide and deviated big toes). Pfeiffer syndrome is caused by mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptors ''FGFR1'' and ''FGFR2''. The syndrome is grouped into three types, type 1 (classic Pfeiffer syndrome) being milder and caused by mutations in either gene and types 2 and 3 being more severe, often leading to death in infancy, caused by mutations in ''FGFR2''. There is no cure for the syndrome. Treatment is supportive and often involves surgery in the earliest years of life to correct skull deformities and respiratory function. Most individuals with Pfeiffer syndrome type 1 have a normal intelligence and life span, while types 2 and 3 typically result in neurodevelopmental disorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Clasped Thumb
Congenital clasped thumb describes an anomaly which is characterized by a fixed thumb into the palm at the metacarpophalangeal joint in one or both hands.Miura T: Flexion deformities of the thumb. In Buck-Gramcko D (ed): Congenital Malformations of the Hand and Forearm. London, Churchill Livingstone, 1998, pp 425-429. The incidence and genetic background are unknown. A study of Weckesser et al. showed that boys are twice as often affected with congenital clasped thumb compared to girls. The anomaly is in most cases bilateral (present in both hands). A congenital clasped thumb can be an isolated anomaly, but can also be attributed to several syndromes. Causes The thumb contains five groups of muscle and/or tendons: # Extensor tendons (to stretch the thumb) # Flexor muscles/tendons (to bend the thumb) # Abductor muscles/tendons (to move the thumb outwards) # Adductor muscle (to move the thumb inwards) # Opposing muscles (to move the thumb opposite the small finger) In order for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince (musician)
Prince Rogers Nelson (June 7, 1958April 21, 2016), more commonly known mononymously as Prince, was an American singer-songwriter, musician, and record producer. The recipient of numerous awards and nominations, he is widely regarded as one of the greatest musicians of his generation. He was known for his flamboyant, androgynous persona; his wide vocal range, which included a far-reaching falsetto and high-pitched screams; and his skill as a multi-instrumentalist, often preferring to play all or most of the instruments on his recordings. Prince produced his albums himself, pioneering the Minneapolis sound. His music incorporated a wide variety of styles, including funk, R&B, rock, new wave, soul In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being". Etymology The Modern English noun ''soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest attes ..., synth-pop, pop music, pop, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrocephalosyndactylia
Acrocephalosyndactyly is a group of autosomal dominant congenital disorders characterized by craniofacial (craniosynostosis) and hand and foot (syndactyly) abnormalities. When polydactyly is present, the classification is acrocephalopolysyndactyly. Acrocephalosyndactyly is mainly diagnosed postnatally, although prenatal diagnosis is possible if the mutation is known to be within the family genome. Treatment often involves surgery in early childhood to correct for craniosynostosis and syndactyly. Characteristics Acrocephalosyndactyly presents in numerous different subtypes, however, considerable overlap in symptoms occurs. Generally, all forms of acrocephalosyndactyly are characterized by craniofacial, hand, and foot abnormalities, such as premature closure of the fibrous joints in between certain bones of the skull, fusion of certain fingers or toes, and/or more than the normal number of digits. Some subtypes also involve structural heart deformations that are present at birth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Cohen (doctor)
M. Michael Cohen Jr. (March 28, 1937 – February 11, 2018) was an American pathologist and geneticist who was Professor Emeritus of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University (Emeritus). He was the first doctor to diagnose Proteus syndrome, in 1979. Life and career Cohen was born in Boston, Massachusetts, and studied at the University of Michigan, Tufts University, the University of Minnesota, and Boston University. His post-graduate training included a fellowship in pathology and medical genetics with Robert Gorlin (1923–2006), an oral pathologist and geneticist who described a large number of syndromes, including one they delineated together known as Gorlin–Cohen syndrome. Cohen held a bachelor's degree and doctorate in anthropology; he received a Doctor of Dental Surgery and a master's degree in oral and maxillofacial pathology; he also held a certificate in international health. After serving as Professor of oral and maxillofacial surgery and pediatrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Paternal Age
The paternal age effect is the statistical relationship between the father's age at conception and biological effects on the child. Such effects can relate to birthweight, congenital disorders, life expectancy and psychological outcomes. A 2017 review found that while severe health effects are associated with higher paternal age, the total increase in problems caused by paternal age is low. While paternal age has increased since 1960–1970, this is not seen as a major public health concern. The genetic quality of sperm, as well as its volume and motility, all may decrease with age, leading the population geneticist James F. Crow to claim that the "greatest mutational health hazard to the human genome is fertile older males". The paternal age effect was first proposed implicitly by physician Wilhelm Weinberg in 1912 and explicitly by psychiatrist Lionel Penrose in 1955. DNA-based research started more recently, in 1998, in the context of paternity testing. Health effects Eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum. Inactive fibroblasts (called fibrocytes) are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have a reduced amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Although disjointed and scattered when they have to cover a large space, fibroblasts, when crowded, often locally align in parallel clusters. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, although they may contribute to basal lamina components in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 10 (human)
Chromosome 10 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 10 spans about 133 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 10. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 10. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases are related to genes on chromos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) also known as CD332 (cluster of differentiation 332) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGFR2'' gene residing on chromosome 10. FGFR2 is a receptor for fibroblast growth factor. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. This particular family member is a high-affinity receptor for acidic, basic and/or ker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 8 (human)
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 145 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells. About 8% of its genes are involved in brain development and function, and about 16% are involved in cancer. A unique feature of 8p is a region of about 15 megabases that appears to have a high mutation rate. This region shows a significant divergence between human and chimpanzee, suggesting that its high mutation rates have contributed to the evolution of the human brain. __TOC__ Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 8. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
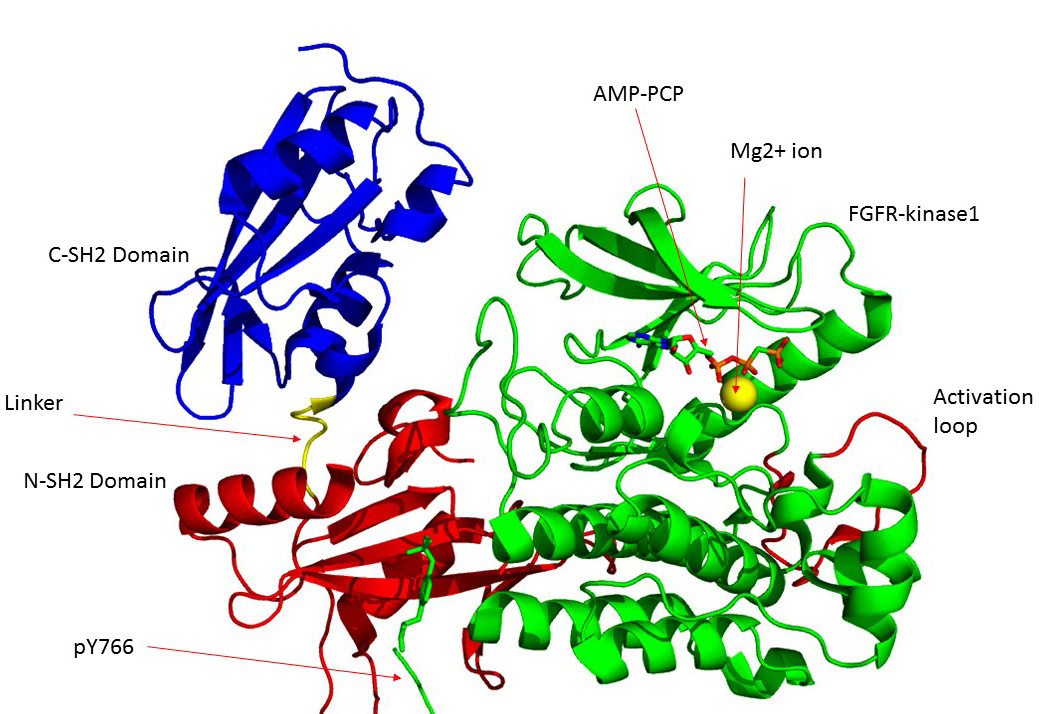
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1), also known as basic fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, fms-related tyrosine kinase-2 / Pfeiffer syndrome, and CD331, is a receptor tyrosine kinase whose ligands are specific members of the fibroblast growth factor family. FGFR1 has been shown to be associated with Pfeiffer syndrome, and clonal eosinophilias. Gene The ''FGFR1'' gene is located on human chromosome 8 at position p11.23 (i.e. 8p11.23), has 24 exons, and codes for a Precursor mRNA that is alternatively spliced at exons 8A or 8B thereby generating two mRNAs coding for two FGFR1 isoforms, FGFR1-IIIb (also termed FGFR1b) and FGFR1-IIIc (also termed FGFR1c), respectively. Although these two isoforms have different tissue distributions and FGF-binding affinities, FGFR1-IIIc appears responsible for most of functions of the FGFR1 gene while FGFR1-IIIb appears to have only a minor, somewhat redundant functional role. There are four other members of the ''FGFR1'' gene family: FGF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)