|
Peziza Cerea
''Peziza cerea'', commonly known as the Cellar Cup is a species of ascomycete fungus in the genus ''Peziza'', family Pezizaceae. In common with other ascomycetes the upper surface of the fungus has a layer of cylindrical spore producing cells called asci, from which the ascospores are forcibly discharged. Description A yellow grey to beige fungus internally, less than 5 cm across with a granular or brittle flesh. The stype is placed in a lateral position, but is small or even entirely absent. The spore colour is white, cream or yellowish; they are elliptical and smooth. The cup exterior is white in colour. Characteristics ''Peziza cerea'' can be initially identified by its growth in cellars, damp mortar, soil between pavement slabs, on rotting sandbags, plant material or manure. Found all year round. Its upper surface (at maturity) is usually somewhat wrinkled near the centre; a whitish and minutely fuzzy under surface; a round, cuplike shape when young, and a flattened-ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Sowerby
James Sowerby (21 March 1757 – 25 October 1822) was an English naturalist, illustrator and mineralogist. Contributions to published works, such as ''A Specimen of the Botany of New Holland'' or ''English Botany'', include his detailed and appealing plates. The use of vivid colour and accessible texts were intended to reach a widening audience in works of natural history. Biography James Sowerby was born in Lambeth, London, his parents were named John and Arabella. Having decided to become a painter of flowers his first venture was with William Curtis, whose ''Flora Londinensis'' he illustrated. Sowerby studied art at the Royal Academy and took an apprenticeship with Richard Wright. He married Anne Brettingham De Carle and they were to have three sons: James De Carle Sowerby (1787–1871), George Brettingham Sowerby I (1788–1854) and Charles Edward Sowerby (1795–1842), the Sowerby family of naturalists. His sons and theirs were to contribute and continue the enormous vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peziza
''Peziza'' is a large genus of saprophytic cup fungi that grow on the ground, rotting wood, or dung. Most members of this genus are of unknown edibility and are difficult to identify as separate species without use of microscopy. The polyphyletic genus has been estimated to contain over 100 species. Species Species include: * '' Peziza ampliata'' * ''Peziza arvernensis'' * ''Peziza badia'' * ''Peziza cerea'' * ''Peziza domiciliana'' * '' Peziza echinospora'' * ''Peziza erini'' * ''Peziza fimeti'' * '' Peziza granulosa'' * '' Peziza halophila'' * ''Peziza infossa'' * ''Peziza micropus'' group * ''Peziza moseri'' * ''Peziza oliviae'' * ''Peziza ostracoderma'' * ''Peziza petersii'' * ''Peziza phyllogena'' * ''Peziza praetervisa'' * ''Peziza repanda'' * ''Peziza succosa'' * ''Peziza sylvestris'' * ''Peziza varia'' * ''Peziza vesiculosa'' * ''Peziza violacea ''Peziza violacea'', commonly known as the violet fairy cup or the violet cup fungus, is a species of fungus in the genus '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pezizaceae
The Pezizaceae (commonly referred to as cup fungi) are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota which produce mushrooms that tend to grow in the shape of a "cup". Spores are formed on the inner surface of the fruit body (mushroom). The cup shape typically serves to focus raindrops into splashing spores out of the cup. Additionally, the curvature enables wind currents to blow the spores out in a different manner than in most agarics and boletes. Cup fungi grow in peculiar shapes, frequently resembling cups or saucers. For example, the orange peel fungus (''Aleuria aurantia'') resembles a discarded orange rind. They may be vividly colored, like the scarlet cup (''Sarcoscypha coccinea''), which is often one of the first signs of spring where it grows. According to one 2008 estimate, the family contains 31 genera and 230 species. Subtaxa Pezizaceae includes the following: *'' Adelphella'' **'' Adelphella babingtonii'' *'' Amylascus'' **'' Amylascus tasmanicus'' *'' Aquapeziza'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
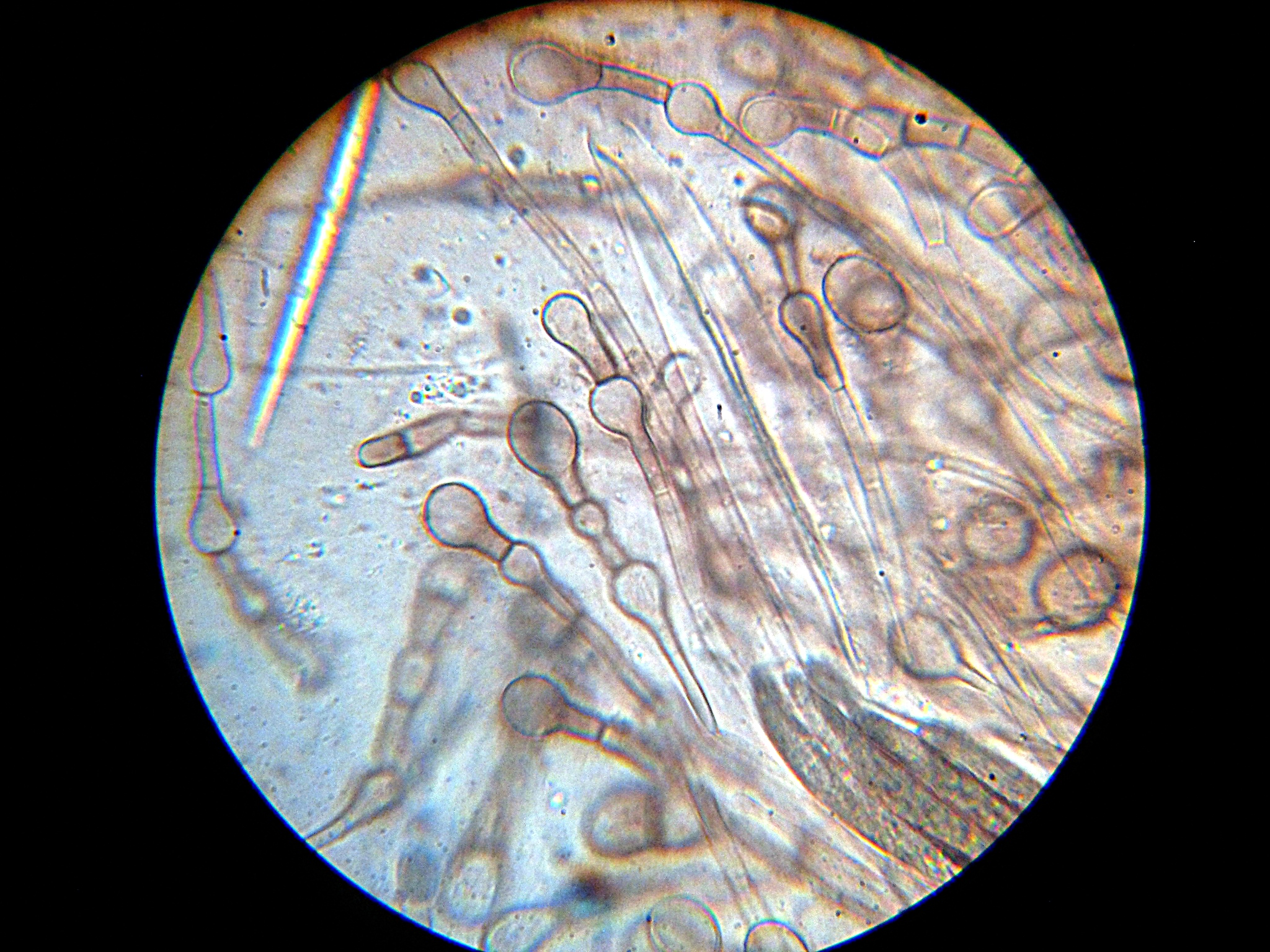
Ascus
An ascus (; ) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. ''Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. ''Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some ''Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the "bourrelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (plural cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that ar ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peziza Cerea Detail
''Peziza'' is a large genus of saprophytic cup fungi that grow on the ground, rotting wood, or dung. Most members of this genus are of unknown edibility and are difficult to identify as separate species without use of microscopy. The polyphyletic genus has been estimated to contain over 100 species. Species Species include: * ''Peziza ampliata'' * '' Peziza arvernensis'' * '' Peziza badia'' * ''Peziza cerea'' * ''Peziza domiciliana'' * '' Peziza echinospora'' * ''Peziza erini'' * '' Peziza fimeti'' * '' Peziza granulosa'' * '' Peziza halophila'' * ''Peziza infossa'' * '' Peziza micropus'' group * '' Peziza moseri'' * '' Peziza oliviae'' * '' Peziza ostracoderma'' * '' Peziza petersii'' * '' Peziza phyllogena'' * '' Peziza praetervisa'' * '' Peziza repanda'' * '' Peziza succosa'' * '' Peziza sylvestris'' * ''Peziza varia ''Peziza varia'', commonly known as the Palomino cup or recurved cup, is a species of fungus in the genus ''Peziza'', family Pezizaceae. Description ''Pez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detail Of Peziza Cerea
Detail(s) or The Detail(s) may refer to: Film and television * ''Details'' (film), a 2003 Swedish film * ''The Details'' (film), a 2011 American film * ''The Detail'', a Canadian television series * "The Detail" (''The Wire''), a television episode Music * ''Details'' (album), by Frou Frou, 2002 * Detail (record producer), Noel Fisher (born c. 1978), American music producer and performer * The Details, a Canadian rock band Periodicals * ''DETAIL'' (professional journal), an architecture and construction journal * ''Details'' (magazine), an American men's magazine See also * Auto detailing, a car-cleaning process * Level of detail (computer graphics), a 3D computer graphics concept * Security detail, a team assigned to protect an individual or group * Detaille Island Detaille Island is a small island off the northern end of the Arrowsmith Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica. From 1956 to 1959 it was home to "Base W" of the British Antarctic Survey and closed after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saprobic
Saprotrophic nutrition or lysotrophic nutrition is a process of chemoheterotrophic extracellular digestion involved in the processing of decayed (dead or waste) organic matter. It occurs in saprotrophs, and is most often associated with fungi (for example ''Mucor'') and soil bacteria. Saprotrophic microscopic fungi are sometimes called saprobes; saprotrophic plants or bacterial flora are called saprophytes ( sapro- 'rotten material' + -phyte 'plant'), although it is now believed that all plants previously thought to be saprotrophic are in fact parasites of microscopic fungi or other plants. The process is most often facilitated through the active transport of such materials through endocytosis within the internal mycelium and its constituent hyphae. states the purpose of saprotrophs and their internal nutrition, as well as the main two types of fungi that are most often referred to, as well as describes, visually, the process of saprotrophic nutrition through a diagram of hyph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peziza Repanda
''Peziza varia'', commonly known as the Palomino cup or recurved cup, is a species of fungus in the genus ''Peziza'', family Pezizaceae. Description ''Peziza varia'' can be identified by its growth on rotted wood or wood chips, its brown upper surface (at maturity) that is usually somewhat wrinkled near the center; a whitish and minutely fuzzy under surface; a round, cuplike shape when young, and a flattened-irregular shape when mature; attachment to the wood under the center of the mushroom, rather than under the whole cup; thin, brittle flesh (rather than thick and gelatinous) and smooth, elliptical spores that lack oil droplets. The cup at first is pale brown or whitish overall, the under surface minutely fuzzy and the upper surface smoother, with a tiny stem-like structure. In maturity it is flattened-irregular or bent backwards, 2–12 cm across, the margin often splitting, upper surface brown and smooth, often "pinched" or somewhat wrinkled over the center, under surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pezizomycetes
Pezizomycetes are a class of fungi within the division Ascomycota. Pezizomycetes are apothecial fungi, meaning that their spore-producing/releasing bodies (ascoma) are typically disk-like, bearing on their upper surfaces a layer of cylindrical spore-producing cells called asci, from which the spores are forcibly discharged. Important groups include: cup fungi (Peziza), morels, Elfin saddles, and truffles A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus ''Tuber''. In addition to ''Tuber'', many other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including ''Geopora'', ''Peziza .... References * * Pezizomycotina Fungus classes Taxa described in 1997 {{Pezizomycetes-stub de:Pezizomycetes ru:Pezizomycetes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of North America
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fungi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi Of Europe
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a Kingdom (biology), kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |