|
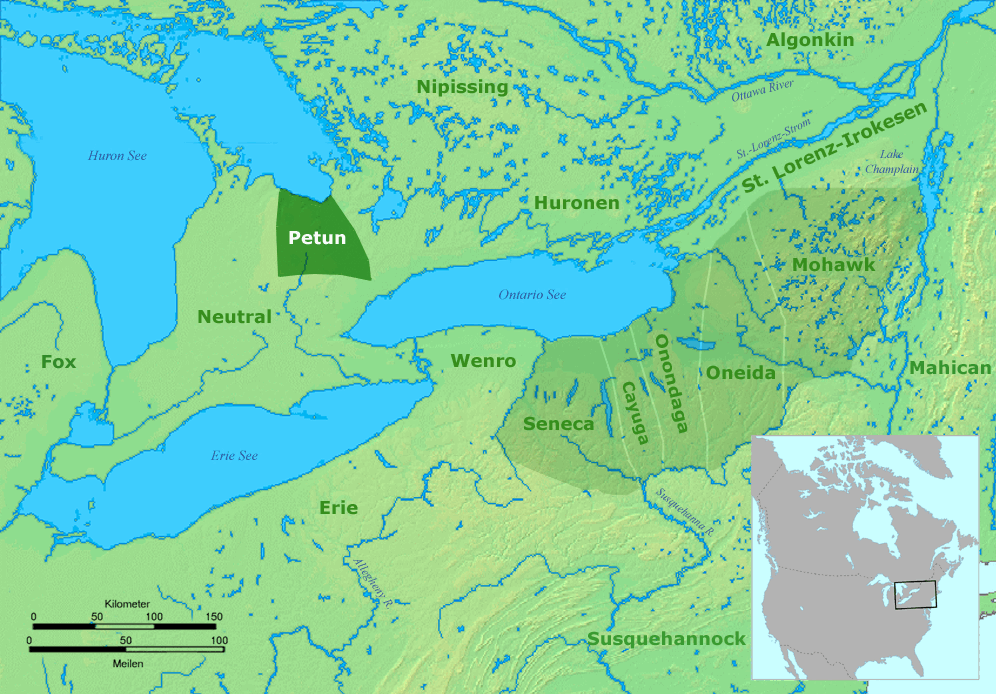
Petun
The Petun (from french: pétun), also known as the Tobacco people or Tionontati ("People Among the Hills/Mountains"), were an indigenous Iroquoian people of the woodlands of eastern North America. Their last known traditional homeland was south of Lake Huron's Georgian Bay, in what is today's Canadian province of Ontario The Petun were closely related to the Huron, or Wendat. Similarly to other Iroquoian peoples, they were structured as a confederacy. One of the less numerous Iroquoian peoples when they became known to Europeans, they had eight or nine villages in the early 17th century, and are estimated to have numbered around 8000 prior to European contact. A number of disease epidemics were documented in Huron–Petun societies between 1634 and 1640, which have been linked to the arrival of settlers from urban Europe; this decimated their population. Although they each spoke Iroquoian languages, they were independent of the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy (Haudeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petun Map
The Petun (from french: pétun), also known as the Tobacco people or Tionontati ("People Among the Hills/Mountains"), were an indigenous Iroquoian people of the woodlands of eastern North America. Their last known traditional homeland was south of Lake Huron's Georgian Bay, in what is today's Canadian province of Ontario The Petun were closely related to the Huron, or Wendat. Similarly to other Iroquoian peoples, they were structured as a confederacy. One of the less numerous Iroquoian peoples when they became known to Europeans, they had eight or nine villages in the early 17th century, and are estimated to have numbered around 8000 prior to European contact. A number of disease epidemics were documented in Huron–Petun societies between 1634 and 1640, which have been linked to the arrival of settlers from urban Europe; this decimated their population. Although they each spoke Iroquoian languages, they were independent of the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy (Haudeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyandot People
The Wyandot people, or Wyandotte and Waⁿdát, are Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands. The Wyandot are Iroquoian Indigenous peoples of North America who emerged as a confederacy of tribes around the north shore of Lake Ontario with their original homeland extending to Georgian Bay of Lake Huron and Lake Simcoe in Ontario, Canada and occupying some territory around the western part of the lake. The Wyandot, not to be mistaken for the Huron-Wendat, predominantly descend from the Tionontati tribe. The Tionontati (or Tobacco/Petun people) never belonged to the Huron (Wendat) Confederacy. However, the Wyandot(te) have connections to the Wendat-Huron through their lineage from the Attignawantan, the founding tribe of the Huron. The four Wyandot(te) Nations are descended from remnants of the Tionontati, Attignawantan and Wenrohronon (Wenro), that were "all unique independent tribes, who united in 1649-50 after being defeated by the Iroquois Confederacy." After thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Nation
The Neutral Confederacy (also Neutral Nation, Neutral people, or ''Attawandaron'' by neighbouring tribes) were an Iroquoian people who lived in what is now southwestern and south-central Ontario in Canada, North America. They lived throughout the area bounded by the southern half of Lake Huron, the entire northern shoreline of Lake Erie, from the Detroit River in the west to the Niagara River in the east, plus northward around the western end of Lake Ontario. Their territory was southwest of the Petun and west of the southern area of the Huron people, or Wendat territory. They were related to other Iroquoian-language speakers: the Huron people, the Petun (who later merged with the Huron), the Wenro to their east, and the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederation further to the east, as well as to the Erie people of the south shore of Lake Erie, and the Susquehannock of Central Pennsylvania. Like others of Iroquoian language and culture, the tribes would raid and feud wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huronia (region)
Huronia is a historical region in the Great Lakes area of eastern North America. It is positioned between Lakes Erie, Ontario, and Huron. Similarly to the latter, it takes its name from the Huron, an Iroquoian society that flourished in the years leading up to contact with Europeans. The term Huronia, which was coined by later Europeans, is distinct from the term the Huron themselves used for their dwelling place, which is ("the peninsula country"). Other translations suggested are "the island apart", "the separate country", "the country with a separate language", "the one village", or "the villagers." At the time of first European contact, Wendake was "one of the most densely populated territories north of Mexico." It consisted of twenty to twenty-five settlements occupying about between Nottawasaga Bay and Lake Simcoe West to East, and Matchedash Bay and the swampy basin of the Nottawasaga River, North to South. The population was estimated to be 20-30 thousand. Following th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nottawasaga Bay
Nottawasaga Bay is a sub- bay within Georgian Bay in Southern Ontario, Canada located at the southernmost end of the main bay. The communities located on Nottawasaga Bay are Meaford, The Blue Mountains, Collingwood, Wasaga Beach and Tiny. The western shore of Nottawasaga Bay is determined by the Niagara Escarpment, which reaches Nottawasaga Bay between Collingwood and Thornbury. The southern shore is flat limestone plain, with cedar marshes. The Nottawasaga River flows into Georgian Bay near the southern end of the bay, and onward to the east the shore is predominantly sand dunes and marshes created by the strong predominant northwest winds. This part of Nottawasaga Bay is heavily built up with summer homes. Nearer to Thornbury and the Beaver River Valley there are some vineyards; many apple orchards also dot the area. The river takes its name from the Ojibwe word "Nottawasaga". ''Nottawa'' (or ''Naadowe'' in modern orthography) means "Iroquois" and ''saga'' (''zaagi'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by Deganawidah the Great Peacemaker, Hiawatha, and Jigonsaseh the Mother of Nations. For nearly 200 years, the Six Nations/Haudenosaunee Confederacy were a powerful factor in North American colonial policy, with some scholars arguing for the concept of the Middle Ground, in that Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquoian Languages
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking. As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian languages are severely or critically endangered, with only a few elderly speakers remaining. The two languages with the most speakers, Mohawk in New York and Cherokee, are spoken by less than 10% of the populations of their tribes. Family division :Northern Iroquoian ::Lake Iroquoian :::Iroquois Proper ::::Seneca (severely endangered) :::: Cayuga (severely endangered) ::::Onondaga (severely endangered) :::: Susquehannock/Conestoga (*) ::::Mohawk–Oneida ::::: Oneida (severely endangered) :::::Mohawk :::Huronian (†) :::: Huron-Wyandot (*) :::: Petun (Tobacco) (*) :::Tuscarora–Nottoway (*) ::::Tuscarora *) :::: Nottoway (*) :::Unclear :::: Wenrohronon/Wenro (*) ::::Neutral (*) ::::Erie (*) :::: Laurentian (*) :Southern Iroquoian: ::::Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the lower Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois against the Hurons, northern Algonquians and their French allies. As a result of this conflict, the Iroquois destroyed several confederacies and tribes through warfare: the Hurons or Wendat, Erie, Neutral, Wenro, Tionontate, Susquehannock, Mahican and northern Algonquins whom they defeated and dispersed, some fleeing to neighboring peoples and others assimilated, routed, or killed. The Iroquois sought to expand their territory and to monopolize the fur trade with European markets. They originally were a confederacy of the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca tribes inhabiting the lands in what is now Upstate New York along the sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To its northwest is the North Channel. Georgian Bay is surrounded by (listed clockwise) the districts of Manitoulin, Sudbury, Parry Sound and Muskoka, as well as the more populous counties of Simcoe, Grey and Bruce. The Main Channel separates the Bruce Peninsula from Manitoulin Island and connects Georgian Bay to the rest of Lake Huron. The North Channel, located between Manitoulin Island and the Sudbury District, west of Killarney, was once a popular route for steamships and is now used by a variety of pleasure craft to travel to and from Georgian Bay. The shores and waterways of the Georgian Bay are the traditional domain of the Anishinaabeg First Nations peoples to the north and Huron-Petun (Wyandot) to the south. The bay was thus a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bureau of Labor Statistics classifies the state as a part of the Mid-Atlantic regionMid-Atlantic Home : Mid-Atlantic Information Office: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics" www.bls.gov. Archived. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the north and east, Maryland to the east and northeast, Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, and Ohio to the northwest. West Virginia is the 10th-smallest state by area and ranks as the 12th-least populous state, with a population of 1,793,716 residents. The capital and largest city is Charleston. West Virginia was admitted to the Union on June 20, 1863, and was a key border state during the American Civil War. It was the only state to form by separating from a Confederate state, the second to sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Sagard
Gabriel Sagard, O.M.R., ( ''fl.'' 1614–1636) was a French lay brother and Recollect friar, a reform branch of the Order of Friars Minor known for their strict poverty. He was among the first Christian missionaries to New France, and is notable for his writings on the colony and on the Hurons (or Wendat). Sagard's origins, and the dates of his birth and death are obscure. Some historians say he was christened Théodat, others believe that Théodat was his religious name, which, however, is less likely as his signature on his works is under the name of Gabriel (see illustration). Sagard arrived in New France 28 June 1623. He was sent to accompany Father Nicholas Viel, where they joined four other members of their Order who had been there since 1615, led by Father Denis Jamet. In August, Sagard traveled to a Huron village on the southern shore of Lake Huron, where he began his missionary work and study of the Huron language. In July 1624, he was ordered by his superiors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohawk Language
Mohawk (; ''Kanienʼkéha'', " anguageof the Flint Place") is an Iroquoian language currently spoken by around 3,500 people of the Mohawk nation, located primarily in current or former Haudenosaunee territories, predominately Canada (southern Ontario and Quebec), and to a lesser extent in the United States (western and northern New York). The word "Mohawk" is an exonym. In the Mohawk language, the people say that they are from ''Kanien:ke'' ('Mohawk Country' or "Flint Stone Place") and that they are ''Kanienʼkehá꞉ka'' "People of the Flint Stone Place" or "People of the Flint Nation". The Mohawks were extremely wealthy traders, as other nations in their confederacy needed their flint for tool-making. Their Algonquian-speaking neighbors (and competitors), the People of ''Muh-heck Heek Ing'' ("food-area place"), a people called by the Dutch "Mohicans" or "Mahicans", called the People of Ka-nee-en Ka "Maw Unk Lin" or ''Bear People''. The Dutch heard and wrote that as "Mohawks" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |