|
Petrokimia Gresik
Petrokimia Gresik is a fertilizer company located in Gresik, East Java, Indonesia, which was initially established under the name 'Project of Petrokimia Surabaya'. The construction agreement was mutually signed on August 10, 1964 with the effective date on December 8, 1964. The project was officially inaugurated by the President of the Republic of Indonesia on July 10, 1972. Hence the date is ultimately commemorated as the anniversary of PT Petrokimia Gresik. Early History After the establishment of PT Pupuk Sriwidjaja located in Palembang in 1959, the government also facilitated the construction of other fertilizer factories. The forerunner of PT Petrokimia Gresik since 1956 through the State Design Bureau (''Biro Perancang Negara'' - BPN). At first, the fertilizer plant built in East Java was called 'Surabaja Petrochemical Project'. The name of ''Petrokimia'' itself comes from 'Petroleum Chemical' which is abbreviated to Petrochemical, namely chemicals made from petroleum a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gresik Regency
Gresik Regency ( older spelling: Grissee, ) is a regency within East Java Province of Indonesia. As well as a large part of the Surabaya northern and western suburbs, it includes the offshore Bawean Island, some 125 km to the north of Java and Madura. The regency's administrative centre is the town of Gresik, about 25 km to the northwest of Surabaya. Gresik Regency (excluding Bawean Island) is also part of Gerbangkertosusila, the metropolitan region of Surabaya. Etymology Thomas Stamford Raffles in his book, The History of Java, reveals that the name of Gresik comes from the word ''Giri Gisik'', which means "mountain near the coast", referring to the hilly topography of the Gresik town center near the coast. History Since the 11th century, Gresik has become an international trade center visited by many nations such as, Chinese, Arabs, Champa, and Gujarat. Gresik Regency is also the first entry point for Islam in Java, which among others is marked by the existence of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-carbohydrate Diet
Low-carbohydrate diets restrict carbohydrate consumption relative to the average diet. Foods high in carbohydrates (e.g., sugar, bread, pasta) are limited, and replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of fat and protein (e.g., meat, poultry, fish, shellfish, eggs, cheese, nuts, and seeds), as well as low carbohydrate foods (e.g. spinach, kale, chard, collards, and other fibrous vegetables). There is a lack of standardization of how much carbohydrate low-carbohydrate diets must have, and this has complicated research. One definition, from the American Academy of Family Physicians, specifies low-carbohydrate diets as having less than 20% of calories from carbohydrates. There is no good evidence that low-carbohydrate dieting confers any particular health benefits apart from weight loss, where low-carbohydrate diets achieve outcomes similar to other diets, as weight loss is mainly determined by calorie restriction and adherence. An extreme form of low-carbohydrate d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fioricet
Butalbital/acetaminophen, sold under the brand name Butapap among others, is a combination medication used to treat tension headaches and migraine headaches. It contains butalbital, a barbiturate and paracetamol (acetaminophen), an analgesic. Versions also containing caffeine are sold under the brand name Fioricet among others. It is taken by mouth. The combination is also sold with codeine. The most common side effects include sleepiness, dizziness, trouble breathing, and abdominal pain. Other severe side effects may include liver problems, confusion, addiction, and allergic reactions. Frequent use may result in medication overuse headache. Barbiturate withdrawal may occur if rapidly stopped following long term use. Use is not generally recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 1984. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, the combination butalbital/acetaminophen/caffeine was the 201st most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form taxon; they do not represent a monophyletic group (the group of all descendants of a single common ancestral species), since swans and geese are not considered ducks. Ducks are mostly aquatic birds, and may be found in both fresh water and sea water. Ducks are sometimes confused with several types of unrelated water birds with similar forms, such as loons or divers, grebes, gallinules and coots. Etymology The word ''duck'' comes from Old English 'diver', a derivative of the verb 'to duck, bend down low as if to get under something, or dive', because of the way many species in the dabbling duck group feed by upending; compare with Dutch and German 'to dive'. This word replaced Old English / 'duck', possibly to avoid confusion with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult male bird, and a younger male may be called a cockerel. A male that has been castrated is a capon. An adult female bird is called a hen and a sexually immature female is called a pullet. Humans now keep chickens primarily as a source of food (consuming both their meat and eggs) and as pets. Traditionally they were also bred for cockfighting, which is still practiced in some places. Chickens are one of the most common and widespread domestic animals, with a total population of 23.7 billion , up from more than 19 billion in 2011. There are more chickens in the world than any other bird. There are numerous cultural references to chickens – in myth, folklore and religion, and in language and literature. Genetic studies have pointed to mult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, and turkeys). The term also includes birds that are killed for their meat, such as the young of pigeons (known as squabs) but does not include similar wild birds hunted for sport or food and known as game. The word "poultry" comes from the French/Norman word ''poule'', itself derived from the Latin word ''pullus'', which means "small animal". Recent genomic study involving the four extant Junglefowl species reveals that the domestication of chicken, the most populous poultry species, occurred around 8,000 years ago in Southeast Asia - although this was previously believed to have occurred later - around 5,400 years ago - in Southeast Asia. The process may have originally occurred as a result of people hatching and rearing young birds fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
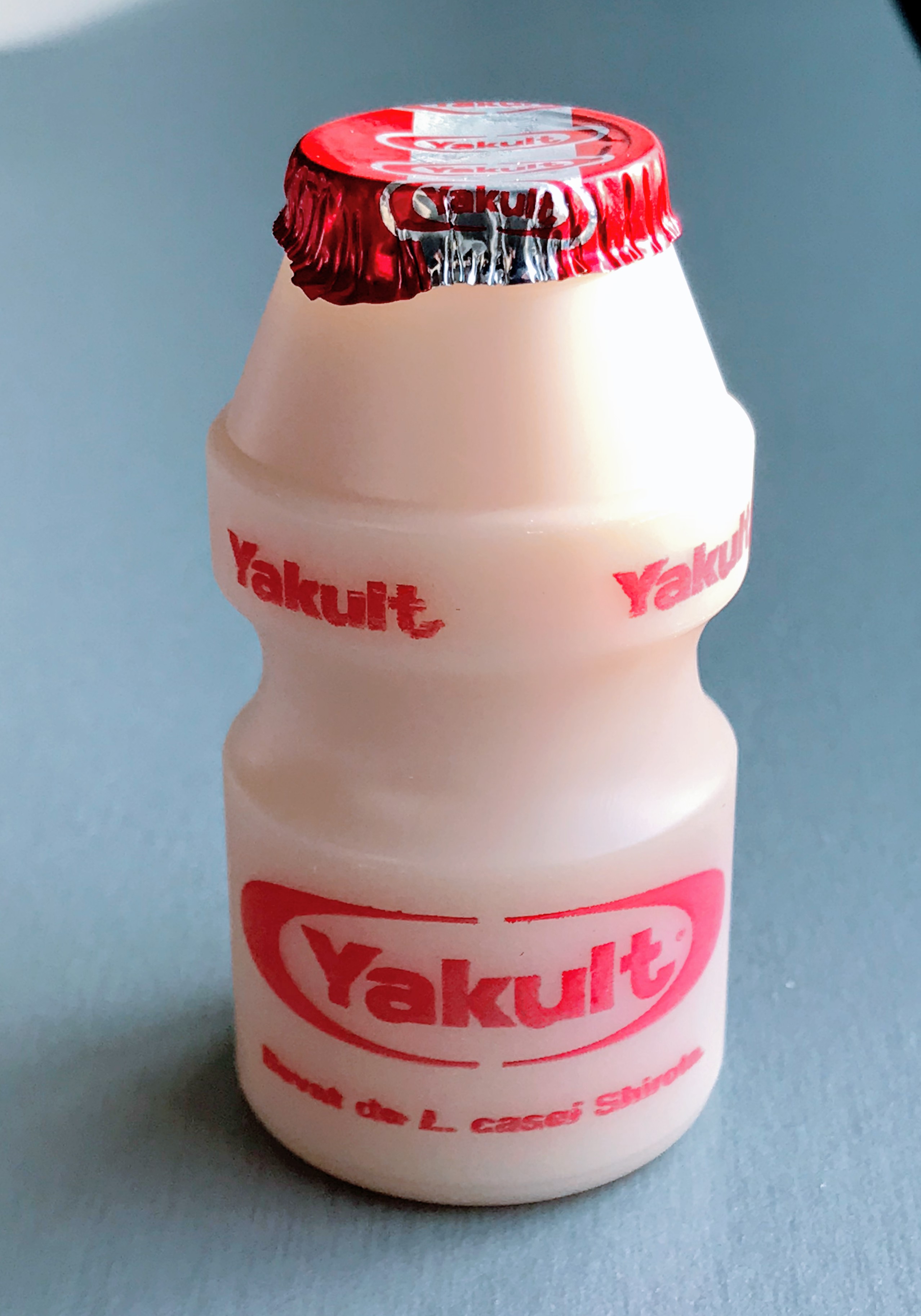
Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, but there is little evidence for many of the health benefits claimed for them. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has led to the need for stricter requirements for scientific substantiation of putative benefits conferred by microorganism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedum
''Sedum'' is a large genus of flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae, members of which are commonly known as stonecrops. The genus has been described as containing up to 600 species, subsequently reduced to 400–500. They are leaf succulents found primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, but extending into the southern hemisphere in Africa and South America. The plants vary from annual and creeping herbs to shrubs. The plants have water-storing leaves. The flowers usually have five petals, seldom four or six. There are typically twice as many stamens as petals. Various species formerly classified as ''Sedum'' are now in the segregate genera '' Hylotelephium'' and ''Rhodiola''. Well-known European species of ''Sedum'' are ''Sedum acre'', ''Sedum album'', '' Sedum dasyphyllum'', '' Sedum reflexum'' (also known as ''Sedum rupestre'') and ''Sedum hispanicum''. Description ''Sedum'' is a genus that includes annual, biennial, and perennial herbs. They are characterised by succulen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofertilizer
A biofertilizer is a substance which contains living micro-organisms which, when applied to seeds, plant surfaces, or soil, colonize the rhizosphere or the interior of the plant and promotes growth by increasing the supply or availability of primary nutrients to the host plant. Biofertilizers add nutrients through the natural processes of nitrogen fixation, solubilizing phosphorus, and stimulating plant growth through the synthesis of growth-promoting substances. The micro-organisms in biofertilizers restore the soil's natural nutrient cycle and build soil organic matter. Through the use of biofertilizers, healthy plants can be grown, while enhancing the sustainability and the health of the soil. Biofertilizers can be expected to reduce the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, but they are not yet able to replace their use. Since they play several roles, a preferred scientific term for such beneficial bacteria is "plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria" (PGPR). Biofertili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
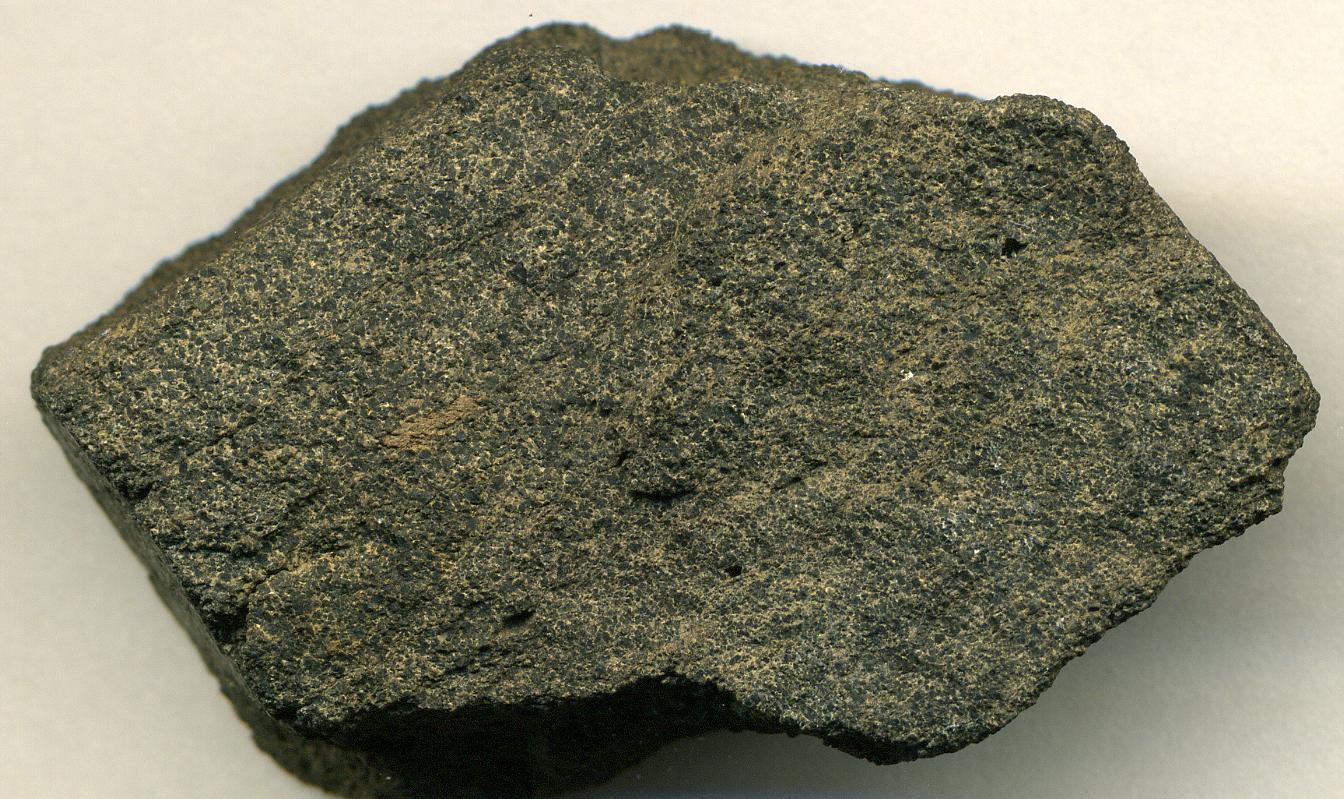
Phosphorite
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5). Marketed phosphate rock is enriched ("beneficiated") to at least 28%, often more than 30% P2O5. This occurs through washing, screening, de-liming, magnetic separation or flotation. By comparison, the average phosphorus content of sedimentary rocks is less than 0.2%.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy, ''Petrology'', Freeman, 1996, 2nd ed. pp. 345–349 The phosphate is present as fluorapatite Ca5(PO4)3F typically in cryptocrystalline masses (grain sizes < 1 μm) referred to as -sedimentary apatite deposits of uncertain origin. It is also present as |
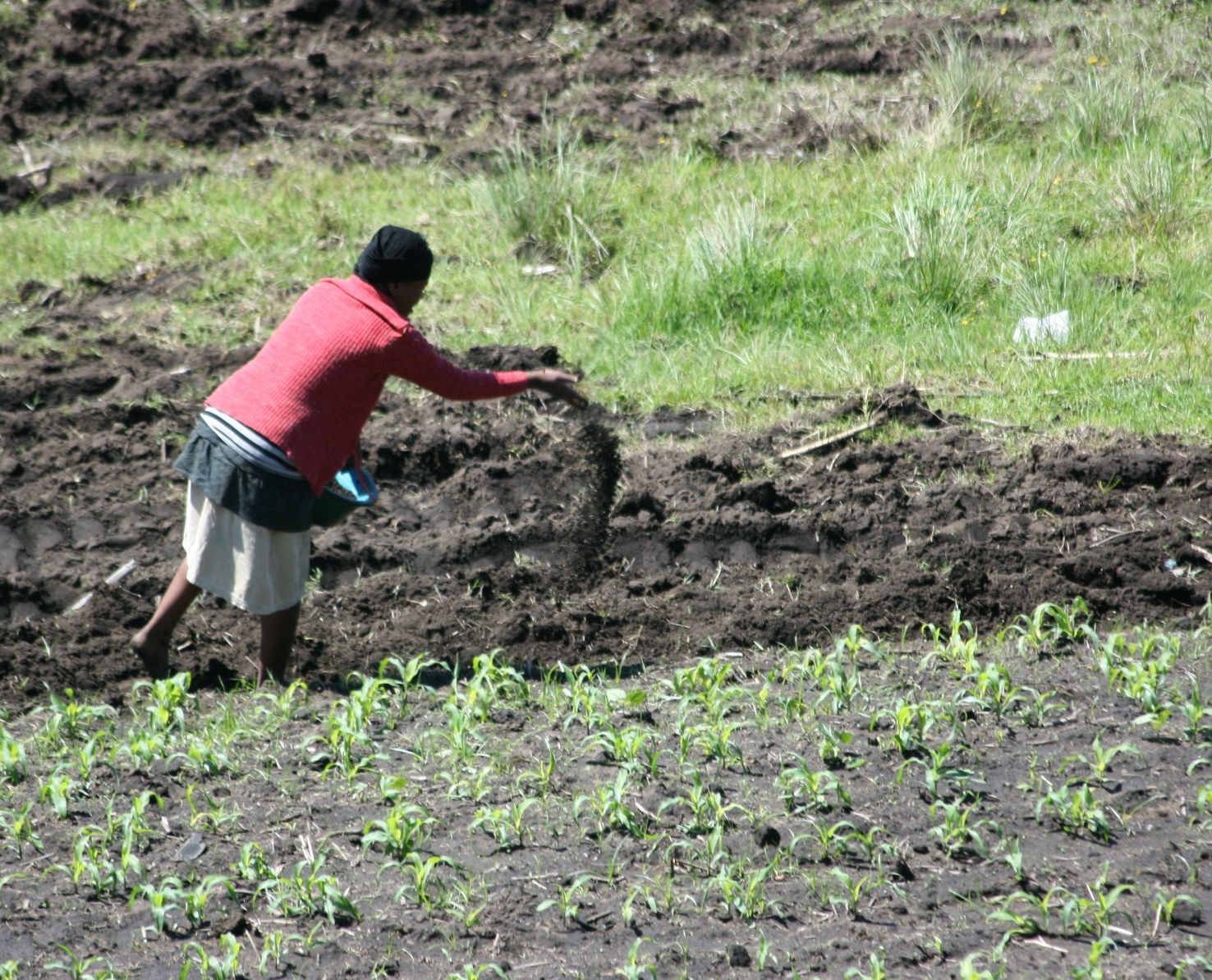
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)