|
Petrified Forest Member
The Petrified Forest Member is a stratigraphic unit of the Chinle Formation in Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, Nevada, and Utah. It preserves fossils dating back to the Triassic period. Subunits Beds (are in alphabetical order, asterisks (*) indicate usage by the U.S. Geological Survey, other usages by state geological surveys): * Capitol Reef Bed (UT*) * Correo Sandstone Bed (NM*) * Sonsela Sandstone Bed (AZ*,NM*) In the Chama Basin of New Mexico, the Chinle Formation is promoted to group status and the Petrified Forest Formation has the following members: * Painted Desert Member * Mesa Montoso Member The Mesa Montosa Member is up to thick and is mostly composed of sandstone (44%) and mudstone (35%), with a lesser proportion of siltstone (20%). The color is reddish brown to brown and the sandstone is thinly bedded and ripple laminated. The Painted Desert Member is up to thick and is primarily reddish brown bentonitic mudstone. The name was originally applied to the beds abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinle Formation Showing Each Member On A Cliff Above Capitol Reef Scenic Drive
Chinle ( nv, ) is a census-designated place (CDP) in Apache County, Arizona, United States. The name in Navajo means "flowing out" and is a reference to the location where the water flows out of the Canyon de Chelly. The population was 4,518 at the 2010 census. Geography Chinle is located at (36.154718, -109.579040). According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , of which is land and , or 0.16%, is water. Climate According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Chinle has a semi-arid climate, abbreviated "BSk" on climate maps. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 5,366 people, 1,358 households, and 1,076 families residing in the CDP. The population density was . There were 1,644 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the CDP was 91.3% Native American, 6.4% White, 0.2% Black or African American, 0.2% Asian, <0.1% |
Fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
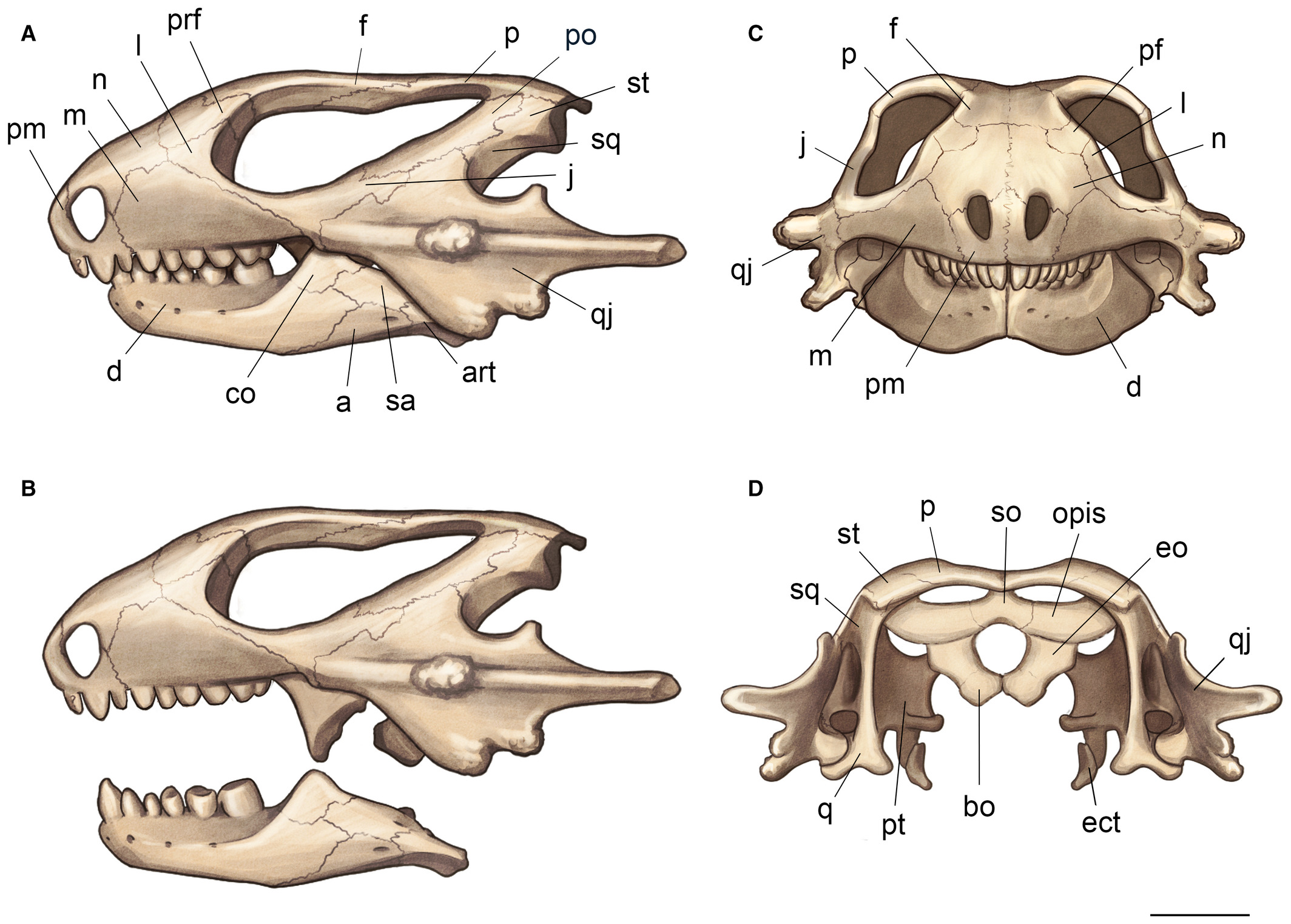
Procolophonid
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial burrowers. While diverse during the Early and Middle Triassic, they had very low diversity during the Late Triassic, and were extinct by the beginning of the Jurassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosaur
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and extinct relatives of crocodilians. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives, and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphological characteristics, such as an antorbital fenestra in the skull, serrated teeth, and an upright stance. Some extinct reptiles, such as proterosuchids and euparkeriids, possessed these features yet originated pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norian
The Norian is a division of the Triassic Period. It has the rank of an age (geochronology) or stage (chronostratigraphy). It lasted from ~227 to million years ago. It was preceded by the Carnian and succeeded by the Rhaetian. Stratigraphic definitions The Norian was named after the Noric Alps in Austria. The stage was introduced into scientific literature by Austrian geologist Edmund Mojsisovics von Mojsvar in 1869. The Norian Stage begins at the base of the ammonite biozones of '' Klamathites macrolobatus'' and '' Stikinoceras kerri'', and at the base of the conodont biozones of '' Metapolygnathus communisti'' and '' Metapolygnathus primitius''. A global reference profile for the base (a GSSP) had in 2009 not yet been appointed. The top of the Norian (the base of the Rhaetian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Cochloceras amoenum''. The base of the Rheatian is also close to the first appearance of conodont species '' Misikella spp.'' and '' Epigondolella mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detrital Zircon Geochronology
Detrital zircon geochronology is the science of analyzing the age of zircons deposited within a specific sedimentary unit by examining their inherent radioisotopes, most commonly the uranium–lead ratio. Zircon is a common accessory or trace mineral constituent of most granite and felsic igneous rocks. Due to its hardness, durability and chemical inertness, zircon persists in sedimentary deposits and is a common constituent of most sands. Zircons contain trace amounts of uranium and thorium and can be dated using several modern analytical techniques. Detrital zircon geochronology has become increasingly popular in geological studies from the 2000s mainly due to the advancement in radiometric dating techniques. Detrital zircon age data can be used to constrain the maximum depositional age, determine provenance, and reconstruct the tectonic setting on a regional scale. Detrital zircon Origin Detrital zircons are part of the sediment derived from weathering and erosion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma (unit)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the mean yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Corners
The Four Corners is a region of the Southwestern United States consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, southeastern corner of Utah, northeastern corner of Arizona, and northwestern corner of New Mexico. The Four Corners area is named after the quadripoint at the intersection of approximately 37° north latitude with 109° 03' west longitude, where the boundaries of the four states meet, and are marked by the Four Corners Monument. It is the only location in the United States where four states meet. Most of the Four Corners region belongs to semi-autonomous Native American nations, the largest of which is the Navajo Nation, followed by Hopi, Ute, and Zuni tribal reserves and nations. The Four Corners region is part of a larger region known as the Colorado Plateau and is mostly rural, rugged, and arid. In addition to the monument, commonly visited areas within Four Corners include Monument Valley, Mesa Verde National Park, Chaco Canyon, Canyons of the Ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bentonite
Bentonite () is an absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelling capacity than Ca-montmorillonite. Bentonite usually forms from the weathering of volcanic ash in seawater, or by hydrothermal circulation through the porosity of volcanic ash beds, which converts (devitrification) the volcanic glass ( obsidian, rhyolite, dacite) present in the ash into clay minerals. In the mineral alteration process, a large fraction (up to 40-50 wt.%) of amorphous silica is dissolved and leached away, leaving the bentonite deposit in place. Bentonite beds are white or pale blue or green (traces of reduced ) in fresh exposures, turning to a cream color and then yellow, red, or brown (traces of oxidized ) as the exposure is weathered further. As a swelling clay, bentonite has the ability to absorb large quantities of water, which increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |