|
Petri Net Unfoldings
Analysis of Petri nets can be performed by means of constructing either reachable state spaces (or reachable markings) or via the process of graph-based unfolding. The prefix of a Petri net unfolding, which is an acyclic Petri net graph, contains the same information about the properties of the Petri net as the reachability graph, plus it contains information about sequence, concurrency and conflict relations between Petri net transitions and Petri net places. The advantages of the use of unfolding in practice are typically associated with the fact that the unfolding prefix is much more compact than the reachability graph of the Petri net being analysed. Petri net unfoldings were originally introduced by Ken McMillan. Later they were studied by several authors, who improved the original criterion for producing the prefix of the unfolding in terms of its compactness and hence efficient analysis. There are applications of Petri net unfoldings in the analysis and synthesis of concurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petri Net
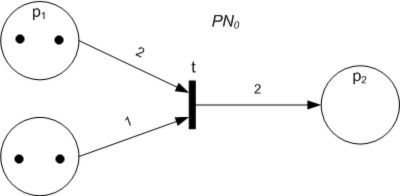
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition (PT) net, is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements, places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri—at the age of 13—for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Petri nets hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth L
Kenneth is an English given name and surname. The name is an Anglicised form of two entirely different Gaelic personal names: ''Cainnech'' and '' Cináed''. The modern Gaelic form of ''Cainnech'' is ''Coinneach''; the name was derived from a byname meaning "handsome", "comely". A short form of ''Kenneth'' is '' Ken''. Etymology The second part of the name ''Cinaed'' is derived either from the Celtic ''*aidhu'', meaning "fire", or else Brittonic ''jʉ:ð'' meaning "lord". People :''(see also Ken (name) and Kenny)'' Places In the United States: * Kenneth, Indiana * Kenneth, Minnesota * Kenneth City, Florida In Scotland: * Inch Kenneth, an island off the west coast of the Isle of Mull Other * "What's the Frequency, Kenneth?", a song by R.E.M. * Hurricane Kenneth * Cyclone Kenneth Intense Tropical Cyclone Kenneth was the strongest tropical cyclone to make landfall in Mozambique since modern records began. The cyclone also caused significant damage in the Comoro Islands and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrency (computer Science)
In computer science, concurrency is the ability of different parts or units of a program, algorithm, or problem to be executed out-of-order or in partial order, without affecting the outcome. This allows for parallel execution of the concurrent units, which can significantly improve overall speed of the execution in multi-processor and multi-core systems. In more technical terms, concurrency refers to the decomposability of a program, algorithm, or problem into order-independent or partially-ordered components or units of computation. According to Rob Pike, concurrency is the composition of independently executing computations, and concurrency is not parallelism: concurrency is about dealing with lots of things at once but parallelism is about doing lots of things at once. Concurrency is about structure, parallelism is about execution, concurrency provides a way to structure a solution to solve a problem that may (but not necessarily) be parallelizable. A number of mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asynchronous Circuit
Asynchronous circuit (clockless or self-timed circuit) is a sequential digital logic circuit that does not use a global clock circuit or signal generator to synchronize its components. Instead, the components are driven by a handshaking circuit which indicates a completion of a set of instructions. Handshaking works by simple data transfer protocols. Many synchronous circuits were developed in early 1950s as part of bigger asynchronous systems (e.g. ORDVAC). Asynchronous circuits and theory surrounding is a part of several steps in integrated circuit design, a field of digital electronics engineering. Asynchronous circuits are contrasted with synchronous circuits, in which changes to the signal values in the circuit are triggered by repetitive pulses called a clock signal. Most digital devices today use synchronous circuits. However asynchronous circuits have a potential to be much faster, have a lower level of power consumption, electromagnetic interference, and better modular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transition Graphs
Signal Transition Graphs (STGs) are typically used in electronic engineering and computer engineering to describe dynamic behaviour of asynchronous circuits, for the purposes of their analysis or synthesis. Main definitions and applications Informally, an STG is a graphical description of the behaviour of an asynchronous circuit in the form where information about causal relations between signalling events is represented directly, as opposed to descriptions based on states. In that way, STGs help to formalise the description of a circuit typically represented by timing diagrams, sometimes also called waveforms. The latter are widely used by electronic engineers. More formally, an STG is a type of an interpreted (or labelled) Petri net whose transitions are labelled with the names of changes in the values of signals (cf. signal transitions). For example, the typical case of the labelling is the case where signals are binary, hence the transition are interpreted as rising and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |