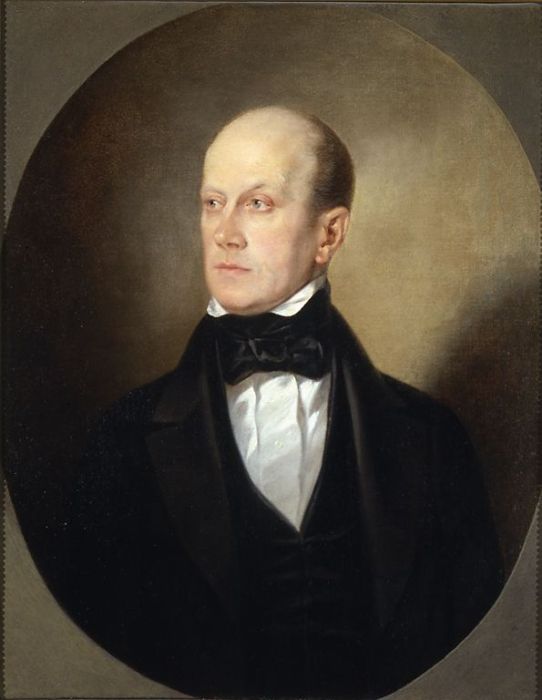|
Petr Chaadaev
Pyotr or Petr Yakovlevich Chaadayev (; also spelled Chaadaev; 7 June [27 May Old Style, O.S.] 1794 – 26 April [14 April O.S.] 1856) was a Russian philosopher. He was one of the Russian Schellingians. Chaadayev was born in Moscow into a wealthy noble family. He interrupted his education to join the military and served with distinction in the Napoleonic Wars. Chaadayev wrote eight "Philosophical Letters" about Russia in French between 1826 and 1831, which circulated among intellectuals in Russia in manuscript form for many years. They comprise an indictment of Russian culture for its laggard role far behind the leaders of Western culture, Western civilization. He cast doubt on the greatness of the Russian past, and ridiculed Orthodoxy for failing to provide a sound spiritual basis for the Russian mind. He extolled the achievements of Europe, especially in rational and logical thought, its progressive spirit, its leadership in science, and its leadership on the path to freedom. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decembrist Revolt
The Decembrist revolt () was a failed coup d'état led by liberal military and political dissidents against the Russian Empire. It took place in Saint Petersburg on , following the death of Emperor Alexander I. Alexander's brother and heir-presumptive Grand Duke Konstantin Pavlovich privately renounced his claim to the throne two years prior to Alexander's sudden death on 1 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 19 November1825. The next in the line of succession therefore was younger brother Nicholas, who would ascend to the throne as Emperor Nicholas I. Neither the Russian government nor the general public were initially aware of Konstantin's renunciation, and as a result, parts of the military took a premature oath of loyalty to Konstantin. A general swearing of loyalty to the true emperor Nicholas was scheduled for in Senate Square, Saint Petersburg. In the midst of this Northern Society, a secret society" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond T
Raymond is a male given name of Germanic origin. It was borrowed into English from French (older French spellings were Reimund and Raimund, whereas the modern English and French spellings are identical). It originated as the Germanic ᚱᚨᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Raginmund'') or ᚱᛖᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Reginmund''). ''Ragin'' ( Gothic) and ''regin'' ( Old German) meant "counsel". The Old High German ''mund'' originally meant "hand", but came to mean "protection". This etymology suggests that the name originated in the Early Middle Ages, possibly from Latin. Alternatively, the name can also be derived from Germanic Hraidmund, the first element being ''Hraid'', possibly meaning "fame" (compare ''Hrod'', found in names such as Robert, Roderick, Rudolph, Roland, Rodney and Roger) and ''mund'' meaning "protector". Despite the German and French origins of the English name, some of its early uses in English documents appear in Latinized form. As a surname, its first recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge ( ; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets with his friend William Wordsworth. He also shared volumes and collaborated with Charles Lamb, Robert Southey, and Charles Lloyd. He wrote the poems '' The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'' and " Kubla Khan", as well as the major prose work '' Biographia Literaria''. His critical works were highly influential, especially in relation to William Shakespeare, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking cultures. Coleridge coined many familiar words and phrases, including "suspension of disbelief". He had a major influence on Ralph Waldo Emerson and American transcendentalism. Throughout his adult life, Coleridge had crippling bouts of anxiety and depression; it has been speculated that he had bipolar disorder, which had not been defined during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apologia
An apologia (Latin for ''apology'', from , ) is a formal defense of an opinion, position or action. The term's current use, often in the context of religion, theology and philosophy, derives from Justin Martyr's '' First Apology'' (AD 155–157) and was later employed by John Henry Newman's '' Apologia Pro Vita Sua'' ( English: ''A Defense of One's Own Life'') of 1864, which presented a formal defense of the history of his Christian life, leading to his acceptance by the Catholic Church in 1845. In Ancient Greece, an apologia was primarily used as a legal defense: The accuser would present a ''kategoria'', or accusation, and the defendant would present his ''apologia'', or defense. In modern usage, ''apologia'' describes a formal defense of an idea or belief, rather than against a legal charge. In both ancient and modern uses it different from an apology, or expression of regret. The main difference between the two is that the act of apologizing is meant to express regret, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apology (act)
An apology is a voluntary expression of regret or remorse for actions, while apologizing (apologising in British English) is the act of expressing regret or remorse. In informal situations, it may be called saying sorry. The goal of an apology is generally forgiveness, reconciliation, and restoration of the relationship between the people involved in a dispute. The nature of an apology involves at least two people where one has offended the other. Alternatively, it can involve two ''groups'' of people, one having previously offended the other. This is seen in the figure, with the Australian Government (an institution) apologizing for previous wrongs to the Indigenous (a large ethnic group). According to attribution theory, giving an apology as early as possible leads to less conflict during the discussion and increases communication satisfaction. The way the apology is given affects the outcome and the process of forgiveness. For example, putting genuine emotion into an apology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Abuse Of Psychiatry
Political abuse of psychiatry, also known as punitive psychiatry, refers to the misuse of psychiatric diagnosis, detention, and treatment to suppress individual or group human rights in society. This abuse involves the deliberate psychiatric diagnosis of individuals who require neither psychiatric restraint nor treatment, often for political purposes. Psychiatrists have been implicated in human rights abuses worldwide, particularly in states where diagnostic criteria for mental illness are expanded to include political disobedience. Scholars have long observed that government and medical institutions tend to label threats to authority as mentally ill during periods of political unrest. In many countries, political prisoners are confined and abused in psychiatric hospitals. Psychiatry is uniquely vulnerable to being used for abusive purposes compared to other specialties of medicine. The power to diagnose mental illness allows the state to detain individuals against their will a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen & Unwin
George Allen & Unwin was a British publishing company formed in 1911 when Sir Stanley Unwin purchased a controlling interest in George Allen & Co. It became one of the leading publishers of the twentieth century and established an Australian subsidiary in 1976. In 1990 Allen & Unwin was sold to HarperCollins, and the Australian branch was the subject of a management buy-out. George Allen & Unwin in the UK George Allen & Sons was established in 1871 by George Allen, with the backing of John Ruskin, becoming George Allen & Co. Ltd. in 1911 when it merged with Swan Sonnenschein and then George Allen & Unwin on 4 August 1914 as a result of Stanley Unwin's purchase of a controlling interest. Frank Arthur Mumby and Frances Helena Swan Stallybrass, Unwin's son Rayner S. Unwin and his nephew Philip helped him to run the company, which published works by Bertrand Russell, Arthur Waley, Roald Dahl, Lancelot Hogben and Thor Heyerdahl. It became well known as J. R. R. Tolkien's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedar Paul
Cedar Paul, ''née'' Gertrude Mary Davenport (1880 – 18 March 1972) was a singer, author, translator and journalist.''Who Was Who'' Biography Gertrude Davenport came from a musical family: she was the granddaughter of the composer George Alexander Macfarren and the daughter of the composer Francis William Davenport (1847–1925). She was educated at convent schools in Belgium, France, Italy and England, and studied music in Germany. She was a member of the Independent Labour Party from 1912 to 1919, and Secretary of the British Section of the Women's International Council of Socialist and Labour Organizations from 1917 to 1919. She married Eden Paul, and from 1915 onwards was active - under the name of Cedar Paul - as a translator and writer in collaboration with her husband. The pair became members of the Communist Party of Great Britain,''The Labour Who's Who'', 1927 and Cedar served on the executive committee of the Plebs League in the 1920s.Chris Wrigley, ''A.J.P. Tay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eden Paul
Maurice Eden Paul (27 September 1865, in Sturminster Marshall – 1 December 1944) was a British socialist activist, physician, writer and translator.'Paul, Maurice Eden' in ''Who Was Who'' Early life Paul was the younger son of the publisher Charles Kegan Paul,Beatrice Webb, ''My Apprenticeship'', 1979, pp. 268–9 and Margaret Colvile. His mother was one of 12 daughters born to Andrew Wedderburn-Colvile (1779–1856) and the Hon. Mary Louisa Eden, fifth daughter of William Eden, 1st Baron Auckland. He was educated at University College School and University College London; he continued his medical studies at London Hospital. In the mid-1880s he helped Beatrice Webb and Ella Pycroft run Katharine Buildings, model dwellings that were the first project of the philanthropically-motivated East End Dwellings Company,''The Letters of Sidney and Beatrice Webb: Volume 3, Pilgrimage 1912–1947'', pgs. 441-2 and in 1886 joined Charles Booth's Board of Statistical Inquiry invest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Griboyedov
Alexander Sergeyevich Griboyedov (; 15 January 179511 February 1829) was a Russian diplomat, playwright, poet, and composer. His one notable work is the 1823 verse comedy '' Woe from Wit''. He was Russia's ambassador to Qajar Persia, where he and all the embassy staff were massacred by an angry mob in the aftermath of the ratification of the Treaty of Turkmenchay (1828), which confirmed the cession to Russia of Persia's northern territories comprising Transcaucasia and parts of the North Caucasus. Griboyedov played a pivotal role in the ratification of the treaty. The immediate cause for the incident was Griboyedov giving refuge to Armenians who had escaped from the harems of the Persian shah and his son. Early life Griboyedov was born in Moscow, the exact year unknown, with biographers debating whether it was in 1790 or 1795. His mother who dreamed of providing him with a career made sure Griboyedov received the best education. He received a master's degree in philology from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |