|
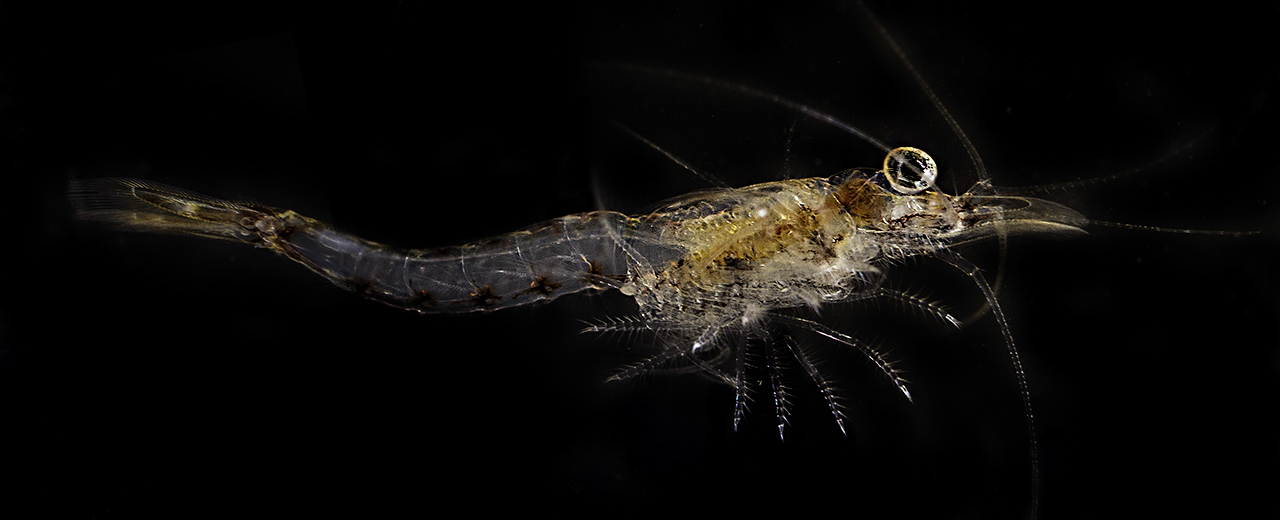
Petalophthalmidae
Petalophthalmidae is a family of marine crustaceans in the order Mysida, the opossum shrimps. Characteristics Petalophthalmidans are distinguished from other mysids by the fact that the first pereopod (walking leg) does not have an exopod (outer branch), the carpopropodus of the endopod (inner branch) of the 3rd to 8th pereopods are not fused and there is no statocyst on the endopod of the uropods (posterior appendage). Female petalophthalmidans have seven oostegites (flexible bristly flaps) forming the base of the marsupium or brood pouch under the thorax. Most species in this genus are bathypelagic The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic ... and live on or near the seabed in the deep ocean. Genera The following genera are recognised in the World Register of Marine Specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysida
Mysida is an order (biology), order of small, shrimp-like crustaceans in the malacostracan superorder Peracarida. Their common name opossum shrimps stems from the presence of a Brood pouch (Peracarida), brood pouch or "marsupium" in females. The fact that the Crustacean larvae, larvae are reared in this pouch and are not Motility, free-swimming characterises the order. The mysid's head bears a pair of stalked eyes and two pairs of antennae. The thorax consists of eight segments each bearing branching limbs, the whole concealed beneath a protective carapace and the abdomen has six segments and usually further small limbs. Mysids are found throughout the world in both shallow and deep marine waters where they can be Benthos, benthic or pelagic, but they are also important in some fresh water and brackish water, brackish ecosystems. Many benthic species make Diel vertical migration, daily vertical migrations into higher parts of the water column. Mysids are filter feeders, omnivores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Pouch (Peracarida)
The marsupium or brood pouch, is a characteristic feature of Peracarida, including the orders Amphipoda, Isopoda, Cladocera, and Cumacea. It is an egg chamber formed by oostegites, which are appendages that are attached to the coxae (first segment) of the first pereiopods. Females lay their eggs directly into the brood chamber, and the young will develop there, undergoing several moults before emerging as miniature adults referred to as mancae. Males have no marsupium. References {{malacostraca-stub Crustacean anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathyal Zone
The bathypelagic zone or bathyal zone (from Greek βαθύς (bathýs), deep) is the part of the open ocean that extends from a depth of below the ocean surface. It lies between the mesopelagic above, and the abyssopelagic below. The bathypelagic is known as the midnight zone because of the lack of sunlight; this feature does not allow for photosynthesis-driven primary production, preventing growth of phytoplankton or aquatic plants. Although larger by volume than the photic zone, our knowledge of the bathypelagic zone remains limited by our ability to explore the deep ocean. Physical characteristics The bathypelagic zone is characterized by a nearly constant temperature of approximately and a salinity range of 33-35 g/kg. This region has little to no light, because sunlight does not reach this deep in the ocean and bioluminescence is limited. The hydrostatic pressure in this zone ranges 100-400 atmospheres (atm), due to the increase of 1 atm for every 10 m depth. It is bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in ''Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, statocysts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uropod
Uropods are posterior appendages found on a wide variety of crustaceans. They typically have functions in locomotion. Definition Uropods are often defined as the appendages of the last body segment of a crustacean. An alternative definition suggested by Frederick R. Schram restricts the term to those structures arising from the segment before the anal segment (the segment which carries the anus). Under this latter definition, the appendages of the anal segment are caudal ramus, caudal rami, which are analogy (biology), analogous to uropods. Form Uropods are typically biramous – comprising an endopod and an exopod. The exopod is typically the larger, and may be divided in two by a transverse suture known as the diaeresis. The uropods may work in concert with the telson to form a "tail fan". References {{Reflist, 32em Crustacean anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |