|
Perkin Reaction
The Perkin reaction is an organic reaction developed by English chemist William Henry Perkin that is used to make cinnamic acids. It gives an α,β-unsaturated aromatic acid or α-substituted β-aryl acrylic acid by the aldol condensation of an aromatic aldehyde and an acid anhydride, in the presence of an alkali salt of the acid. The alkali salt acts as a base catalyst, and other bases can be used instead. Several reviews have been written. Reaction mechanism Cleary from the reaction mechanism, the anhydride of aliphatic acid must contain at least 2 α-H for the reaction to occur. The above mechanism is not universally accepted, as several other versions exist, including decarboxylation without acetic group transfer.Bansal, Raj K. (1998) ''Organic Reaction Mechanisms'', Tata McGraw Hill, 3rd Edition , pp. 199–201, . Applications *Benzaldehyde reacts with acetic anhydride in the presence of sodium or potassium acetate to form cinnamic acid. *One notable application fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Perkin
Sir William Henry Perkin (12 March 1838 – 14 July 1907) was a British chemist and entrepreneur best known for his serendipitous discovery of the first commercial synthetic organic dye, mauveine, made from aniline. Though he failed in trying to synthesise quinine for the treatment of malaria, he became successful in the field of dyes after his first discovery at the age of 18. Perkin set up a factory to produce the dye industrially. Lee Blaszczyk, professor of business history at the University of Leeds, states, "By laying the foundation for the synthetic organic chemicals industry, Perkin helped to revolutionize the world of fashion." Early years William Perkin was born in the East End of London, the youngest of the seven children of George Perkin, a successful carpenter. His mother, Sarah, was of Scottish descent and moved to East London as a child.UXL Encyclopedia of World Biography (2003). Accessed 18 March 2008. He was baptized in the Anglican parish church of St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their applica .... A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as Sodium hydroxide, NaOH or Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pechmann Condensation
The Pechmann condensation is a synthesis of coumarins, starting from a phenol and a carboxylic acid or ester containing a β- carbonyl group. The condensation is performed under acidic conditions. The mechanism involves an esterification/transesterification followed by attack of the activated carbonyl ortho to the oxygen to generate the new ring. The final step is a dehydration, as seen following an aldol condensation. It was discovered by the German chemist Hans von Pechmann . With simple phenols, the conditions are harsh, although yields may still be good. With highly activated phenols such as resorcinol, the reaction can be performed under much milder conditions. This provides a useful route to umbelliferone derivatives: For coumarins unsubstituted at the 4-position, the method requires the use of formylacetic acid or ester. These are unstable and not commercially available, but the acid may be produced ''in situ'' from malic acid and sulfuric acid above 100 ° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stobbe Condensation
The Claisen condensation reaction, condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming organic reaction, reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base, resulting in a β-keto ester or a β-diketone. It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen, who first published his work on the reaction in 1887. Requirements At least one of the reagents must be enolizable (have an alpha carbon, α-proton and be able to undergo deprotonation to form the enol, enolate anion). There are a number of different combinations of enolizable and nonenolizable carbonyl compounds that form a few different Claisen condensation#Types, types of Claisen. The base used must not interfere with the reaction by undergoing nucleophilic substitution or nucleophilic addition, addition with a carbonyl carbon. For this reason, the conjugate sodium alkoxide base of the alcohol formed (e.g. sodium ethoxide if ethanol is formed) is often used, since the alkoxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erlenmeyer–Plöchl Azlactone And Amino-acid Synthesis
The Erlenmeyer–Plöchl azlactone and amino acid synthesis, named after Friedrich Gustav Carl Emil Erlenmeyer who partly discovered the reaction, is a series of chemical reactions which transform an ''N''- acyl glycine to various other amino acids via an oxazolone (also known as an azlactone). Hippuric acid, the benzamide derivative of glycine, cyclizes in the presence of acetic anhydride, condensing to give 2-phenyl-oxazolone. This intermediate also has two acidic protons and reacts with benzaldehyde, acetic anhydride and sodium acetate to a so-called azlactone. This compound on reduction gives access to phenylalanine. Variations Variants of the azlactone synthesis in which analogues of azlactones are used are sometimes advantageous. Hydantoin (in Bergmann modification), thiohydantoin and rhodanine have each been employed as the enolate-forming component of the condensation. 2,5-Diketopiperazine can be used as a methylene component as well; its condensation products with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fo-ti
''Reynoutria multiflora'' (syn. ''Fallopia multiflora'' and ''Polygonum multiflorum'') is a species of flowering plant in the buckwheat family Polygonaceae native to central and southern China. It is known by the English common names tuber fleeceflower and Chinese (climbing) knotweed. It is known as ''he shou wu'' in China and East Asia. Another name for the species is ''fo-ti'', which is a misnomer. The name ''he shou wu'' means 'the black-haired Mr. He'. It can be difficult to prevent the spread of this vining plant and to remove it once established. The leaves are thin and fragile but the stems, although narrow in diameter, can be very strong. Description ''Reynoutria multiflora'' is a herbaceous perennial vine growing to tall from a woody tuber. The leaves are long and broad, broad arrowhead-shaped, with an entire margin. The flowers are diameter, white or greenish-white, produced on short, dense panicles up to long in summer to mid autumn. The fruit is an achene long. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resveratrol
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-''trans''-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts. Although commonly used as a dietary supplement and studied in laboratory models of human diseases, there is no high-quality evidence that resveratrol improves lifespan or has a substantial effect on any human disease. Research Resveratrol has been studied for its potential therapeutic use, with little evidence of anti-disease effects or health benefits in humans. Cardiovascular disease There is no evidence of benefit from resveratrol in people who already have heart disease. A 2018 meta-analysis found no effect on systolic or diastolic blood pressure; a sub-analysis revealed a 2 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure only from res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stilbene
{{Chemistry index ...
Stilbene may refer to one of the two stereoisomers of 1,2-diphenylethene: * (''E'')-Stilbene (''trans'' isomer) * (''Z'')-Stilbene (''cis'' isomer) See also * Stilbenoids, a class of molecules found in plants * 1,1-Diphenylethylene 1,1-Diphenylethylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon with chemical formula CH. Properties 1,1-Diphenylethylene mediates the radical polymerization of methyl acrylate or styrene. Meditation by 1,1-Diphenylethylene generates low molecular weight polymer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
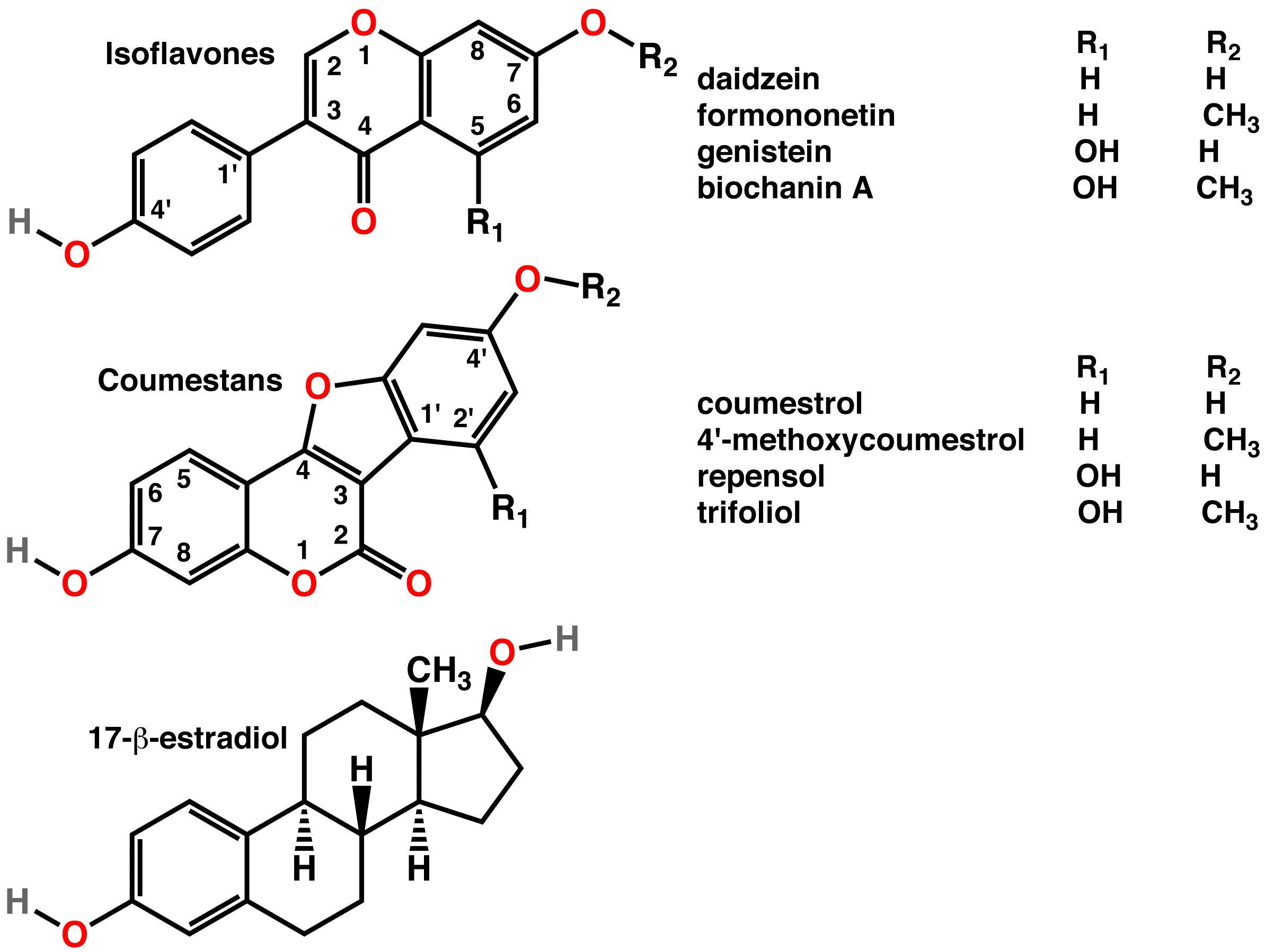
Phytoestrogens
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots (see Food Sources section below for bigger list). Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" - Greek οίστρος - means "sexual desire", and "gene" - Greek γόνο - is "to generate". It has been hypoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkin Reaction Mechanism , an American-origin global corporation
{{disambiguation ...
Perkin may refer to: People * Perkin (surname) * Perkin Warbeck (c. 1474 – 1499), imposter and pretender to the English throne Other uses * Perkin (crater), on the Moon * 2482 Perkin, asteroid * Perkin Medal, awarded annually by the American section of the Society of Chemical Industry * a character in The Flumps See also * Perkins (other) * Parkin (other) * PerkinElmer PerkinElmer, Inc., previously styled Perkin-Elmer, is an American global corporation focused in the business areas of diagnostics, life science research, food, environmental and industrial testing. Its capabilities include detection, imaging, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)