|
Perfect Conductor
In electrostatics, a perfect conductor is an idealized model for real conducting materials. The defining property of a perfect conductor is that static electric field and the charge density both vanish in its interior. If the conductor has excess charge, it accumulates as an infinitesimally thin layer of surface charge. An external electric field is screened from the interior of the material by rearrangement of the surface charge. Alternatively, a perfect conductor is an idealized material exhibiting infinite electrical conductivity or, equivalently, zero resistivity (cf. perfect dielectric). While perfect electrical conductors do not exist in nature, the concept is a useful model when electrical resistance is negligible compared to other effects. One example is ideal magnetohydrodynamics, the study of perfectly conductive fluids. Another example is electrical circuit diagrams, which carry the implicit assumption that the wires connecting the components have no resistance. Yet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies slow-moving or stationary electric charges. Since classical antiquity, classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after triboelectric effect, rubbing. The Greek language, Greek word (), meaning 'amber', was thus the Root (linguistics), root of the word ''electricity''. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and photocopier and laser printing, laser printer operation. The electrostatic model accurately predicts electrical phenomena in "classical" cases where the velocities are low and the system is macroscopic so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
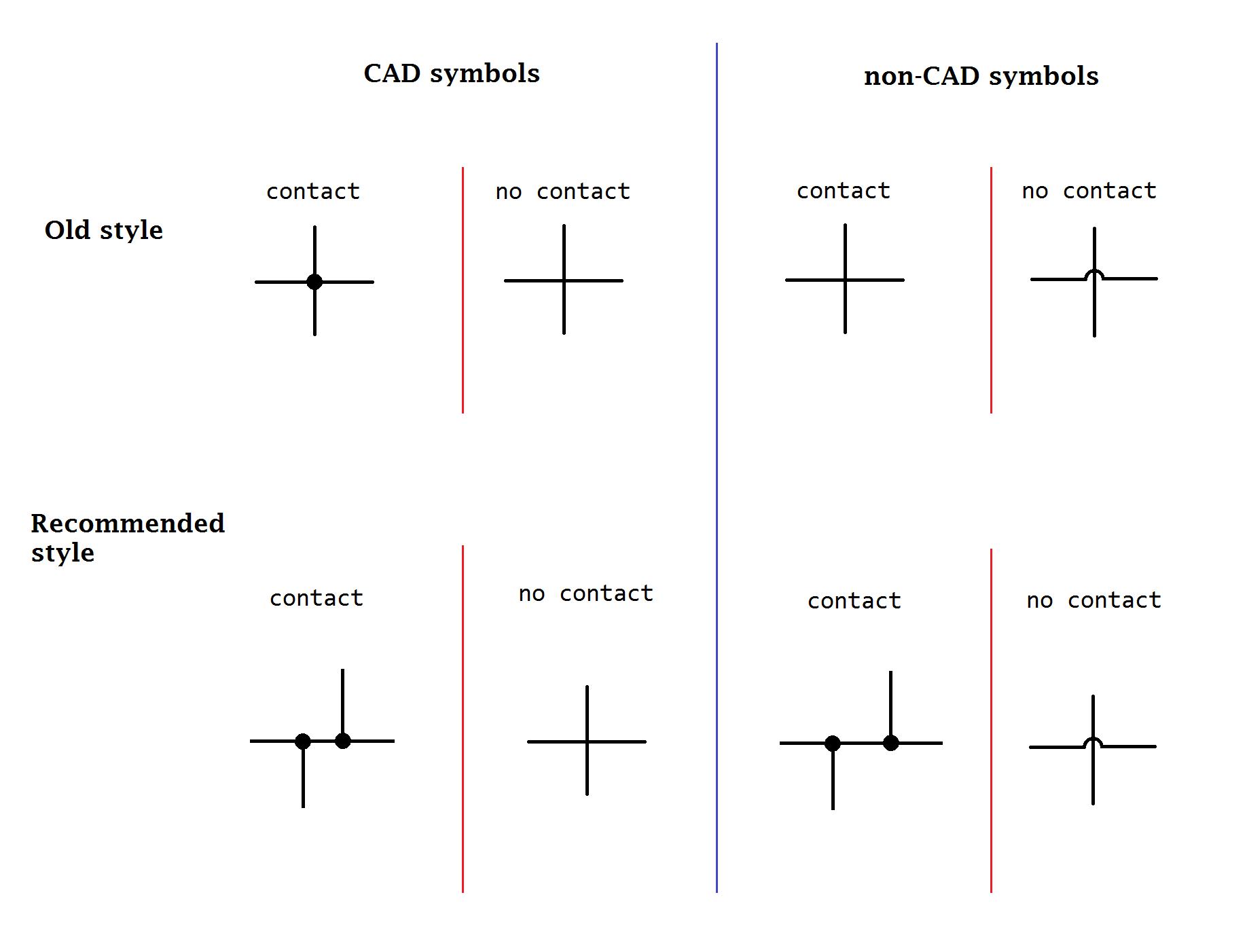
Circuit Diagram
A circuit diagram (or: wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an Electrical network, electrical circuit. A pictorial circuit diagram uses simple images of components, while a schematic diagram shows the components and interconnections of the circuit using standardized symbolic representations. The presentation of the interconnections between circuit components in the schematic diagram does not necessarily correspond to the physical arrangements in the finished device. Unlike a block diagram or Integrated circuit layout, layout diagram, a circuit diagram shows the actual electrical connections. A drawing meant to depict the physical arrangement of the wires and the components they connect is called ''artwork'' or ''Integrated circuit layout, layout'', ''physical design'', or ''wiring diagram''. Circuit diagrams are used for the design (circuit design), construction (such as Printed circuit board, PCB layout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Current
In physics, persistent current is a perpetual electric current that does not require an external power source. Such a current is impossible in normal electrical devices, since all commonly used conductors have a non-zero resistance, and this resistance would rapidly dissipate any such current as heat. However, in superconductors and some mesoscopic devices, persistent currents are possible and observed due to quantum effects. In resistive materials, persistent currents can appear in microscopic samples due to size effects. Persistent currents are widely used in the form of superconducting magnets. In magnetized objects In electromagnetism, all magnetizations can be seen as microscopic persistent currents. By definition a magnetization \mathbf can be replaced by its corresponding microscopic form, which is an electric current density: : \mathbf = \nabla\times\mathbf . This current is a bound current, not having any charge accumulation associated with it since it is divergence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic State of matter, states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma (physics), plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical property, physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition States of matter Phase transitions commonly refer to when a substance tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantization (physics)
Quantization (in British English quantisation) is the systematic transition procedure from a classical understanding of physical phenomena to a newer understanding known as quantum mechanics. It is a procedure for constructing quantum mechanics from classical mechanics. A generalization involving infinite degrees of freedom is field quantization, as in the "quantization of the electromagnetic field", referring to photons as field " quanta" (for instance as light quanta). This procedure is basic to theories of atomic physics, chemistry, particle physics, nuclear physics, condensed matter physics, and quantum optics. Historical overview In 1901, when Max Planck was developing the distribution function of statistical mechanics to solve the ultraviolet catastrophe problem, he realized that the properties of blackbody radiation can be explained by the assumption that the amount of energy must be in countable fundamental units, i.e. amount of energy is not continuous but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissner Effect
In condensed-matter physics, the Meissner effect (or Meißner–Ochsenfeld effect) is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state when it is cooled below the critical temperature. This expulsion will repel a nearby magnet. The German physicists Walther Meissner, Walther Meißner (anglicized ''Meissner'') and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered this phenomenon in 1933 by measuring the magnetic field distribution outside superconducting tin and lead samples. The samples, in the presence of an applied magnetic field, were cooled below their Superconductivity#Superconducting phase transition, superconducting transition temperature, whereupon the samples cancelled nearly all interior magnetic fields. They detected this effect only indirectly because the magnetic flux is conserved by a superconductor: when the interior field decreases, the exterior field increases. The experiment demonstrated for the first time that superconducto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic Electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and Atomic spectral line, atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Flux
In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber (Wb; in derived units, volt–seconds or V⋅s), and the CGS unit is the maxwell. Magnetic flux is usually measured with a fluxmeter, which contains measuring coils, and it calculates the magnetic flux from the change of voltage on the coils. Description The magnetic interaction is described in terms of a vector field, where each point in space is associated with a vector that determines what force a moving charge would experience at that point (see Lorentz force). Since a vector field is quite difficult to visualize, introductory physics instruction often uses field lines to visualize this field. The magnetic flux, through some surface, in this simplified picture, is proportional to the number of field lines passing through that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Electromagnetics
Computational electromagnetics (CEM), computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with physical objects and the environment using computers. It typically involves using computer programs to compute approximate solutions to Maxwell's equations to calculate antenna performance, electromagnetic compatibility, radar cross section and electromagnetic wave propagation when not in free space. A large subfield is antenna modeling computer programs, which calculate the radiation pattern and electrical properties of radio antennas, and are widely used to design antennas for specific applications. Background Several real-world electromagnetic problems like electromagnetic scattering, electromagnetic radiation, modeling of waveguides etc., are not analytically calculable, for the multitude of irregular geometries found in actual devices. Computational numerical techniques can overcome the inability to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamics
In physics and engineering, magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is a model of electrically conducting fluids that treats all interpenetrating particle species together as a single Continuum mechanics, continuous medium. It is primarily concerned with the low-frequency, large-scale, magnetic behavior in Plasma (physics), plasmas and liquid metals and has applications in multiple fields including space physics, geophysics, astrophysics, and engineering. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. History The MHD description of electrically conducting fluids was first developed by Hannes Alfvén in a 1942 paper published in Nature (journal), ''Nature'' titled "Existence of Electromagnetic–Hydrodynamic Waves" which outlined his discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |