|
Perceptual Attack Time
Perceptual Attack Time (often abbreviated "PAT") is a subjective measure of the time instant at which a musical sound's rhythmic emphasis is heard. It is analogous to the perceptual centre (aka "p-centre") in speech. It is different from both the physical onset (i.e., the time at which the sound's acoustic energy first begins) and the perceptual onset (i.e., the subjective time at which a listener first notices that the sound has begun). For a very percussive sound such as a note played on a closed hi hat cymbal the perceptual attack time may be just a few millisecond A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called ...s, while for a note bowed slowly on a violin the perceptual attack time may be as much as 50–100 milliseconds after the physical onset. Applications Understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subjective Measures Of Time
Subjective may refer to: * Subjectivity, a subject's personal perspective, feelings, beliefs, desires or discovery, as opposed to those made from an independent, objective, point of view ** Subjective experience, the subjective quality of conscious experience * Subjectivism, a philosophical tenet that accords primacy to subjective experience as fundamental of all measure and law * Subjective case, grammatical case for a noun * Subject (philosophy), who has subjective experiences or a relationship with another entity * Subjective theory of value, an economic theory of value * A school of bayesian probability stating that the state of knowledge corresponds to personal belief * ''Subjectivity'' (journal), an academic journal See also * Subjectivist fallacy * Subjunctive * Objective (other) Objective may refer to: * Objective (optics), an element in a camera or microscope * ''The Objective'', a 2008 science fiction horror film * Objective pronoun, a personal pronoun t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ... , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry#Symmetry in music, symmetry") generally means a "motion, movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a Frequency, periodicity or frequency of anything from microseconds to several seconds (as with the riff in a rock music song); to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years. Rhythm is related to and distinguished from pulse, meter, and beats: In the performance arts, rhythm is the timing of events on a human scale; of music, musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
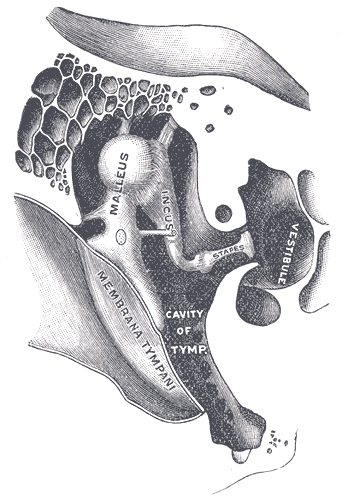
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceptual Centre
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Vision involves light striking the retina of the eye; smell is mediated by odor molecules; and hearing involves pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's learning, memory, expectation, and attention. Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level information (e.g., extracts shapes for object recognition). The process that follows connects a person's concepts and expectations (or knowledge), restorative and selective mechanisms (such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onset (audio)
Onset refers to the beginning of a musical note or other sound. It is related to (but different from) the concept of a transient: all musical notes have an onset, but do not necessarily include an initial transient. Onset detection In signal processing, onset detection is an active research area. For example, the MIREX annual competition features aAudio Onset Detection contest Approaches to onset detection can operate in the time domain, frequency domain, phase domain, or complex domain, and include looking for: * Increases in spectral energy * Changes in spectral energy distribution ( spectral flux) or phase * Changes in detected pitch - e.g. using a polyphonic pitch detection algorithm * Spectral patterns recognisable by machine learning techniques such as neural networks. Simpler techniques such as detecting increases in time-domain amplitude can typically lead to an unsatisfactorily high amount of false positives or false negatives. The aim is often to judge onsets sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hi-hat (instrument)
A hi-hat (hihat, high-hat, etc.) is a combination of two cymbals and a pedal, all mounted on a metal stand. It is a part of the standard drum kit used by drummers in many styles of music including rock, pop, jazz, and blues. Hi-hats consist of a matching pair of small to medium-sized cymbals mounted on a stand, with the two cymbals facing each other. The bottom cymbal is fixed and the top is mounted on a rod which moves the top cymbal toward the bottom one when the pedal is depressed (a hi-hat that is in this position is said to be "closed" or "closed hi-hats"). The hi-hat evolved from a "sock cymbal", a pair of similar cymbals mounted at ground level on a hinged, spring-loaded foot apparatus. Drummers invented the first sock cymbals to enable one drummer to play multiple percussion instruments at the same time. Over time these became mounted on short stands—also known as "low-boys"—and activated by pedals similar to those used in modern hi-hats. When extended upward ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
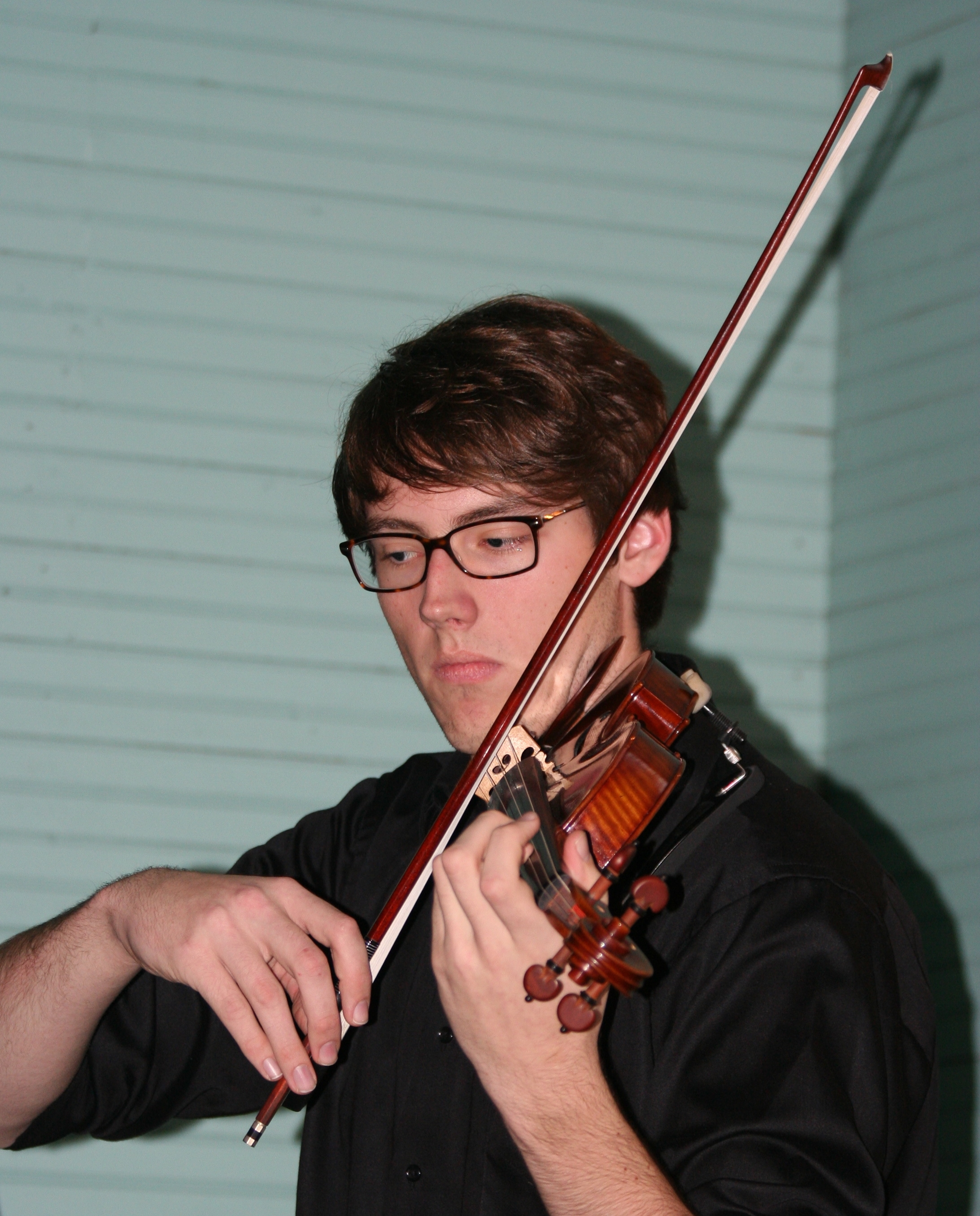
Playing The Violin
Playing the violin entails holding the instrument between the jaw and the collar bone (see below for variations of this posture). The strings are sounded either by drawing the bow across them (''arco''), or by plucking them (''pizzicato''). The left hand regulates the sounding length of the strings by stopping them against the fingerboard with the fingers, producing different pitches. Posture It is possible to play the violin holding it in a variety of ways. Most players hold the lower bout of the instrument between the left shoulder and the jaw, often assisted by a semi-permanently attached chinrest and detachable shoulder rest. If held properly under the chin, the violinist can let go of the instrument with their hands and it will stay there firmly. Other common ways to hold the instrument include the seated Carnatic attitude, with the scroll resting on a foot, or the dancing-master's "kit" or "''pochette''" hold, along the forearm, by the lower margin of the rib cage, ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klangfarbenmelodie
''Klangfarbenmelodie'' (German for "sound-color melody") is a musical technique that involves splitting a musical line or melody between several instruments, rather than assigning it to just one instrument (or set of instruments), thereby adding color (timbre) and texture to the melodic line. The technique is sometimes compared to " pointillism", a neo-impressionist painting technique. History The term derives from Arnold Schoenberg's ''Harmonielehre'', where he discusses the creation of "timbre structures". Schoenberg and Anton Webern are particularly noted for their use of the technique, Schoenberg most notably in the third of his '' Five Pieces for Orchestra'' (Op. 16), and Webern in his Op. 10 (likely a response to Schoenberg's Op. 16), his Concerto for Nine Instruments (Op. 24), the Op. 11 pieces for cello and piano, and his orchestration of the six-part ''ricercar'' from Bach's ''Musical Offering'': This may be compared with Bach's open score of the subject and the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Psychology
Experimental psychology refers to work done by those who apply experimental methods to psychological study and the underlying processes. Experimental psychologists employ human participants and animal subjects to study a great many topics, including (among others) sensation & perception, memory, cognition, learning, motivation, emotion; developmental processes, social psychology, and the neural substrates of all of these. History Early experimental psychology Wilhelm Wundt Experimental psychology emerged as a modern academic discipline in the 19th century when Wilhelm Wundt introduced a mathematical and experimental approach to the field. Wundt founded the first psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany. Other experimental psychologists, including Hermann Ebbinghaus and Edward Titchener, included introspection in their experimental methods. Charles Bell Charles Bell was a British physiologist whose main contribution to the medical and scientific commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |