|
Perception Learning
Perceptual learning is learning better perception skills such as differentiating two musical tones from one another or categorizations of spatial and temporal patterns relevant to real-world expertise. Examples of this may include reading, seeing relations among chess pieces, and knowing whether or not an X-ray image shows a tumor. Sensory modalities may include visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, and taste. Perceptual learning forms important foundations of complex cognitive processes (i.e., language) and interacts with other kinds of learning to produce perceptual expertise. Underlying perceptual learning are changes in the neural circuitry. The ability for perceptual learning is retained throughout life. Category learning vs. perceptual learning It can be fairly easy to confuse category learning and perceptual learning. Category learning is "an assumed fixed, pre-established perceptual representation to describe the objects to be categorized." Category learning is built upo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals, and some machine learning, machines; there is also evidence for some kind of learning in certain plants. Some learning is immediate, induced by a single event (e.g. being burned by a Heat, hot stove), but much skill and knowledge accumulate from repeated experiences. The changes induced by learning often last a lifetime, and it is hard to distinguish learned material that seems to be "lost" from that which cannot be retrieved. Human learning starts at birth (it might even start before in terms of an embryo's need for both interaction with, and freedom within its environment within the womb.) and continues until death as a consequence of ongoing interactions between people and their environment. The nature and processes involved in learning are studied in many established fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor Gibson
Eleanor Jack Gibson (7 December 1910 – 30 December 2002) was an American psychologist who focused on reading development and perceptual learning in infants. Gibson began her career at Smith College as an instructor in 1932, publishing her first works on research conducted as an undergraduate student. Gibson was able to circumvent the many obstacles she faced due to the Great Depression and gender discrimination, by finding research opportunities that she could meld with her own interests. Gibson, with her husband James J. Gibson, created the Gibsonian ecological theory of development, which emphasized how important perception was because it allows humans to adapt to their environments. Perhaps her most well-known contribution to psychology was the "visual cliff,” which studied depth perception in both human and animal species, leading to a new understanding of perceptual development in infants. Gibson was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 1971, the National Academy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have large bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
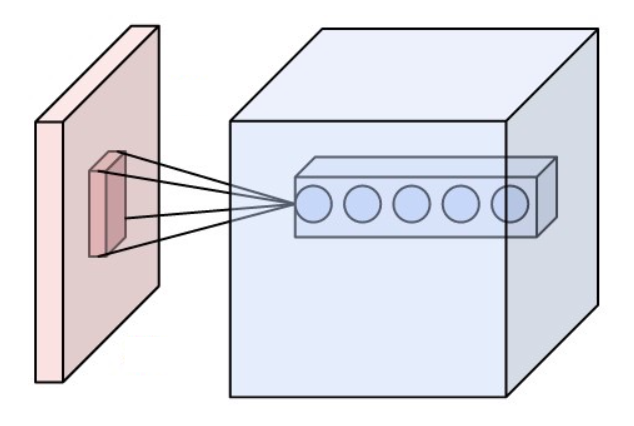
Receptive Field
The receptive field, or sensory space, is a delimited medium where some physiological stimuli can evoke a sensory neuronal response in specific organisms. Complexity of the receptive field ranges from the unidimensional chemical structure of odorants to the multidimensional spacetime of human visual field, through the bidimensional skin surface, being a receptive field for touch perception. Receptive fields can positively or negatively alter the membrane potential with or without affecting the rate of action potentials. A sensory space can be dependent of an animal's location. For a particular sound wave traveling in an appropriate transmission medium, by means of sound localization, an auditory space would amount to a reference system that continuously shifts as the animal moves (taking into consideration the space inside the ears as well). Conversely, receptive fields can be largely independent of the animal's location, as in the case of place cells. A sensory space can also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulus (psychology)
In psychology Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries betwe ..., a stimulus is any object or event that elicits a sensory or behavioral response in an organism. In this context, a distinction is made between the ''distal stimulus'' (the external, perceived object) and the ''proximal stimulus'' (the stimulation of sensory organs). *In perceptual psychology, a stimulus is an energy change (e.g., light or sound) which is registered by the senses (e.g., vision, hearing, taste, etc.) and constitutes the basis for perception. *In behavioral psychology (i.e., classical conditioning, classical and operant conditioning, operant conditioning), a stimulus constitutes the basis for behavior. The stimulus–response model emphasizes the relation between stimulus and behavior rather than an anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system receives signals from the senses which continuously receive information from the environment, interprets these signals, and causes the body to respond, either chemically or physically.) Although traditionally five human senses were identified as such (namely Visual perception, sight, Olfaction, smell, Somatosensory system, touch, taste, and hearing), it is now recognized that there are many more. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for Transduction (physiology), transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Although disagreement exists as to how to precisely define behavior in a biological context, one common interpretation based on a meta-analysis of scientific literature states that "behavior is the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to internal and/or external stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Load
In cognitive psychology, cognitive load refers to the amount of working memory resources used. There are three types of cognitive load: ''intrinsic'' cognitive load is the effort associated with a specific topic; ''extraneous'' cognitive load refers to the way information or tasks are presented to a learner; and ''germane'' cognitive load refers to the work put into creating a permanent store of knowledge (a schema). Cognitive load theory was developed in the late 1980s out of a study of problem solving by John Sweller. Sweller argued that instructional design can be used to reduce cognitive load in learners. Much later, other researchers developed a way to measure perceived mental effort which is indicative of cognitive load. Task-invoked pupillary response is a reliable and sensitive measurement of cognitive load that is directly related to working memory. Information may only be stored in long term memory after first being attended to, and processed by, working memory. Workin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Sensory Areas
The primary sensory areas are the primary cortical regions of the five sensory systems in the brain (taste, olfaction, touch, hearing and vision). Except for the olfactory system, they receive sensory information from thalamic nerve projections. The term ''primary'' comes from the fact that these cortical areas are the first level in a hierarchy of sensory information processing in the brain. This should not be confused with the function of the primary motor cortex, which is the ''last'' site in the cortex for processing motor commands. Though some areas of the human brain that receive primary sensory information remain poorly defined, each of the five sensory modalities has been recognized to relate to specific groups of brain cells that begin to categorize and integrate sensory information. * Somatosensory system: The primary somatosensory cortex (SI) is across the central sulcus and behind the primary motor cortex configured to generally correspond with the arrangement of nearb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)