|
Peninnah
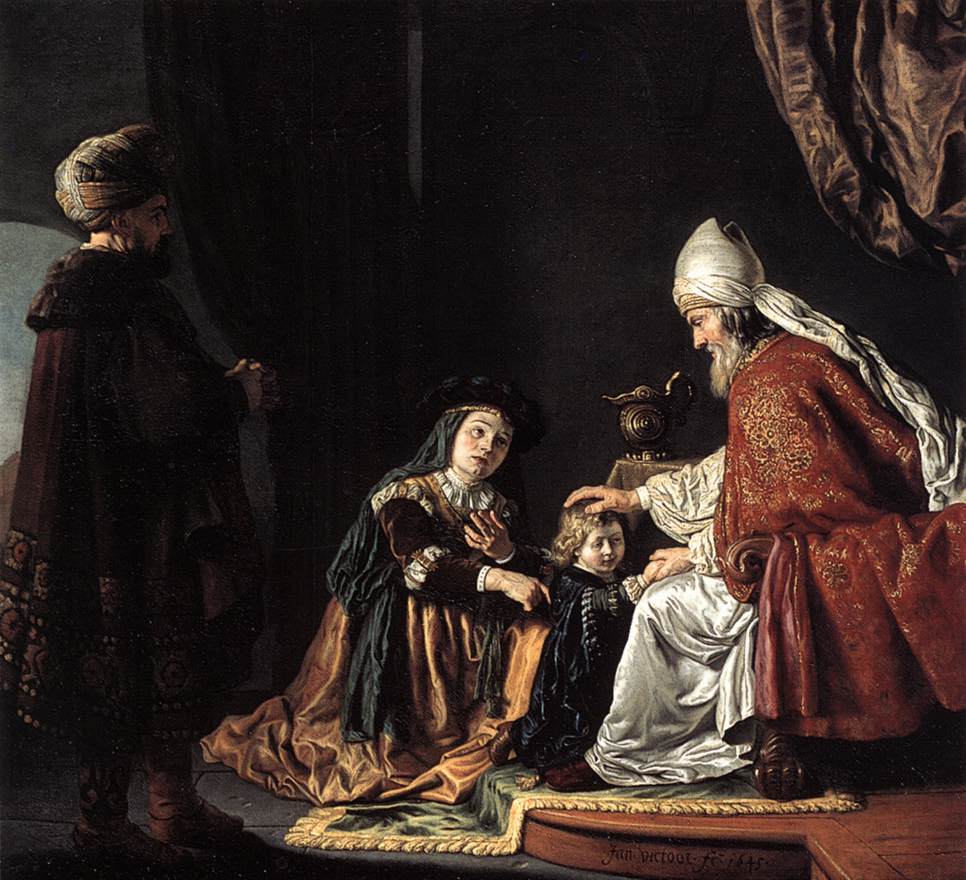
Peninnah ( ''Pəninnā''; sometimes transliterated ''Penina'') was one of Elkanah's two wives, briefly mentioned in the first Book of Samuel ( 1 Samuel 1:2). Her name may derive from (''pəninā''), meaning "pearl." Biblical account Peninnah was less favored than Elkanah's other wife, Hannah; although she had borne him children whilst Hannah was childless, Peninnah also brought grief and disharmony to the household by her mocking of the infertile Hannah. Every year, when Elkanah offered up a sacrifice at Shiloh, he would share out the portions of meat and give Hannah a double portion, which incited the jealousy of Peninnah. Peninnah would taunt Hannah for being childless. She would grieve Hannah by means of ordinary everyday activities, taking pains to remind her, at all hours of the day, of the difference between them. According to Jewish writer Lillian Klein, "Because the reader’s sympathies are directed toward the childless Hannah, Peninnah comes across as a malicious woman. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women In The Hebrew Bible
Women in the Bible are wives, mothers and daughters, victors and victims, women who change the course of important events, and women who are powerless to affect even their own destinies. Ancient Near Eastern societies have traditionally been described as patriarchal, and the Bible, as a document written by men, has traditionally been interpreted as patriarchal in its overall views of women. Marital laws in the Bible favor men, as do the inheritance laws there, and women are under strict laws of sexual behavior with adultery a crime punishable by stoning. A woman in ancient biblical times was always subject to strict purity laws, both ritual and moral. The majority of women in the Bible are unnamed, with named women making up only 5.5 to 8 percent of all named characters in the Bible. Recent scholarship accepts the presence of patriarchy in the Bible, but shows that '' heterarchy'' is also present: heterarchy acknowledges that different power structures between people can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel
Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the biblical judges to the United Kingdom of Israel under Saul, and again in the monarchy's transition from Saul to David. He is venerated as a prophet in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In addition to his role in the Hebrew scriptures, Samuel is mentioned in Jewish rabbinic literature, rabbinical literature, in the Christian New Testament, and in the second chapter of the Quran (although Islamic texts do not mention him by name). He is also treated in the fifth through seventh books of ''Antiquities of the Jews'', written by the Jewish scholar Josephus in the first century. He is first called "the Seer" in Books of Samuel, 1 Samuel 9:9. Biblical account Family Samuel's mother was Hannah (biblical figure), Hannah and his father was Elkanah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elkanah And His Two Wives
Elkanah ( he, אֱלְקָנָה ''’Ĕlqānā'' "El (deity), El has purchased") was, according to the Books of Samuel, First Book of Samuel, the husband of Hannah (biblical figure), Hannah, and the father of her children including her first, Samuel. Elkanah practiced polygamy; his other wife, less favoured but bearing more children, was named Peninnah. The names of Elkanah's other children apart from Samuel are not given. Elkanah plays only a minor role in the narrative, and is mostly a supporting character to Eli, Hannah, and Samuel. Lineage According to 1 Samuel 1, Elkanah was the son of Jeroham, who was the son of Elihu, who was the son of Tohu, who was the son of Zuph. He is described as having originated from Zuph, specifically Ramathaim-Zophim, which was part of the tribal lands of Ephraim. While he is called an Ephraimite in 1 Samuel, the Books of Chronicles state that he was a Levite. Elkanah lived in the Mount of Ephraim, mountains of Ephraim (1 Chronicles 6:16-30, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Joshua, Judges, Samuel, and Kings) that constitute a theological history of the Israelites and that aim to explain God's law for Israel under the guidance of the prophets. According to Jewish tradition, the book was written by Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, who together are three prophets who had appeared within 1 Chronicles during the account of David's reign. Modern scholarly thinking posits that the entire Deuteronomistic history was composed ''circa'' 630–540 BCE by combining a number of independent texts of various ages. The book begins with Samuel's birth and Yahweh's call to him as a boy. The story of the Ark of the Covenant follows. It tells of Israel's oppression by the Philistines, which brought about S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elkanah (husband Of Hannah)
Elkanah ( he, אֱלְקָנָה ''’Ĕlqānā'' " El has purchased") was, according to the First Book of Samuel, the husband of Hannah, and the father of her children including her first, Samuel. Elkanah practiced polygamy; his other wife, less favoured but bearing more children, was named Peninnah. The names of Elkanah's other children apart from Samuel are not given. Elkanah plays only a minor role in the narrative, and is mostly a supporting character to Eli, Hannah, and Samuel. Lineage According to 1 Samuel 1, Elkanah was the son of Jeroham, who was the son of Elihu, who was the son of Tohu, who was the son of Zuph. He is described as having originated from Zuph, specifically Ramathaim-Zophim, which was part of the tribal lands of Ephraim. While he is called an Ephraimite in 1 Samuel, the Books of Chronicles state that he was a Levite. Elkanah lived in the mountains of Ephraim (1 Chronicles 6:16-30, 33-37); the Tribe of Levi had no contiguous parcel of land, but were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eli (Bible)
Eli (, ; grc, Ἠλί, translit=Ēli; la, Heli) was, according to the Books of Samuel, a high priest and Judge of the Israelites in the city of Shiloh, ancient Israel. When Hannah came to Shiloh to pray for a son, Eli initially accused her of drunkenness, but when she protested her innocence, Eli wished her well. Hannah's eventual child, Samuel, was raised by Eli in the tabernacle. When Eli failed to rein in the abusive behavior of his sons, God promised to punish his family, which resulted in the death of Eli and his sons. Later biblical passages mention the fortunes of several of his descendants, and he figures prominently in Samaritan religious tradition. Biblical narrative Eli was the high priest (''kohen gadol'') of Shiloh, the second-to-last Israelite judge (succeeded only by Samuel) before the rule of the Kings of Israel and Judah. Hannah This story of Hannah, with which the Books of Samuel begin, involves Eli. Hannah was the wife of Elkanah. She was childless. Elka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenenna Of Kuyavia
Fenenna of Kuyavia (also known as of Inowrocław; pl, Fenenna kujawska or inowrocławska; c. 1276–1295) was Queen of Hungary by marriage to King Andrew III. Fenenna was the daughter of Duke Ziemomysł of Inowrocław by his wife Salomea, daughter of Duke Sambor II of Pomerania. Fenenna's existence is corroborated by only two sources: the '' Genealogia sanctae Hedwigis'' (Genealogy of Saint Hedwig) and the Chronicles of Jan Długosz, as well in the Hungarian sources. The ''Genealogy'' states that an unnamed daughter of Duke Ziemomysł was betrothed to the King of Hungary. Based on this information, Jan Długosz stated that Fenenna married King Stephen V. This erroneous information was maintained by the later historiography until the 19th century, when Fenenna was correctly described as the wife of King Andrew III. Although Fenenna did not play a significant role in the Hungarian court, her marriage did strengthen the alliance between her husband and her uncle Władysław I t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannah (Bible)
Hannah or Hanna may refer to: People, biblical figures, and fictional characters * Hannah (name), a female given name of Hebrew origin * Hanna (Arabic name), a family and a male given name of Christian Arab origin * Hanna (Irish surname), a family name of Irish origin Places United States * Hannah, Georgia * Hanna City, Illinois * Hanna, Indiana * Hanna, Louisiana * Hannah, Michigan * Hanna, Missouri * Hannah, North Dakota * Hanna, Oklahoma * Hannah, South Carolina * Hanna, South Dakota * Hanna, Utah * Hanna, West Virginia * Hanna, Wyoming * Hannah Run, a stream in Ohio Elsewhere * Hanna, Alberta, Canada, a town * Hannah, a small village in Hannah cum Hagnaby, a civil parish in Lincolnshire, England * Hana, Iran, a city in Isfahan Province * Hanna, Lublin Voivodeship, Poland, a village * Haná (German spelling: Hanna), an ethnic region in Moravia, Czech Republic * Hannah Island (Greenland) * Hanna Lake, a lake near Quetta, Pakistan Ships * , a destroyer escort acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
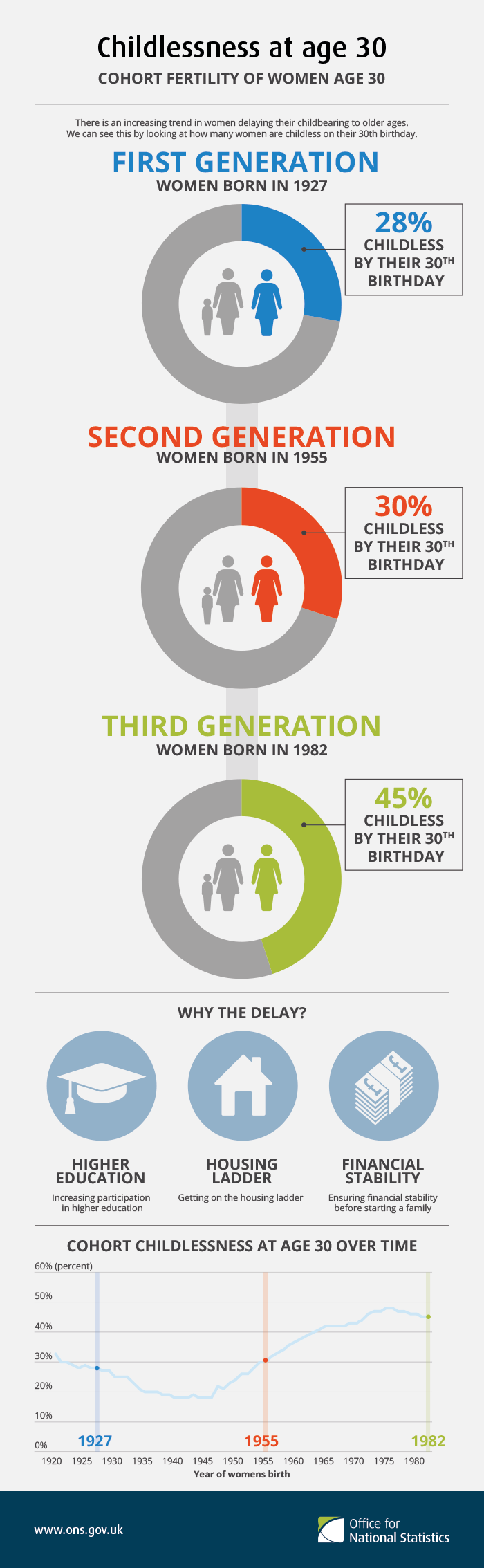
Childlessness
Childlessness is the state of not having children. Childlessness may have personal, social or political significance. Childlessness, which may be by choice or circumstance, is distinguished from voluntary childlessness, which is voluntarily having no children, and from antinatalism, wherein childlessness is promoted. Types Types of childlessness can be classified into several categories: * ''natural sterility'' randomly affects individuals. One can think of it as the minimum level of permanent childlessness that we can observe in any given society, and is of the order of 2 percent, in line with data from the Hutterites, a group established as the demographic standard in the 1950s. * ''social sterility'', which one can also call poverty driven childlessness, or endogenous sterility, describes the situation of poor women whose fecundity has been affected by poor living conditions. * people who are childless by circumstance. These people can be childless because they have not me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity. In humans, infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner.Chowdhury SH, Cozma AI, Chowdhury JH. Infertility. Essentials for the Canadian Medical Licensing Exam: Review and Prep for MCCQE Part I. 2nd edition. Wolters Kluwer. Hong Kong. 2017. There are many causes of infertility, including some that medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiloh (biblical City)
Shiloh (; he, שִׁלֹה, שִׁלוֹ ,שִׁילֹה, and שִׁילוֹ, variably, ''Šīlō'') was an ancient city and sanctuary in Samaria. According to the Hebrew Bible, Shiloh was the central sanctuary of the Israelites during the pre-monarchic period, before the First Temple in Jerusalem was built. After the Israelite conquest of Canaan, the Tabernacle was moved to Shiloh, and remained there during the period of the biblical judges. Shiloh has been positively identified with modern Khirbet Seilun, a tell known in Modern Hebrew as Tel Shiloh. It is located 31 km north of Jerusalem, in the West Bank, to the west of the modern Israeli settlement town of Shilo and to the north of the Palestinian town of Turmus Ayya. Relative to other archaeological sites, it is south of the biblical town of Lebonah and north of Bethel. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transliteration
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus ''trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → , Cyrillic → , Greek → the digraph , Armenian → or Latin → . For instance, for the Modern Greek term "", which is usually translated as " Hellenic Republic", the usual transliteration to Latin script is , and the name for Russia in Cyrillic script, "", is usually transliterated as . Transliteration is not primarily concerned with representing the sounds of the original but rather with representing the characters, ideally accurately and unambiguously. Thus, in the Greek above example, is transliterated though it is pronounced , is transliterated though pronounced , and is transliterated , though it is pronounced (exactly like ) and is not long. Transcription, conversely, seeks to capture sound rather than spelling; "" corresponds to in the International Phonetic Alphabet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)