|
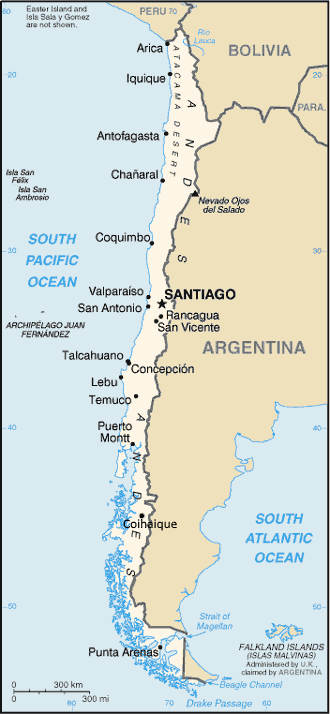
Penco, Chile
Penco (Mapudungun: See (''Pen''), Water (''Ko'')), is a Chilean city and commune in ConcepciĂłn Province, BĂo BĂo Region on the Bay of ConcepciĂłn. Founded as the city of ConcepciĂłn del Nuevo Extremo ('beginning of the new extreme') on February 12, 1550 by Pedro de Valdivia, it is the third oldest city in Chile, after capital Santiago founded first in 1541 and La Serena second in 1544. As there may be confusion between the demonyms of the inhabitants of ConcepciĂłn and Penco. Due to the previous location of ConcepciĂłn, inhabitants of that city are called ''penquistas'' while inhabitants of Penco are known as ''pencones''. History In previous centuries, in the current location of Penco, was the first location where the city of ConcepciĂłn was established, which is now the capital of the BĂobĂo Region. It was destroyed by Lautaro in 1554, and rebuilt and destroyed again by Lautaro in 1555. * It was reestablished in 1557 during the governorship of marquess GarcĂa Hurtado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Chile
This is a list of cities in Chile. A city is defined by Chile's National Statistics Institute (INE) as an "urban entity"An "urban entity" is defined by Chile's National Statistics Institute as a concentrated group of dwellings with over 2,000 inhabitants, or between 1,001 and 2,000 inhabitants if 50% or more of its population is economically active, dedicated to secondary and/or tertiary activities. Exceptionally, populated centers dedicated to tourism and recreation with over 250 concentrated dwellings and that do not meet the population requirement are considered urban. with more than 5,000 inhabitants. This list is based on a June 2005 report by the INE based on the 2002 census which registered 239 cities across the country. Complete list of cities by region Largest urban agglomerations This list includes conurbations, "absorptions" and cities with over 100,000 inhabitants, according to the 2017 census. {, {, class="wikitable sortable" , - !, !!Urban Entity!!Region!!Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Serena, Chile
La Serena () is a city and commune in northern Chile, capital of the Coquimbo Region. Founded in 1544, it is the country's second oldest city after the national capital, Santiago. As of 2012, it had a communal population of roughly 200,000, and was one of the fastest-growing areas of Chile. The city is an important tourist destination, especially during the summer, where people go to visit the beaches. It is in the headquarters of the University of La Serena and also is home to the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of La Serena, one of five Catholic Archdioceses of the Catholic Church in Chile. History The sector is currently located where the city was inhabited by the pre-Hispanic village called Viluma or Vilumanque (MapudungĂşn Snakes and condors). La Serena was founded on the orders of the Spaniard Pedro de Valdivia in order to provide a sea link to maintain permanent contact between Santiago and Lima in the Viceroyalty of Peru. For this he would need a place for his troops to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
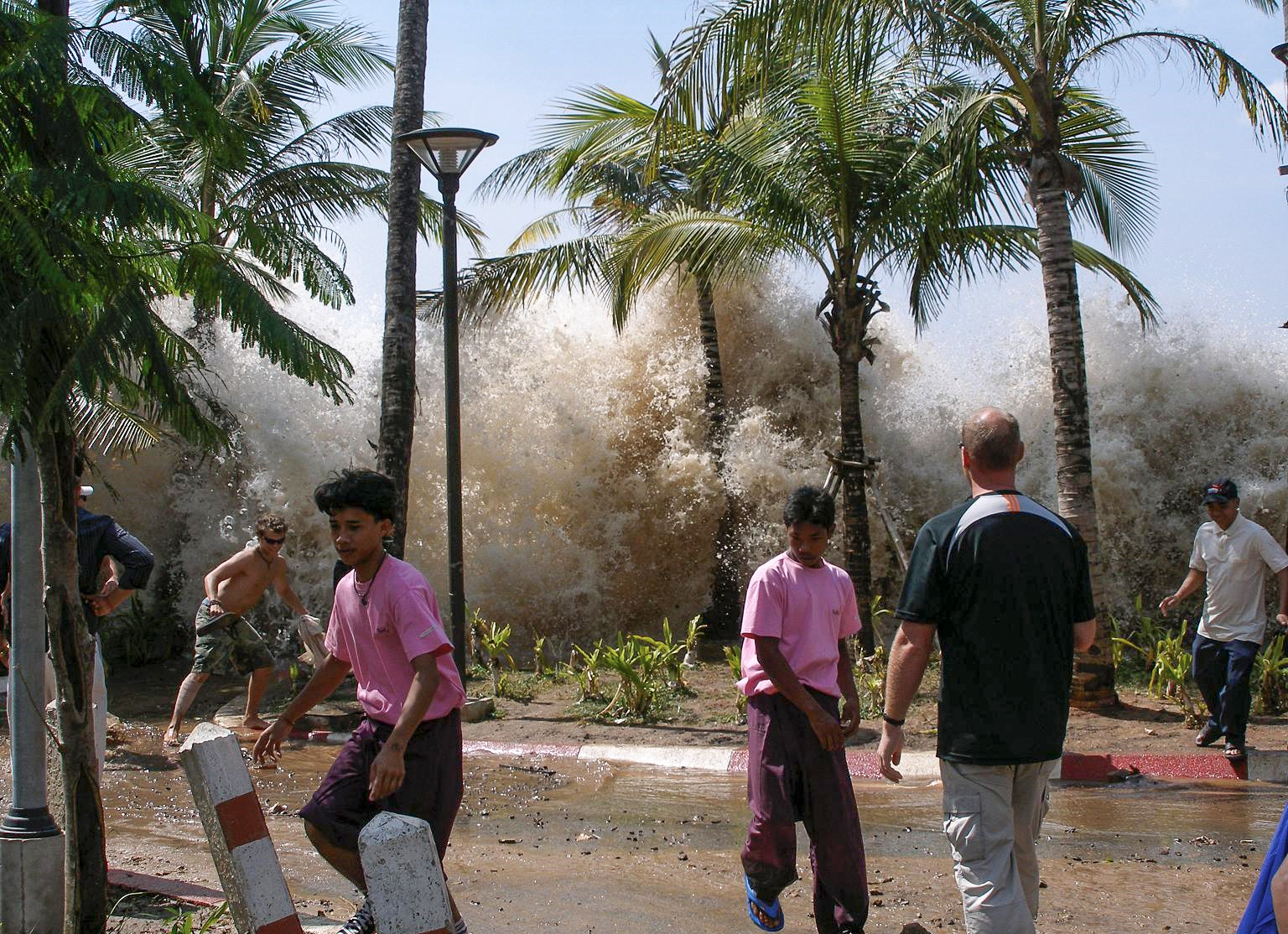
1751 ConcepciĂłn Earthquake
The 1751 ConcepciĂłn earthquake was one of the strongest and most destructive recorded quakes in Chilean history. It struck the Central Valley of the country, destroying the cities of ConcepciĂłn, ChillĂĄn, Cauquenes, CuricĂł and Talca,CrĂłnica de la Araucania: Descubrimiento i conquista, pacificaciĂłn definitiva, Horacio LaraHistoria General de Chile, Diego Barros Arana probably on May 24, 1751, although there is currently a debate among scholars as to the exact date of the earthquake (see also " Other dates"). Background The city of ConcepciĂłn had already been hit by several earthquakes. On this occasion the city was still in the process of recovering from the earthquake and tsunami that completely destroyed the city in 1730. Hours before the earthquake, on the night of May 23, there were several tremors. This had caused some ConcepciĂłn residents, accustomed to earthquakes, to prepare for the worst. Development The disaster was composed of two parts: the earthquake itsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1570 ConcepciĂłn Earthquake
The 1570 Concepción earthquake occurred at 9:00, on February 8, 1570. The strong earthquake destroyed Concepción, Chile. It was accompanied by a tsunami, and aftershocks were felt for months. According to NOAA at least 2000 lives were lost and every house was destroyed. Because of a delay between the earthquake and the tsunami, much of the population was able to escape to higher ground. The earthquake's magnitude was 8.3 Ms, located at . See also * List of earthquakes in Chile __NOTOC__ Chile lay in a region which is adjacent to the fast-moving Nazca Plate, and has high tectonic activity. The records for earlier centuries are apparently incomplete. Of the world's 46 known earthquakes with M ⼠8.5 since the year 15 ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Concepcion, 1575 1570 Concepción 16th-century earthquakes 1570 in science 1570s in the Captaincy General of Chile 1570s in the Viceroyalty of Peru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsunamis
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 洼波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquakes
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Archdiocese Of ConcepciĂłn
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of ConcepciĂłn ( la, Sanctissimae Conceptionis) is an archdiocese located in the city of ConcepciĂłn in Chile."Archdiocese of ConcepciĂłn (Santissima Concezione)" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016"Metropolitan Archdiocese of ConcepciĂłn" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved February 29, 2016 History * 22 March 1563: Established as Diocese of La Imperial f ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of La Imperial
La Imperial or Ciudad Imperial was a city founded by Pedro de Valdivia on 16 April 1552 and named in honor of the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, then (also) king of Spain. It was abandoned on 5 April 1600 and destroyed as a result of the Mapuche Uprising of 1598 during the War of Arauco. The ruins ('old city') were called Antigua Imperial. A city was refounded there in 1882 under the name Carahue. Ecclesiastical history * Established on 1563.05.22 as Diocese of La Imperial (Spanish) / Civitatis Imperialis (Latin, actually corresponding to 'Ciudad Imperial') on territory split off (with border at the river Maule) from the only two year older Diocese of Santiago de Chile (now Metropolitan, in the Chilean national capital) as Suffragan of the (Peruvian) Archdiocese of Lima * Suppressed in 1603, as the city was destroyed in 1600, its territory being reassigned to establish (at present Penco) the then Roman Catholic Archdiocese of ConcepciĂłn (now Metropolitan). ;''Suffragan bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. The art of conducting and resisting sieges is called siege warfare, siegecraft, or poliorcetics. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to Surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block the provision of supplies and the reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "Investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AraucanĂa (historic Region)
AraucanĂa or Araucana Gomez de Vidaurre ''Historia Geografica, Natural y Civil Del Reino de Chile, Tomo II''; ''Coleccion de historiadores de Chile'', Tomo XV, Imprenta Ercilla, Santiago, 1889Original from the University of Michigan, Digitized Aug 4, 2005 (History of Chile 1535-1764) was the Spanish name given to the region of Chile inhabited by the Mapuche peoples known as the Moluche (also known as Araucanos by the Spanish) in the 18th century. Prior to the Spanish conquest of Chile, the lands of the Moluche lay between the Itata River and ToltĂŠn River. History Following the great rising of the Moluche and Huilliche after the Battle of Curalaba in 1598 during the Arauco War, they expelled the Spanish from south of the BĂo-BĂo River. After many decades of further warfare, the bounds of Araucania were recognized by the Spanish as being between the BĂo-BĂo and ToltĂŠn rivers. This old region of AraucanĂa now is divided between the southern part of the BĂo-BĂo Region and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their habitat once extended from Aconcagua Valley to ChiloĂŠ Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the AraucanĂa region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities. The Mapuche traditional economy is based on agriculture; their traditional social organization consists of extended families, under the direction of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GarcĂa Hurtado De Mendoza, 5th Marquis Of CaĂąete
GarcĂa Hurtado de Mendoza y Manrique, 5th Marquis of CaĂąete (July 21, 1535 â May 19, 1609) was a Spanish Governor of Chile, and later Viceroy of Peru (from January 8, 1590 to July 24, 1596). He is often known simply as "Marquis of CaĂąete". Belonging to an influential family of Spanish noblemen Hurtado de Mendoza successfully fought in the Arauco War during his stay as Governor of Chile. The city of Mendoza is named after him. In his later position as Viceroy of Peru he sponsored Ălvaro de MendaĂąa's transpacific expedition of 1595, who named the Marquesas Islands after him. Early life He was the son of AndrĂŠs Hurtado de Mendoza, 3rd Marquis of CaĂąete — also a viceroy of Peru — and Magdalena Manrique, daughter of the Count of Osorno. Both his parents belonged to some of the most influential families in the Spanish aristocracy. In 1552 Hurtado de Mendoza ran away from home with the intention of serving his king, Charles I (Emperor Charles V), in an expedition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |