|
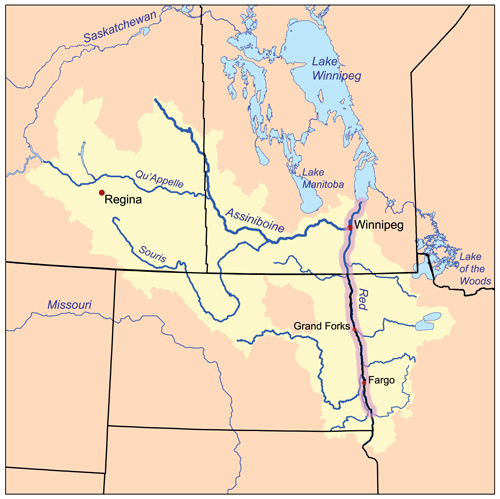
Pembina Trail
The Pembina Trail was a 19th century trail used by Métis and European settlers to travel between Fort Garry and Fort Pembina in what is today the Canadian province of Manitoba and U.S. state of North Dakota. The trail followed the west bank of the Red River. There were many alternative routes depending on conditions and which communities travellers wanted to avoid. The Pembina Trail was the part of the larger Red River Trail network and is no longer in use today as a trail, however, a modified version of it is now the Lord Selkirk and Pembina Highways in Manitoba. History The Pembina Trail and network of Red River Trails have been in regular use since at least 1823. As communities along the Red River between Fort Garry and Pembina grew, churches were built and residents began to communicate with other communities, resulting in increased travel to and from. The Pembina Trail was not only used for travel between Fort Garry and Pembina for social or political reasons, it was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis Nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Provencher
Joseph Alfred Norbert Provencher (1843–1887) was a Canadian pioneer, politician and newspaper editor. He served as a member of the Council of Keewatin from 1876 to 1877 and as Indian Agent for the Government of the Northwest Territories. Political career Provencher ran for a seat in the House of Commons of Canada in the first 1867 Canadian federal election. In a close race for the electoral district of Yamaska he was defeated by Moïse Fortier Moïse (Moyse) Fortier (November 6, 1815 – October 17, 1877) was a Quebec businessman and political figure. He was a Liberal member of the House of Commons of Canada representing Yamaska from 1867 to 1872. He was born in Saint-Léon in 1815 .... Provencher was appointed to the Council of Keewatin on November 25, 1876, serving as one of six appointed members. He served on the council until he was asked to resign along with the rest of the council April 16, 1877 References External links * 1843 births 1887 deaths Distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Trails And Roads In North Dakota
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Trails And Roads In Manitoba
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bison Hunting
Bison hunting (hunting of the American bison, also commonly known as the American buffalo) was an activity fundamental to the economy and society of the Plains Indians peoples who inhabited the vast grasslands on the Interior Plains of North America, prior to the animal's near-extinction in the late 19th century following US expansion into the West. Bison hunting was an important spiritual practice and source of material for these groups, especially after the European introduction of the horse in the 16th through 18th centuries enabled new hunting techniques. The species' dramatic decline was the result of habitat loss due to the expansion of ranching and farming in western North America, industrial-scale hunting practiced by non-Indigenous hunters, increased Indigenous hunting pressure due to non-Indigenous demand for bison hides and meat, and cases of deliberate policy by settler governments to destroy the food source of the Indigenous peoples during times of conflict. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metis In The United States
Metis or Métis may refer to: Ethnic groups * Métis, recognized Indigenous communities in Canada and America whose distinct culture and language emerged after early intermarriage between First Nations peoples and early European settlers, primarily French fur trappers * Métis in Canada are a recognized Indigenous nation, descended from specific First Nations peoples and early European settlers, and who trace their lineage to the Métis Homeland. Métis people are a nation with distinct cultural practices and language. * Métis in the United States are also a specific cultural community, with a recognized culture, lineage and homeland, and not just any "mixed" people Organizations in Canada Organizations with "Metis" or "Métis" in their names. May or may not have the same criteria for membership * Métis National Council ** Métis Nation British Columbia ** Métis Nation of Alberta ** Métis Nation-Saskatchewan Other * Manitoba Métis Federation * Métis Nation of Ontario * Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis In Canada
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives from specific mixed European (primarily French) and Indigenous ancestry which became a distinct culture through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three major groups of Indigenous peoples that were legally recognized in the Constitution Act of 1982, the other two groups being the First Nations and Inuit. Smaller communities who self-identify as Métis exist in Canada and the United States, such as the Little Shell Tribe of Chippewa Indians of Montana. The United States recognizes the Little Shell Tribe as an Ojibwe Native American tribe. Alberta is the only Canadian province with a recognized Métis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitoba Highway 75
, maint= Manitoba Infrastructure , map= , map_custom=yes , map_notes=PTH 75 highlighted in red , length_km=101 , length_notes= , direction_a=South , terminus_a= at the Pembina–Emerson Border Crossing , junction= , direction_b=North , terminus_b= in Winnipeg , established=1949 , towns=Morris , cities=Winnipeg , rural_municipalities= Emerson – Franklin, Montcalm, Morris, Ritchot , previous_type=Hwy , previous_route=68 , next_type=Hwy , next_route=77 Provincial Trunk Highway 75 (PTH 75, also officially known as the Lord Selkirk Highway) is a major highway in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It is the main link between the city of Winnipeg and the United States border, where it connects with Interstate 29/U.S. Route 81 (I-29/US 81). Route description The highway, which is part of Canada's National Highway System, begins at the Pembina-Emerson Border Crossing and runs approximately 101 kilometres (63 miles) north, along on the west side of the Red River, to Winn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a term is regarded as pejorative in some social or ethnic groups but not in others, or may be originally pejorative but later adopt a non-pejorative sense (or vice versa) in some or all contexts. Etymology The word ''pejorative'' is derived from a Late Latin past participle stem of ''peiorare'', meaning "to make worse", from ''peior'' "worse". Pejoration and melioration In historical linguistics, the process of an inoffensive word becoming pejorative is a form of semantic drift known as pejoration. An example of pejoration is the shift in meaning of the word ''silly'' from meaning that a person was happy and fortunate to meaning that they are foolish and unsophisticated. The process of pejoration can repeat itself around a single concept, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bois-Brûlés
Bois-Brûlés (''burnt wood'') are Métis. The name is most frequently associated with the French-speaking Métis of the Red River Colony in the Red River valley of Canada and the United States. The Bois-Brûlés, led by their leader Cuthbert Grant, took part in the Battle of Seven Oaks (1816). The "Chanson de la Grenouillère", composed in 1816 by Métis bard Pierre Falcon in honour of the Battle of Seven Oaks, also called "Falcon's Song" or "la Bataille des sept chênes", refers to the Métis participants as victorious "Bois-Brûlés", and the song remained central to Métis lore for generations. In 1837 Pierre Falcon also wrote "The Dickson Song" or "''Ballade du Général Dickson''". The song is about "General" James Dickson who planned to raise an army of Bois-Brûlés for the purpose of setting up a kingdom in California. William H. Keating described a group of Métis buffalo hunters he encountered at Pembina by the Red River of the North in 1823 as ''Bois brulés''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada–United States Border
The border between Canada and the United States is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Canada's border with the contiguous United States to its south, and with the U.S. state of Alaska to its west. The bi-national International Boundary Commission deals with matters relating to marking and maintaining the boundary, and the International Joint Commission deals with issues concerning boundary waters. The agencies currently responsible for facilitating legal passage through the international boundary are the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). History 18th century The Treaty of Paris of 1783 ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain and the United States. In the second article of the Treaty, the parties agreed on all boundaries of the United States, including, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Garry
Fort Garry, also known as Upper Fort Garry, was a Hudson's Bay Company trading post at the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers in what is now downtown Winnipeg. It was established in 1822 on or near the site of the North West Company's Fort Gibraltar established by John Wills in 1810 and destroyed by Governor Semple's men in 1816 during the Pemmican War. Fort Garry was named after Nicholas Garry, deputy governor of the Hudson's Bay Company. It served as the centre of fur trade within the Red River Colony. In 1826, a severe flood destroyed the fort. It was rebuilt in 1835 by the HBC and named Upper Fort Garry to differentiate it from "the Lower Fort," or Lower Fort Garry, 32 km downriver, which was established in 1831. Throughout the mid-to-late 19th century, Upper Fort Garry played a minor role in the actual trading of furs, but was central to the administration of the HBC and the surrounding settlement. The Council of Assiniboia, the administrative and judicial b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)