|
Pedunculopontine
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) or pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPT or PPTg) is a collection of neurons located in the upper pons in the brainstem. It lies caudal to the substantia nigra and adjacent to the superior cerebellar peduncle. It has two divisions of subnuclei; the pars compacta containing mainly cholinergic neurons, and the pars dissipata containing mainly glutamatergic neurons and some non-cholinergic neurons. The pedunculopontine nucleus is one of the main components of the reticular activating system. It was first described in 1909 by Louis Jacobsohn-Lask, a German neuroanatomist. Projections Pedunculopontine nucleus neurons project axons to a wide range of areas in the brain, particularly parts of the basal ganglia such as the subthalamic nucleus, substantia nigra pars compacta, and globus pallidus internus. It also sends them to targets in the thalamus, cerebellum, basal forebrain, and lower brainstem, and in the cerebral cortex, the supplementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticular Activating System
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts. Neurons of the reticular formation, particularly those of the ascending reticular activating system, play a crucial role in maintaining behavioral arousal and consciousness. The overall functions of the reticular formation are modulatory and premotor, involving somatic motor control, cardiovascular control, pain modulation, sleep and consciousness, and habituation. The modulatory functions are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
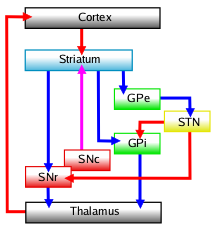
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an external and internal region, and in the division of the striatum. The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum ( caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum ( nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globus Pallidus Internus
The internal globus pallidus (GPi or medial globus pallidus; in rodents its homologue is known as the entopeduncular nucleus) and the external globus pallidus (GPe) make up the globus pallidus. The GPi is one of the output nuclei of the basal ganglia (the other being the substantia nigra pars reticulata). The GABAergic neurons of the GPi send their axons to the ventral anterior nucleus (VA) and the ventral lateral nucleus (VL) in the dorsal thalamus, to the centromedian complex, and to the pedunculopontine complex. The efferent bundle is constituted first of the ansa and lenticular fasciculus, then crosses the internal capsule within and in parallel to the Edinger's comb system then arrives at the laterosuperior corner of the subthalamic nucleus and constitutes the field H2 of Forel, then H, and suddenly changes its direction to form field H1 that goes to the inferior part of the thalamus. The distribution of axonal islands is widespread in the lateral region of the thalamus. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure involving the placement of a medical device called a neurostimulator, which sends electrical impulses, through implanted electrodes, to specific targets in the brain (the brain nucleus) for the treatment of movement disorders, including Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and other conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and epilepsy. While its underlying principles and mechanisms are not fully understood, DBS directly changes brain activity in a controlled manner. DBS has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a treatment for essential tremor and Parkinson's disease (PD) since 1997. DBS was approved for dystonia in 2003, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) in 2009, and epilepsy in 2018. DBS has been studied in clinical trials as a potential treatment for chronic pain for various affective disorders, including major depression. It is one of few neurosurgical procedures tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex believed to be involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements. The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately anterior to the central sulcus. Components of the motor cortex The motor cortex can be divided into three areas: 1. The primary motor cortex is the main contributor to generating neural impulses that pass down to the spinal cord and control the execution of movement. However, some of the other motor areas in the brain also play a role in this function. It is located on the anterior paracentral lobule on the medial surface. 2. The premotor cortex is responsible for some aspects of motor control, possibly including the preparation for movement, the sensory guidance of movement, the spatial guidance of reaching, or the direct control of some movements with an emphasis on control of proximal and trunk muscles of the body. Located anter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Jacobsohn-Lask
Louis Jacobsohn-Lask (born Louis Jacobsohn; 2 March 1863, in Bromberg – 17 May 1941, in Sevastopol) was a German neurologist and neuroanatomist. He studied medicine at the University of Berlin under Heinrich Wilhelm Waldeyer, Rudolf Virchow, Emil du Bois-Reymond, Ernst Viktor von Leyden and Robert Koch. In 1899 Jacobsohn and Edward Flatau wrote ''Handbuch der Anatomie und vergleichenden Anatomie des Centralnervensystems der Säugetiere'', which included one of the first attempts to classify sulci and gyri of human brain cortex. In 1904 he wrote, together with Flatau and Lazar Minor, another monograph, ''Handbuch der pathologischen Anatomie der Nervensystems''. He described a finger flexion reflex called the Bekhterev-Jacobsohn reflex or Jacobsohn reflex. In 1909 he first described the pedunculopontine nucleus. In 1936 he emigrated to the Soviet Union with his wife, Berta Jacobsohn-Lask, a communist of Jewish provenance, whom he had married in 1901. He was encouraged t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subthalamic Nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the subthalamic nucleus is located ventral to the thalamus. It is also dorsal to the substantia nigra and medial to the internal capsule. It was first described by Jules Bernard Luys in 1865, and the term ''corpus Luysi'' or ''Luys' body'' is still sometimes used. Anatomy Structure The principal type of neuron found in the subthalamic nucleus has rather long, sparsely spiny dendrites. In the more centrally located neurons, the dendritic arbors have a more ellipsoidal shape. The dimensions of these arbors (1200 μm, 600 μm, and 300 μm) are similar across many species—including rat, cat, monkey and human—which is unusual. However, the number of neurons increases with brain size as well as the external dimensions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arousal
Arousal is the physiological and psychological state of being awoken or of sense organs stimulated to a point of perception. It involves activation of the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) in the brain, which mediates wakefulness, the autonomic nervous system, and the endocrine system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure and a condition of sensory alertness, desire, mobility, and readiness to respond. Arousal is mediated by several neural systems. Wakefulness is regulated by the ARAS, which is composed of projections from five major neurotransmitter systems that originate in the brainstem and form connections extending throughout the cortex; activity within the ARAS is regulated by neurons that release the neurotransmitters acetylcholine, norepinephrine, dopamine, histamine, and serotonin. Activation of these neurons produces an increase in cortical activity and subsequently alertness. Arousal is important in regulating consciousness, attention, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata
The pars reticulata (SNpr) is a portion of the substantia nigra and is located lateral to the pars compacta. Most of the neurons that project out of the pars reticulata are inhibitory GABAergic neurons (i.e., these neurons release GABA, which is an inhibitory neurotransmitter). Anatomy Neurons in the pars reticulata are much less densely packed than those in the pars compacta (they were sometimes named pars diffusa). They are smaller and thinner than the dopaminergic neurons and conversely identical and morphologically similar to the pallidal neurons (see primate basal ganglia). Their dendrites as well as the pallidal are preferentially perpendicular to the striatal afferents. The massive striatal afferents correspond to the medial end of the nigrostriatal bundle. Nigral neurons have the same peculiar synaptology with the striatal axonal endings. They make connections with the dopamine neurons of the pars compacta whose long dendrites plunge deeply in the pars reticulata. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatosensory Cortex
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is a subset of the sensory nervous system, which also represents visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustatory stimuli. Somatosensation begins when mechano- and thermosensitive structures in the skin or internal organs sense physical stimuli such as pressure on the skin (see mechanotransduction, nociception). Activation of these structures, or receptors, leads to activation of peripheral sensory neurons that convey signals to the spinal cord as patterns of action potentials. Sensory information is then processed locally in the spinal cord to drive reflexes, and is also conveyed to the brain for conscious perception of touch and proprioception. Note, somatosensory information from the face and head enters the brain through peripheral se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |