|
Peckoltia Brevis
''Peckoltia brevis'' is a small species of ''Peckoltia'' belonging to the catfish family Loricariidae. ''Peckoltia brevis'' possesses the L-number L205. Distribution ''Peckoltia brevis'' is found in the middle and upper Amazon within the Purus river basin. Appearance ''Peckoltia brevis'' grows to around 11 cm and has numerous black spots and stripes on its yellow coloured body. Males can be distinguished from females by their slimmer profile and small teeth-like projections or odontodes Odontodes, or dermal teeth, are hard structures found on the external surfaces of animals or near internal openings. They consist of a soft pulp surrounded by dentine and covered by a mineralized substance such as enamel, a structure similar to th ... across the back half of their body. Habits ''Peckoltia brevis'' inhabits tangled woody backwaters and feeds primarily on small meaty foods (such as carrion) and algae. In the aquarium ''Peckoltia brevis'' requires a tropical softwater aq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesca La Monte
Francesca LaMonte (1895–1982) was a noted ichthyologist and a founding figure of the International Game Fish Association. She worked as an Assistant Curator at the American Museum of Natural History from 1920 to 1962. She began working with the museum two years after graduating from Wellesley College by translating scientific articles to English from French, German, Spanish, Italian, and Russian. LaMonte conducted significant field work, specializing in big game fish such as marlins and swordfish. She authored numerous scientific papers and best-selling fishing guides with vivid descriptors. Her years of science writing gained her the respect of prominent literary figures, including Ernest Hemingway Ernest Miller Hemingway (July 21, 1899 – July 2, 1961) was an American novelist, short-story writer, and journalist. His economical and understated style—which he termed the iceberg theory—had a strong influence on 20th-century fic ..., whom she advised on fish anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peckoltia
''Peckoltia'' is a genus of small South American Loricariidae, armored suckermouth catfishes. Many of these fish are popular aquarium fish. Taxonomy ''Peckoltia'' is a Basal (phylogenetics), basal genus within the tribe Ancistrini of the subfamily Hypostominae. This genus is paraphyly, paraphyletic. At this point, many undescribed taxon, undescribed species remain. Many of the possibly undescribed species have an identification through the L-number system. ''Peckoltia'' species can be distinguished from most other in the genera in the tribe Ancistrini by having a lateral ridge on the opercle that usually has no odontodes and the teeth on their upper jaw (dentary) forming an angle under 90 degrees; while some genera also have an angled dentary, ''Peckoltia'' species lack synapomorphy, synapomorphies of these genera. This genus and the closely related ''Hemiancistrus'' may be synonym (taxonomy), synonymous, as neither genus is supported by synapomorphies. Generally, ''Peckoltia'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores (species that eat dead material on the bottom), and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, ''Vandellia cirrhosa''. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus ''Corydoras'', are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loricariidae
The Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish (order Siluriformes), with 92 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as " plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, ''Hypostomus plecostomus'', and are popular as aquarium fish. Common names Members of the family Loricariidae are commonly referred to as loricariids, suckermouth armoured catfishes, or armoured catfish. The name "plecostomus", and its shortened forms "pleco" and "plec", are used for many Loricariidae, since ''Plecostomus plecostomus'' (now called ''Hypostomus plecostomus'') was one of the first loricariid species imported for the fish-keeping hobby. Some loricariids are not normally considered "plecostomus", such as ''Farlowella'' catfish. In their native range, these fish are known as ''cascudos'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-number
The L-number system is a semi-scientific classification system of catfish based on photographs of shipments of tropical catfish of the family Loricariidae published by the German aquarium magazine DATZ (Die Aquarien- und Terrarienzeitschrift (The Aquarium and Terrarium Magazine)). The first L-number was published in 1988. An L-number is not a formal scientific designation, but it allows people to identify various loricariid catfish by a "common name" before the fish is officially described. When a loricariid receives an official scientific name, the L-number (or numbers) is retired; best practice is then to use the scientific name. A specific L-number classification does not guarantee a discrete species, multiple L numbers have been given to different populations of the same species. To add to the confusion, sometimes a single L-number may be used for multiple species. Additionally the aquarium magazine 'Das Aquarium' introduced a similar system using the prefix 'LDA'. L-numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
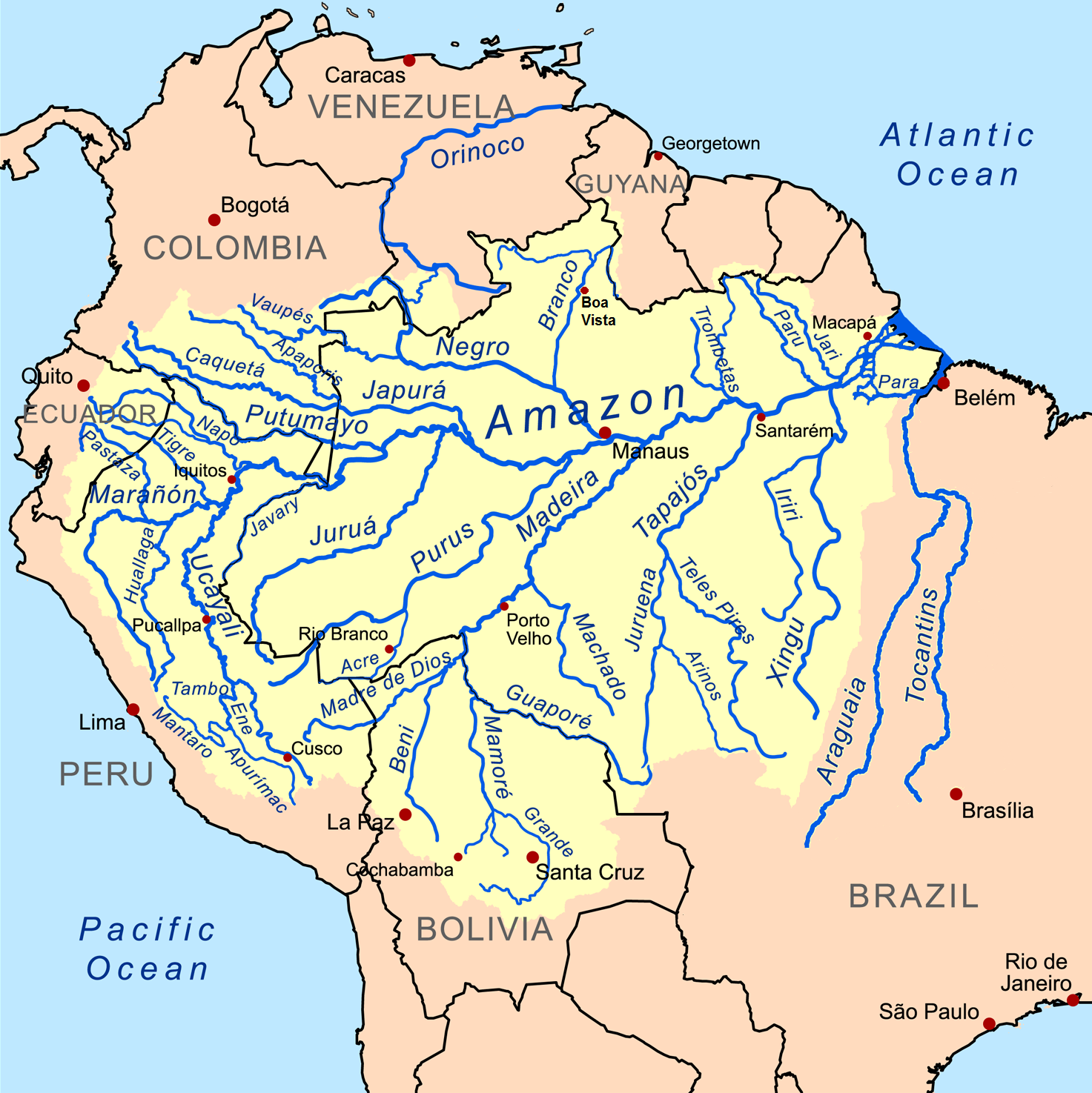
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purus River
The Purus River (Portuguese: ''Rio Purus''; Spanish: ''Río Purús'') is a tributary of the Amazon River in South America. Its drainage basin is , and the mean annual discharge is . The river shares its name with the Alto Purús National Park and the Purús Province (and its conformed Purús District), one of the four provinces of Peru in the Ucayali Region. Geography The Purus River rises in Peru. It defines the boundary between Peru and Brazil in the centre of the state of Acre, then runs for a short distance along the boundary of the Santa Rosa do Purus National Forest, a sustainable use conservation unit created in 2001 after it is joined by the Santa Rosa River. It then flows north east through Manoel Urbano It runs through a continuous forest at the bottom of the great depression, lying between the Madeira River, which skirts the edge of the Brazilian sandstone plateau, and the Ucayali River, which hugs the base of the Andes. In the state of Amazonas the river runs th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontodes
Odontodes, or dermal teeth, are hard structures found on the external surfaces of animals or near internal openings. They consist of a soft pulp surrounded by dentine and covered by a mineralized substance such as enamel, a structure similar to that of teeth. They generally do not have the same function as teeth, and are not replaced the same way teeth are in most fish. In some animals (notably catfish), the presence or size of odontodes can be used in determining the sex. Odontodes typically cover the body of chondrichthyans (cartilaginous fishes), while mineralized dermal scales are characteristic of bony fishes. During the evolution to bony fishes, ancestral odontodes have been modified to become dermal scales, including elasmoid scales in teleost Teleostei (; Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts ), is, by far, the largest infraclass in the class Actinopterygii, the ray-finned fishes, containing 96% of all extant specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
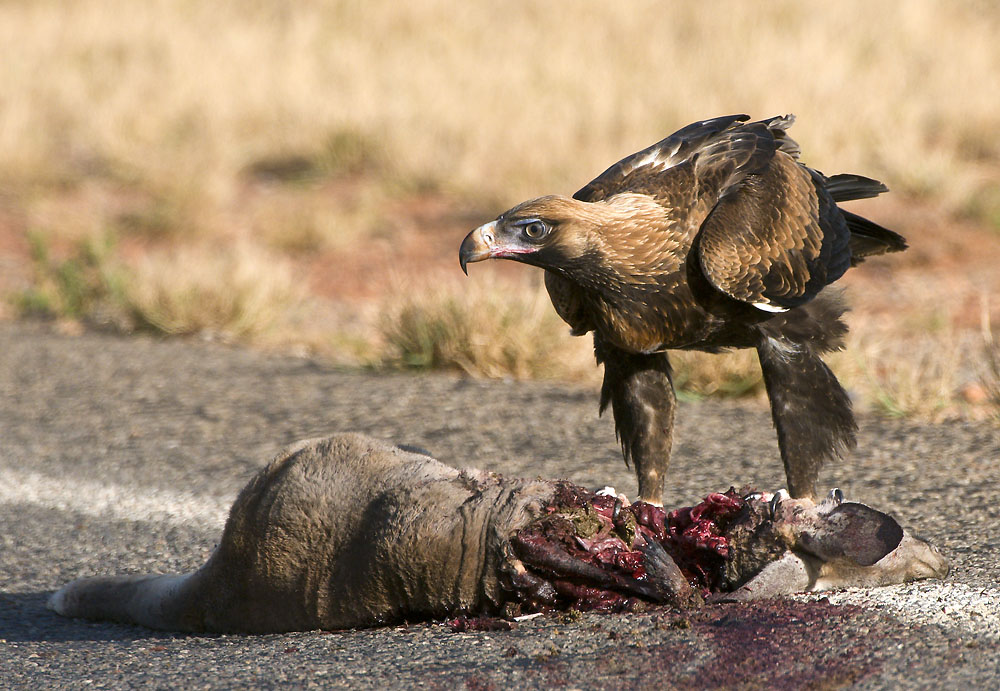
Carrion
Carrion () is the decaying flesh of dead animals, including human flesh. Overview Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures, condors, hawks, eagles, hyenas, Virginia opossum, Tasmanian devils, coyotes and Komodo dragons. Many invertebrates, such as the carrion and burying beetles, as well as maggots of calliphorid flies (such as one of the most important species in '' Calliphora vomitoria'') and flesh-flies, also eat carrion, playing an important role in recycling nitrogen and carbon in animal remains. Carrion begins to decay at the moment of the animal's death, and it will increasingly attract insects and breed bacteria. Not long after the animal has died, its body will begin to exude a foul odor caused by the presence of bacteria and the emission of cadaverine and putrescine. Some plants and fungi smell like decomposing carrion and attract insects that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)