|
Pea Patch Island
Pea Patch Island is a small island, approximately 1 mi (1.6 km) long, in the U.S. state of Delaware, located in the mid channel of the Delaware River near its entrance into Delaware Bay. It is a low, marshy island, located in New Castle County, facing Delaware City on the Delaware shore, and Finns Point on the New Jersey shore. Once the location of strategic military defenses, the island is currently owned by the State of Delaware as Fort Delaware State Park. The island emerged as a mud bank in the river in the 18th century. According to folklore, the island received its name after a ship full of peas ran aground on it, spilling its contents and leading to a growth of the plant on the island. In the 1790s, Pierre L'Enfant suggested the use of the island as part of the defenses of New Castle, Delaware and Philadelphia. During the War of 1812, a seawall and dykes were built on the island, with a view to building a Martello tower there.Dobbs, Kelli W., Rebecca J. Siders. ''F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of New York (state), New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, before emptying into Delaware Bay. It is the longest free-flowing river in the Eastern United States. The river has been recognized by the National Wildlife Federation as one of the country's Great Waters. The river's drainage basin, watershed drains an area of and provides drinking water for 17 million people. The river has two branches that rise in the Catskill Mountains of New York: the West Branch Delaware River, West Branch at Mount Jefferson (New York), Mount Jefferson in Jefferson, New York, Jefferson, Schoharie County, New York, Schoharie County, and the East Branch Delaware River, East Branch at Grand Gorge, New York, Grand Gorge, Delaware County, New York, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Fort
A bastion fort or ''trace italienne'' (a phrase derived from non-standard French, literally meaning ''Italian outline'') is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era. The design of the fort is normally a polygon with bastions at the corners of the walls. These outcroppings eliminated protected blind spots, called "dead zones", and allowed fire along the curtain from positions protected from direct fire. Many bastion forts also feature cavaliers, which are raised secondary structures based entirely inside the primary structure. Origins Their predecessors, medieval fortresses, were usually placed on high hills. From there, arrows were shot at the enemies. The enemies' hope was to either ram the gate or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as bays, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Miles
Fort Miles was a United States Army World War II installation located on Cape Henlopen near Lewes, Delaware. Although funds to build the fort were approved in 1934, it was 1938 before construction began on the fort. On 3 June 1941 it was named for Lieutenant General Nelson A. Miles. As the primary fort of the Harbor Defenses of the Delaware, it was built to defend Delaware Bay and the Delaware River and to protect domestic shipping from enemy fire between Cape May and Cape Henlopen, particularly from the German surface fleet. The fort also operated a controlled underwater minefield to prevent ships entering the Delaware River estuary. One of these mines was revealed following 2016 Hurricane Hermine by local Cape Henlopen state park staff. The sea mine and anchor were archaeologically conserved. By 1950 the Army's coast defense role had been transferred to the Navy and coastal artillery defenses were obsolete with the fort becoming surplus. The Army continued to use portions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Mott (New Jersey)
Fort Mott, located in Pennsville, Salem County, New Jersey, United States, was part of the Harbor Defenses of the Delaware, a three-fort defense system designed for the Delaware River during the postbellum and Endicott program modernization periods following the American Civil War and in the 1890s. The other two forts in the system were Fort Delaware on Pea Patch Island and Fort DuPont in Delaware City, Delaware. It is now part of Fort Mott State Park. History The original plans for Fort Mott (initially called the "Battery at Finn's Point") specified eleven gun emplacements for Rodman smoothbore guns and a mortar battery with six emplacements. Construction was started in 1872; however, only two of the gun emplacements and two magazines in the mortar battery were completed by 1876 when all work stopped due to a general suspension of fort work. The Board of Fortifications, often called the Endicott Board, recommended a comprehensive program of new fortifications in 1885. A new Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort DuPont
Fort DuPont, named in honor of Rear Admiral Samuel Francis Du Pont, is located between the original Delaware City and the modern Chesapeake and Delaware Canal on the original Reeden Point tract, which was granted to Henry Ward in 1675. Along with two other forts of the Harbor Defenses of the Delaware, it defended the Delaware River and the water approach to Philadelphia from 1900 through 1942. In 2016, the acreage which is not in the state park system was annexed into Delaware City. The first fortification built was the Ten Gun Battery, an auxiliary to nearby Fort Delaware during the American Civil War. The Twenty Gun Battery was constructed on the reservation during the 1870s, later followed by a mine control casemate for an underwater minefield in 1876. In 1897-1904, Endicott-era emplacements were constructed for long-range rifles, mortars, and rapid-fire guns. In 1922 the post became headquarters for the 1st Engineer Regiment, which remained at the post until 1941. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Fortifications
Several boards have been appointed by US presidents or Congress to evaluate the US defensive fortifications, primarily coastal defenses near strategically important harbors on the US shores, its territories, and its protectorates. Endicott Board In 1885 US President Grover Cleveland appointed a joint Army, Navy and civilian board, headed by Secretary of War William Crowninshield Endicott, known as the Board of Fortifications (now usually referred to simply as the Endicott Board). The findings of the Board in its 1886 report illustrated a grim picture of neglect of America's coast defenses and recommended a massive $127 million construction program for a series of new forts with breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coast. Coast Artillery fortifications built between 1885 and 1905 are often referred to as Endicott Period fortifications. Prior efforts at harbor defense construction had ceased in the 1870s. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
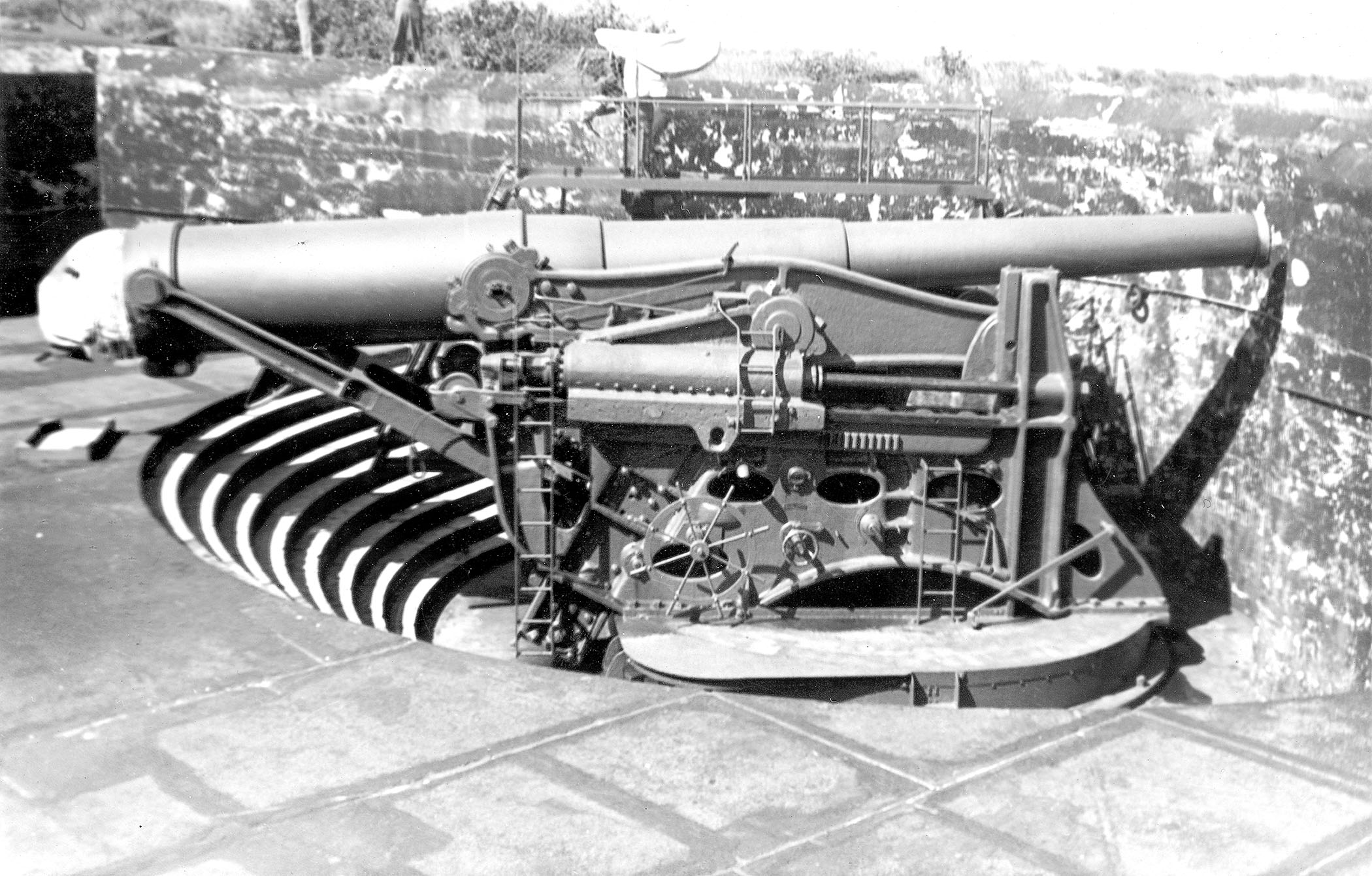
Disappearing Carriage
A disappearing gun, a gun mounted on a ''disappearing carriage'', is an obsolete type of artillery which enabled a gun to hide from direct fire and observation. The overwhelming majority of carriage designs enabled the gun to rotate backwards and down behind a parapet, or into a pit protected by a wall, after it was fired; a small number were simply barbette mounts on a retractable platform. Either way, retraction lowered the gun from view and direct fire by the enemy while it was being reloaded. It also made reloading easier, since it lowered the breech to a level just above the loading platform, and shells could be rolled right up to the open breech for loading and ramming. Other benefits over non-disappearing types were a higher rate of repetitive fire and less fatigue for the gun crew. Some disappearing carriages were complicated mechanisms, protection from aircraft observation and attack was difficult, and almost all restricted the elevation of the gun. With a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-inch Gun M1888
The 12-inch coastal defense gun M1895 (305 mm) and its variants the M1888 and M1900 were large coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1895 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Most were installed on disappearing carriages, with early installations on low-angle barbette mountings. From 1919, 19 long-range two-gun batteries were built using the M1895 on an M1917 long-range barbette carriage. Almost all of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped during and after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's secretary of war, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses, and in its 1886 report recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finns Point National Cemetery
Finn's Point National Cemetery is a United States National Cemetery located in Pennsville Township, Salem County, New Jersey, United States. It encompasses , and as of February 2009, had 3,033 interments. Adjacent to Fort Mott, it is governed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs and administered by the Washington Crossing National Cemetery. History Originally purchased by the federal government to build a battery to protect the port of Philadelphia, the land became a cemetery by 1863 for Confederate prisoners of war who died while in captivity at Fort Delaware. One hundred and thirty five Union soldiers who died while serving as guards at the prison camp are also buried here. The death toll among prisoners of war and the guards was high, especially in the latter part of 1863 and throughout 1864. By July 1863, there were 12,595 prisoners on the island at nearby Fort Delaware which was only about in size. Disease was rampant and nearly 2,700 prisoners died fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Potomac defeated attacks by Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia, halting Lee's invasion of the North. The battle involved the largest number of casualties of the entire war and is often described as the war's turning point due to the Union's decisive victory and concurrence with the Siege of Vicksburg.Rawley, p. 147; Sauers, p. 827; Gallagher, ''Lee and His Army'', p. 83; McPherson, p. 665; Eicher, p. 550. Gallagher and McPherson cite the combination of Gettysburg and Vicksburg as the turning point. Eicher uses the arguably related expression, " High-water mark of the Confederacy". After his success at Chancellorsville in Virginia in May 1863, Lee led his army through the Shenandoah Valley to begin his second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also declared secession and had full representation in the Confederate Congress, though their territory was largely controlled by Union forces. The Confederacy was formed on February 8, 1861, by seven slave states: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. All seven were in the Deep South region of the United States, whose economy was heavily dependent upon agriculture—particularly cotton—and a plantation system that relied upon enslaved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Gun_on_Moncrieff_disappearing_mount%2C_at_Scaur_Hill_Fort%2C_Bermuda.jpg)