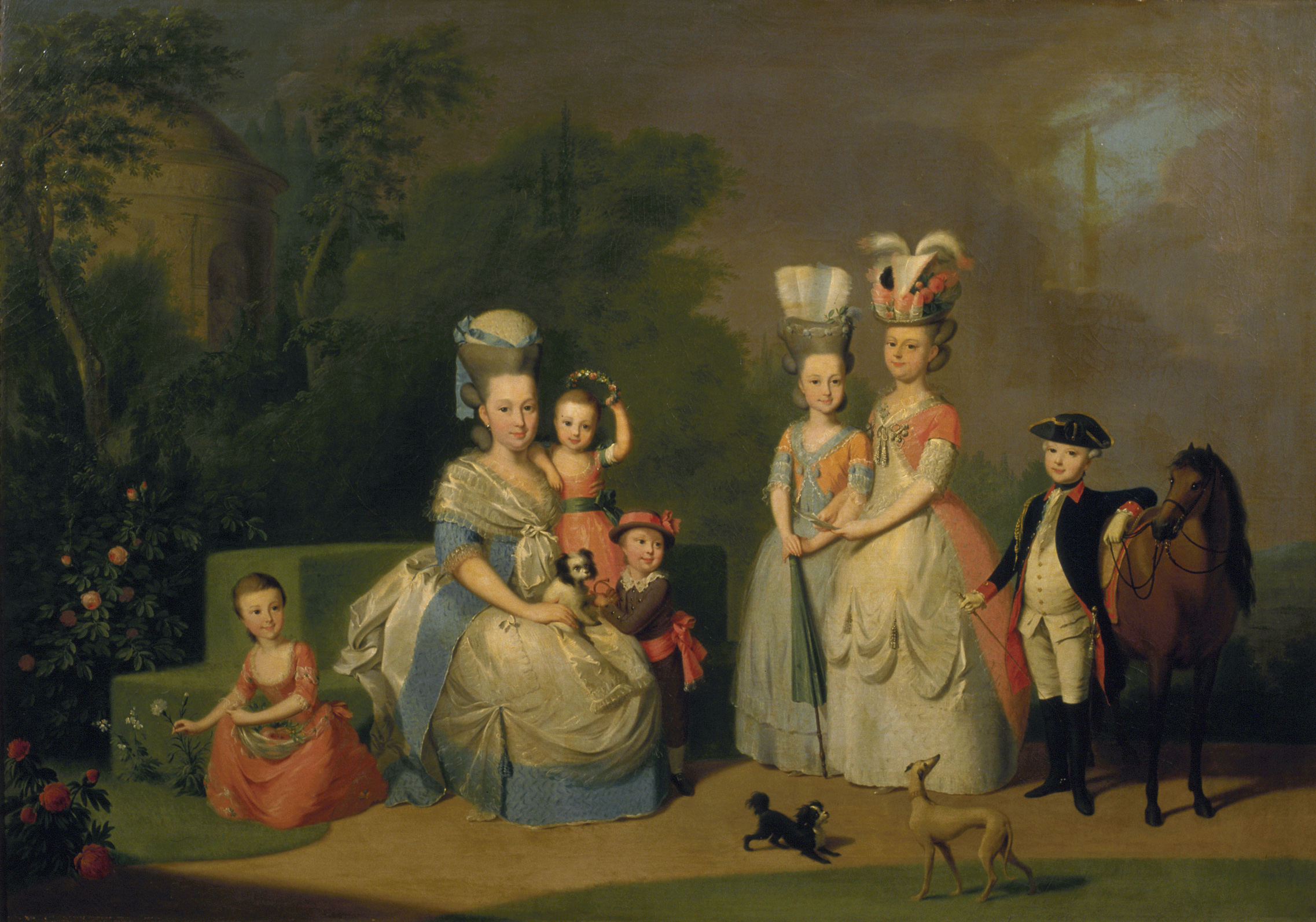|
Pauline Therese Of Württemberg
Pauline of Württemberg (4 September 1800 – 10 March 1873) was a Queen consort of Württemberg by marriage to her first cousin King William I of Württemberg. Early life Pauline Therese was born in Riga, one of the five children of Duke Louis of Württemberg and his wife, Princess Henriette of Nassau-Weilburg. Her siblings included Maria Dorothea, Archduchess of Austria; Amelia, Duchess of Saxe-Hildburghausen; Elisabeth Alexandrine, Princess of Baden, and Duke Alexander of Württemberg himself the founder of the Teck branch of the family. Her paternal grandparents were Frederick II Eugene, Duke of Württemberg, and Friederike Dorothea of Brandenburg-Schwedt. Her maternal grandparents were Charles Christian, Prince of Nassau-Weilburg, and Princess Carolina of Orange-Nassau, a daughter of William IV, Prince of Orange. She was tutored by her governess, the known memoirist Alexandrine des Écherolles, who described her pupils in her memoirs. Queen On 15 April 1820 in St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchess Amelia Of Württemberg
Duchess Amelia of Württemberg (; 28 June 179928 November 1848) was a Duchess of Württemberg and an ancestor of the British, Greek, Romanian, Yugoslavian and Spanish Royal Families. She was a daughter of Duke Louis of Württemberg and Princess Henrietta of Nassau-Weilburg. She was tutored by her governess, the known memoirist Alexandrine des Écherolles, who described her pupils in her memoirs.Side Lights on the Reign of Terror; being the memoirs of Mademoiselle des Écherolles (London, 1900) Marriage and children She married Joseph, Duke of Saxe-Altenburg (1789–1868), on 24 April 1817, at Kirchheim unter Teck. Amalie and Joseph had six daughters: * Princess ''Alexandrine'' Marie Wilhelmine Katharine Charlotte Therese Henriette Luise Pauline Elisabeth Friederike Georgine of Saxe-Altenburg (14 April 1818, Hildburghausen9 January 1907, Gmunden); married on 18 February 1843 to King George V of Hanover. * Princess ''Pauline'' Friederike Henriette Auguste of Saxe-Altenburg (24 No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Frederica Of Württemberg
Katherine, also spelled Catherine, and other variations are feminine names. They are popular in Christian countries because of their derivation from the name of one of the first Christian saints, Catherine of Alexandria. In the early Christian era it came to be associated with the Greek adjective (), meaning "pure", leading to the alternative spellings ''Katharine'' and ''Katherine''. The former spelling, with a middle ''a'', was more common in the past and is currently more popular in the United States than in Britain. ''Katherine'', with a middle ''e'', was first recorded in England in 1196 after being brought back from the Crusades. Popularity and variations English In Britain and the U.S., ''Catherine'' and its variants have been among the 100 most popular names since 1880. The most common variants are ''Katherine,'' ''Kathryn,'' and ''Katharine''. The spelling ''Catherine'' is common in both English and French. Less-common variants in English include ''Katheryn' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of 1848 In The German States
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due to perceived oppression (political, social, economic) or political incompetence. Revolutions have occurred throughout human history and vary widely in terms of methods, duration, and motivating ideology. Their results include major changes in culture, economy, and socio- political institutions, usually in response to perceived overwhelming autocracy or plutocracy. Scholarly debates about what does and does not constitute a revolution center on several issues. Early studies of revolutions primarily analyzed events in European history from a psychological perspective, but more modern examinations include global events and incorporate perspectives from several social sciences, including sociology and political science. Several generatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchess Catherine Pavlovna Of Russia
Grand Duchess Catherine Pavlovna of Russia (russian: Екатерина Павловна; 21 May 1788 S 10 May 1788– 9 January 1819) later Queen Catharina Pavlovna of Württemberg, was the fourth daughter of Tsar Paul I of Russia and Duchess Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg. She became the Queen of Württemberg upon her marriage to her first cousin Crown Prince William who eventually became King William I of Württemberg in 1816. Early life Ekaterina was born in Tsarskoye Selo and named after her grandmother, Catherine the Great. Described as beautiful and vivacious, she had a happy childhood and her education was carefully supervised by her mother. Ekaterina received the best education and constantly furthered her education through reading new literary publications and personal contacts with various outstanding persons. Known as Katya in the family, she was very close to her siblings, particularly her eldest brother Tsar Alexander I. Throughout her life she would mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy Of The Netherlands
The monarchy of the Netherlands is a constitutional monarchy. As such, the role and position of the monarch are governed by the Constitution of the Netherlands. Consequently, a large portion of it is devoted to the monarch. Roughly a third of the document explains the succession, mechanisms of accession & abdication to the throne, and the roles & duties of the monarch. This includes the formalities of communication between the States-General and the monarch's role in creating laws. The Kingdom of the Netherlands has been an independent monarchy since 16 March 1815, but its once sovereign provinces had been intermittently "governed" by members of the House of Orange-Nassau and the House of Nassau from 1559, when Philip II of Spain appointed William of Orange as stadtholder, until 1747. William became the leader of the Dutch Revolt and the independent Dutch Republic. As a stadtholder, he was followed by several of his descendants. In 1747, the function of stadtholder became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophie Of Württemberg
Sophie of Württemberg (Sophie Friederike Matilda; 17 June 1818 – 3 June 1877) was Queen of the Netherlands as the first wife of King William III. Sophie separated from William in 1855 but continued to perform her duties as queen in public. She was known for her progressive and liberal views and corresponded with several famous intellectuals. Biography Sophie was born in Stuttgart; her parents were King William I of Württemberg and Grand Duchess Catherine Pavlovna of Russia, the fourth eldest daughter of Tsar Paul I. Shortly after Sophie's birth, her mother died, and she was cared for by her aunt, Catharina of Württemberg. She was niece of tsars Alexander I and Nicholas I of Russia. She had a close relationship with her father and her sister Marie, but not to her stepmother.Fia Dieteren, Sophie van Württemberg, in: Digitaal Vrouwenlexicon van Nederland. URL: http://resources.huygens.knaw.nl/vrouwenlexicon/lemmata/data/SophievanWurtemberg 3/01/2014/ref> She was given a bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandrine Des Écherolles
Alexandrine Etiennette Marie Charlotte des Écherolles (1779 – 1850) was a French memoirist, writing of her experiences during the French Revolution. Life She was born in the Château des Écherolles in La Ferté-Hauterive, Allier, the daughter of Joseph-Étienne Giraud des Écherolles, a royalist officer of the provincial lower nobility. Her mother, Marie Anne Odile (née de Tarade), died while Alexandrine was still a child, so she was brought up by her paternal aunt. In 1792, the family fled from their home town of Moulins to Lyon, where they experienced the Lyon uprising and the following Siege of Lyon in 1793. Her aunt was arrested and executed during the Reign of Terror following the Siege, while her father fled to Switzerland.Yalom, Marilyn, 1995: ''Blood Sisters: the French Revolution in Women's Memory''. Pandora: London She was reunited with her father after the fall of Robespierre. In later life she was appointed governess to the princesses of the royal fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William IV, Prince Of Orange
William IV (Willem Karel Hendrik Friso; 1 September 1711 – 22 October 1751) was Prince of Orange from birth and the first hereditary stadtholder of all the United Provinces of the Netherlands from 1747 until his death in 1751. During his whole life he was furthermore ruler of the Principality of Orange-Nassau within the Holy Roman Empire. Early life William was born in Leeuwarden, Netherlands, the son of John William Friso, Prince of Orange, head of the Frisian branch of the House of Orange-Nassau, and of his wife Landgravine Marie Louise of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel). He was born six weeks after the death of his father. William succeeded his father as Stadtholder of Friesland and also, under the regency of his mother until 1731, as Stadtholder of Groningen. In 1722 he was elected Stadtholder of Guelders. The four other provinces of the Dutch Republic:, Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht and Overijssel had in 1702 decided not to appoint a stadtholder after the death of stadtholder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Carolina Of Orange-Nassau
Princess Carolina of Orange-Nassau (''Wilhelmine Carolina''; 28 February 1743 – 6 May 1787) was a Dutch regent. She was the daughter of William IV, Prince of Orange, Stadtholder of the Netherlands, and Anne, Princess Royal. She was regent of the Netherlands from 1765 until 1766 during the minority of her brother, William V. Life Princess Carolina was born in Leeuwarden, the eldest daughter of William IV, Prince of Orange, Stadtholder of the Netherlands, and Anne, Princess Royal. In 1747, it was declared that the position of stadtholder could be inherited by females, thus making the young Princess Carolina the heir presumptive to the position of stadtholder. However, in 1748, a male heir, William, was born to her parents, thus displacing her and putting her second in line to the position. She was given a good education in music. Princess Carolina's father died in 1751, making her three-year-old brother William V of Orange. At that point, her mother was appointed regent. Her marria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Christian, Prince Of Nassau-Weilburg
Charles Christian, Prince of Nassau-Weilburg (Weilburg, 16 January 1735 – Münster-Dreissen, near Kirchheim, 28 November 1788), till 1753 Count of Nassau-Weilburg, was the first ruler of the Principality of Nassau-Weilburg between 1753 and 1788. Family and rule He was the son of Charles August, Prince of Nassau-Weilburg and Princess Auguste Friederike of Nassau-Idstein. He succeeded his father in 1753 and united his territories in 1783 with Nassau-Saarbrücken, Nassau-Usingen and Nassau-Dietz. Marriage He married on 5 March 1760 in The Hague Princess Carolina of Orange-Nassau (1743–1787), daughter of William IV, Prince of Orange and Anne, Princess Royal. He became a general in the Dutch infantry, governor of Bergen op Zoom and governor of Maastricht (1773–1784). He negotiated in vain with the Patriots in 1787. After the death of his wife, he concluded a morganatic marriage with Barbara Giessen von Kirchheim. He died in 1788 and was succeeded by his eldest surviving so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friederike Dorothea Of Brandenburg-Schwedt
Friederike of Brandenburg-Schwedt (Friederike Sophia Dorothea; 18 December 1736 – 9 March 1798) was Duchess of Württemberg by marriage to Frederick II Eugene, Duke of Württemberg. She is an ancestor to many European royals of the 19th and 20th century. Biography Friederike was a daughter of Margrave Frederick William of Brandenburg-Schwedt and Princess Sophia Dorothea of Prussia. Her mother was a sister of Frederick the Great. Her siblings included Elisabeth Louise, Princess Augustus Ferdinand of Prussia and Philippine, Landgravine of Hesse-Cassel. On 2 November 1753, she married Frederick Eugen of Württemberg. He would succeed his brother in 1795, making her Duchess consort of Württemberg. Friederike was described as witty and charming. She belonged to the reformed faith, while her husband was Catholic; however, she brought up her children as Lutheran upon agreement with the Lutheran council, from whom she received an allowance. From 1769, she lived at Montbélia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |