|
Paulina Álvarez
Raimunda Paula Peña Álvarez (June 29, 1912 – July 22, 1965), better known as Paulina Álvarez, was a renowned Cuban singer of danzonetes (sung danzones). She became the leading exponent of the genre during the 1930s, being nicknamed La Emperatriz del Danzonete (The Empress of the Danzonete). Her greatest hit was the song "Rompiendo la rutina", the first danzonete, composed by Aniceto Díaz in 1929. In 1960 she recorded her only LP record. Life and career Early life and career Paulina Álvarez was born Raimunda Paula Peña Álvarez on June 29, 1912 in Cienfuegos, Cuba. By the time she was eight or nine years old she was singing at parties and school functions. In 1926, at age 14, her family moved to Havana, where she started her professional singing career in societies, theatres and radio shows. She sang boleros and canciones, but quickly became specialized in a new style of sung danzón influenced by the son cubano called danzonete. In 1931 she became the singer for Orquesta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cienfuegos
Cienfuegos (), capital of Cienfuegos Province, is a city on the southern coast of Cuba. It is located about from Havana and has a population of 150,000. Since the late 1960s, Cienfuegos has become one of Cuba's main industrial centers, especially in the energy and sugar sectors. The city is dubbed ''La Perla del Sur'' (Pearl of the South). Although ''Cienfuegos'' literally translates to "one hundred fires" (''cien'', "one hundred"; ''fuegos'', "fires"), the city takes its name from the surname of José Cienfuegos, Captain General of Cuba (1816–19). In 2005, UNESCO inscribed the '' Urban Historic Centre of Cienfuegos'' on the World Heritage List, citing Cienfuegos as the best extant example of early 19th century Spanish Enlightenment implementation in urban planning. The downtown area contains six buildings from 1819–50, 327 buildings from 1851–1900, and 1188 buildings from the 20th century. There is no other place in the Caribbean which contains such a remarkable cluster o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obdulio Morales
Obdulio Morales Ríos (April 7, 1910 – January 9, 1981) was a Cuban pianist, conductor, composer and ethnomusicologist, an important figure in the late afrocubanismo movement. He championed Afro-Cuban music traditions and sponsored artists such as Merceditas Valdés. Career Early life and career Obdulio Morales Ríos was born in Havana on April 7, 1910. He learned piano from an American teacher and furthered his studies at the conservatory. At age 12 he began to play piano at the silent cinema, and a year later he was playing in private dance parties as a reserve pianist. Around the same time, while working as an apprentice for his father, who was a tailor, he began to attend black societies such as the Club Bohemio. In 1924 he joined the first lineup of Los Hermanos Martínez orchestra. 1930s Morales worked for the radio since 1928, specializing in Afro-Cuban music. In 1938 he premiered ''Batamú'' in collaboration with musician Julio Chappottín (father of Félix Chappo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EGREM
EGREM (Empresa de Grabaciones y Ediciones Musicales, Spanish for ''Enterprise of Recordings and Musical Editions'') is the national record label of Cuba. It is headquartered in Centro Habana, where its main record studios (''Estudios Areito'' 101 & 102) operate. It was founded in 1964 after the nationalization of the Cuban music industry, absorbing the assets of Panart. EGREM had a monopoly on music production activities from 1964 until the late 1980s when independent labels reemerged.Cubadisco: Cuba's premier music awards show Cuba Absolutely. April 2013. EGREM's archive comprises "the most extensive catalog of Cuban music in the world". Since 2002, EGREM has a commercial director, a public relations department and a we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilberto Valdés
Gilberto S. Valdés (21 May 1905, in Jovellanos, Matanzas – 12 May 1972, in New York City) was a Cuban music director and composer who specialised in the afro genre of Cuban popular music. Valdés was one of the first popular bandleaders to introduce African melody, rhythm and traditional themes into his music."El Concierto Afro-Cubano de Gilberto S. Valdés," 344 Estudios Afrocubanos , 1 (1937), 139-145. His Afro-Cuban compositions first gained attention in 1935, when Rita Montaner, accompanied by the pianist Rafael Betancourt, presented his songs "Bembé", "Baró", "Tambó" y "Sangre africana" in the Teatro Principal de la Comedia. Discography *''Cuban ballet'' Orquesta de Cámara de Madrid dir. Gilberto Valdés LP Montilla 92: *''Hi Fi in the tropics'' LP Montilla 94 *''Gran Orquesta Típica Nacional'' LP Puchito SP-114: *''Rezo de santo – Ritmo de santo de la tierra de África en Arará. '' LP Maype 180 *''La música del maestro Gilberto Valdés – Con su orquesta'' LP Pana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubén González (pianist)
Rubén González Fontanills (26 May 1919 – 8 December 2003) was a Cuban pianist. Together with Lilí Martínez and Peruchín he is said to have "forged the style of modern Cuban piano playing in the 1940s". Between the 1940s and his retirement in the 1980s, he played with Cuba's most successful acts, including Paulina Álvarez, Arsenio Rodríguez, Orquesta América del 55, Orquesta Riverside and Enrique Jorrín. In the 1990s, he came out of retirement to play in the revival ensembles Afro-Cuban All Stars and Buena Vista Social Club, also recording solo material and performing live until 2002. Biography Early life and career González was born in Santa Clara, Cuba, on 26 May 1919. His family moved to the small village of Encrucijada when he was 6 years old. He took up the piano at age seven and graduated from the Cienfuegos Conservatory at age 15.Lucy Duran. Sleeve notes from ''Introducing... Rubén González'', World Circuit Records WCD 049, 1997. He grew up wanting to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Fajardo (musician)
José Antonio Fajardo (October 18, 1919 – December 11, 2001) was a Cuban charanga bandleader and flautist, who played the traditional five-keyed wooden flute. Born in Pinar del Río, Cuba, Fajardo after performing with the band of Antonio María Romeu Antonio María Romeu Marrero (11 September 1876 – 18 January 1955) was a Cuban pianist, composer and bandleader. His orchestra was Cuba's leading Charanga (Cuba), charanga for over thirty years, specializing in the danzón. Throughout his ca ..., formed his own charanga band in 1949. Fajardo died in December 2001, at the age of 82. References 1919 births 2001 deaths Cuban bandleaders Cuban flautists Cuban composers Male composers Mambo musicians Cha-cha-cha musicians Danzón musicians People from Pinar del Río Cuban charanga musicians Cuban male musicians 20th-century flautists {{Cuba-musician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMQ (Cuba)
CMQ was a Cuban radio and television station located in Havana, Cuba, reaching an audience in the 1940s and 1950s, attracting viewers and listeners with a program that ranged from music and news dissemination. It later expanded into radio and television networks. As a radio network it was a heated competitor of the RHC-Cadena Azul network. Founding The company was founded on March 12, 1933, by Miguel Gabriel and Ángel Cambó. Ten years later, on August 1, 1943, half of it was acquired by the business group of Goar Mestre. In the beginning, it transmitted only in the capital expanding later to the rest of the country. Pre-revolutionary Cuba was an early adopter of new technology, including TV. Cuba was the first Latin American country to have television. In December 1946, station CM-21P conducted an experimental multi-point live broadcast. Regular commercial broadcasting began in October 1950 with Gaspar Pumarejo's Unión Radio TV. This was followed by Goar Mestre Espinosa's CMQ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solfège
In music, solfège (, ) or solfeggio (; ), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a music education method used to teach aural skills, Pitch (music), pitch and sight-reading of Western classical music, Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Syllables are assigned to the notes of the Scale (music), scale and enable the musician to Gordon music learning theory#Audiation, audiate, or mentally hear, the pitches of a piece of music being seen for the first time and then to sing them aloud. Through the Renaissance music, Renaissance (and much later in some shapenote publications) various interlocking 4, 5 and 6-note systems were employed to cover the octave. The tonic sol-fa method popularized the seven syllables commonly used in English-speaking countries: ''do'' (or ''doh'' in tonic sol-fa),''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd Ed. (1998) ''re'', ''mi'', ''fa'', ''so(l)'', ''la'', and ''ti'' (or ''si'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunto
The term ''conjunto'' (, literally 'group', 'ensemble') refers to several types of small musical ensembles present in different Latin American musical traditions, mainly in Mexico and Cuba. While Mexican conjuntos play styles such as '' norteño'' and '' tejano'', Cuban ''conjuntos'' specialize in the ''son'', as well as its derivations such as ''salsa''. Mexican Mexican conjunto music, also known as ''conjunto tejano'', was born in south Texas at the end of the 19th century, after German settlers introduced the button accordion. The ''bajo sexto'' has come to accompany the button accordion and is integral to the ''conjunto'' sound. Many ''conjuntos'' are concentrated in the Southwestern portion of the United States, primarily in Texas and California. In Mexico, the term ''conjunto'' is associated with '' norteño'' and ''tejano'' music. Since ''tejano'' was bred out of ''norteño'' music originally, this association is not entirely false. However, due to various cultural and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Rumba
Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based ''coros de clave''. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles. Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and ''solares'' (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. '' Cajones'' (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustavo Tamayo
Gustavo E. Tamayo is a Colombian ophthalmologist known for developing a refractive surgery method known as Contoured Ablation Patterns (CAP), which enables doctors to make surgeries faster and at an easier rate. Tamayo has also developed and patented a procedure to treat presbyopia, which is at the moment being tested by AMO (Abbott Medical Optics) in order to massively apply this procedure in a global manner once approved by the FDA. He also has other patents dealing with cataract removal through laser application. Tamayo was designated subdirector of the Subspecialty Refractive Surgery Day at American Academy of Ophthalmology meeting in 2008 which took place in Atlanta Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ... and was appointed director for the same meeting in its 2009 edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
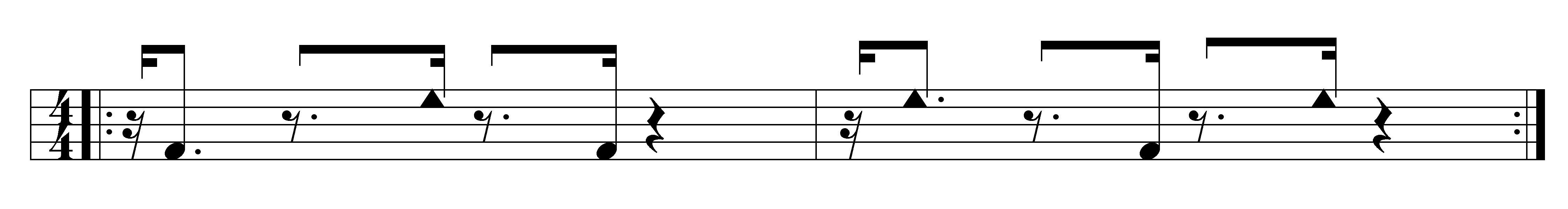
Güiro
The güiro () is a Puerto Rican percussion instrument consisting of an open-ended, hollow gourd with parallel notches cut in one side. It is played by rubbing a stick or tines (see photo) along the notches to produce a ratchet sound. The güiro is commonly used in Puerto Rican, Cuban and other forms of Latin American music, and plays a key role in the typical rhythm section of important genres like son, trova and salsa. Playing the güiro usually requires both long and short sounds, made by scraping up and down in long or short strokes. The güiro, like the maracas, is often played by a singer. It is closely related to the Cuban guayo, Dominican güira, and Haitian graj which are made of metal. Other instruments similar to the güiro are the Colombian guacharaca, the Brazilian reco-reco, the quijada (cow jawbone) and the frottoir (French) or fwotwa (French Creole) ( washboard). Etymology In the Arawakan language, a language of the indigenous people of Latin America and sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |