|
Paul Neill
Paul Neill (September 6, 1882 – October 1968) was an American electrical engineer at Bell Labs in the 1940s. He is credited with helping to invent the BNC, TNC, and Type N connectors used for microwave and RF communications. He joined Bell in 1916 after spending 12 years at the Westinghouse Electric Company. He retired from Bell on September 30, 1947. See also *RF connector *Carl Concelman Carl Concelman (December 23, 1912 – August 1975) was the electrical engineer who, while working for Amphenol, invented the C connector and teamed up with Paul Neill of Bell Labs to invent the BNC connector and TNC connector. See also *RF ... References External links * 1882 births 1968 deaths Scientists at Bell Labs American electrical engineers 20th-century American inventors {{US-electrical-engineer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineer
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is now divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984), then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996) and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007), is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by multinational company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. Researchers working at Bell Laboratories are credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B, C, C++, S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others. Nine Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organization of the Bell System telephone conglomerate. In the late 19th century, the laboratory began as the Western Electric Engineering Department, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
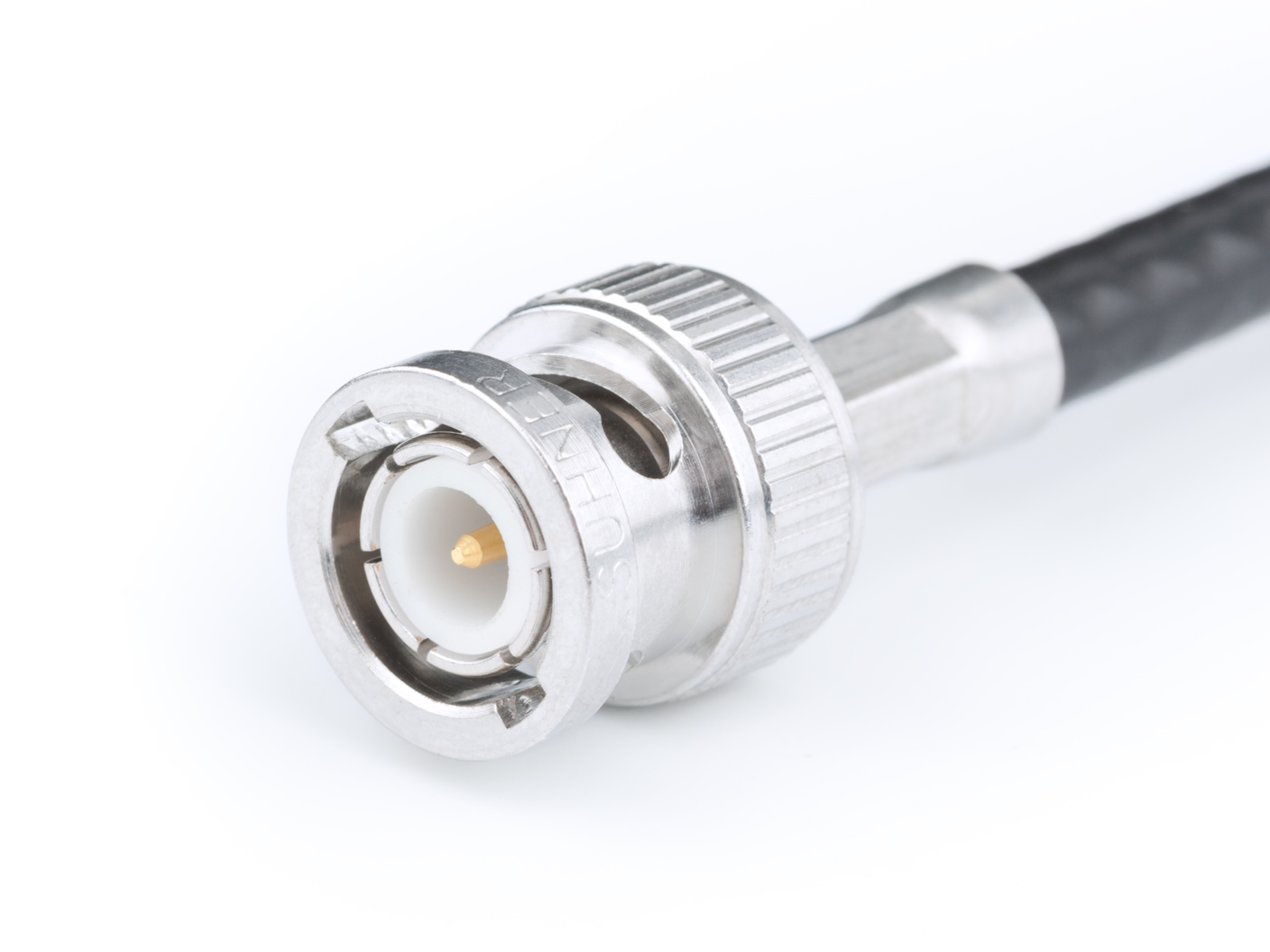
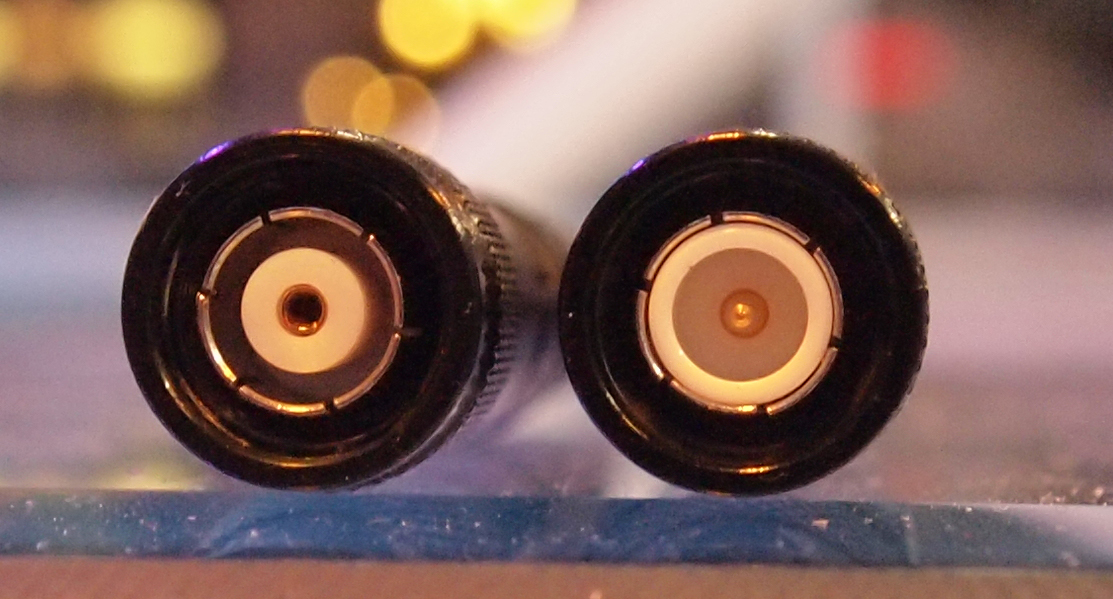
BNC Connector
The BNC connector (initialism of "Bayonet Neill–Concelman") is a miniature quick connect/disconnect radio frequency connector used for coaxial cable. It is designed to maintain the same characteristic impedance of the cable, with 50 ohm and 75 ohm types being made. It is usually applied for video and radio frequency connections up to about 2 GHz and up to 500 volts. The connector has a twist to lock design with two lugs in the female portion of the connector engaging a slot in the shell of the male portion. The type was introduced on military radio equipment in the 1940s and has since become widely applied in radio systems, and is a common type of video connector. Similar radio-frequency connectors differ in dimensions and attachment features, and may allow for higher voltages, higher frequencies, or three-wire connections. Description The BNC connector features two bayonet lugs on the female connector; mating is fully achieved with a quarter turn of the coupling nut. It u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNC Connector
The TNC connector (acronym of "Threaded Neill–Concelman") is a threaded version of the BNC connector. Description The interface specifications for the TNC and many other connectors are referenced in MIL-STD-348. The connector has a 50 Ω impedance and operates best in the 0–11 GHz frequency spectrum. It has better performance than the BNC connector at microwave frequencies. Invented in the late 1950s and named after Paul Neill of Bell Labs and Carl Concelman of Amphenol, the TNC connector has been employed in a wide range of radio and wired applications. The TNC connector features a 7/16"-28 thread, not to be confused with a 7/16 DIN connector, which is the diameter of the mating surfaces as specified in millimeters. Variations Reverse-polarity TNC Reverse-polarity TNC (RP-TNC, sometimes RTNC) is a variation of the TNC specification which reverses the polarity of the interface. This is usually achieved by incorporating the female contacts normally found in jacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
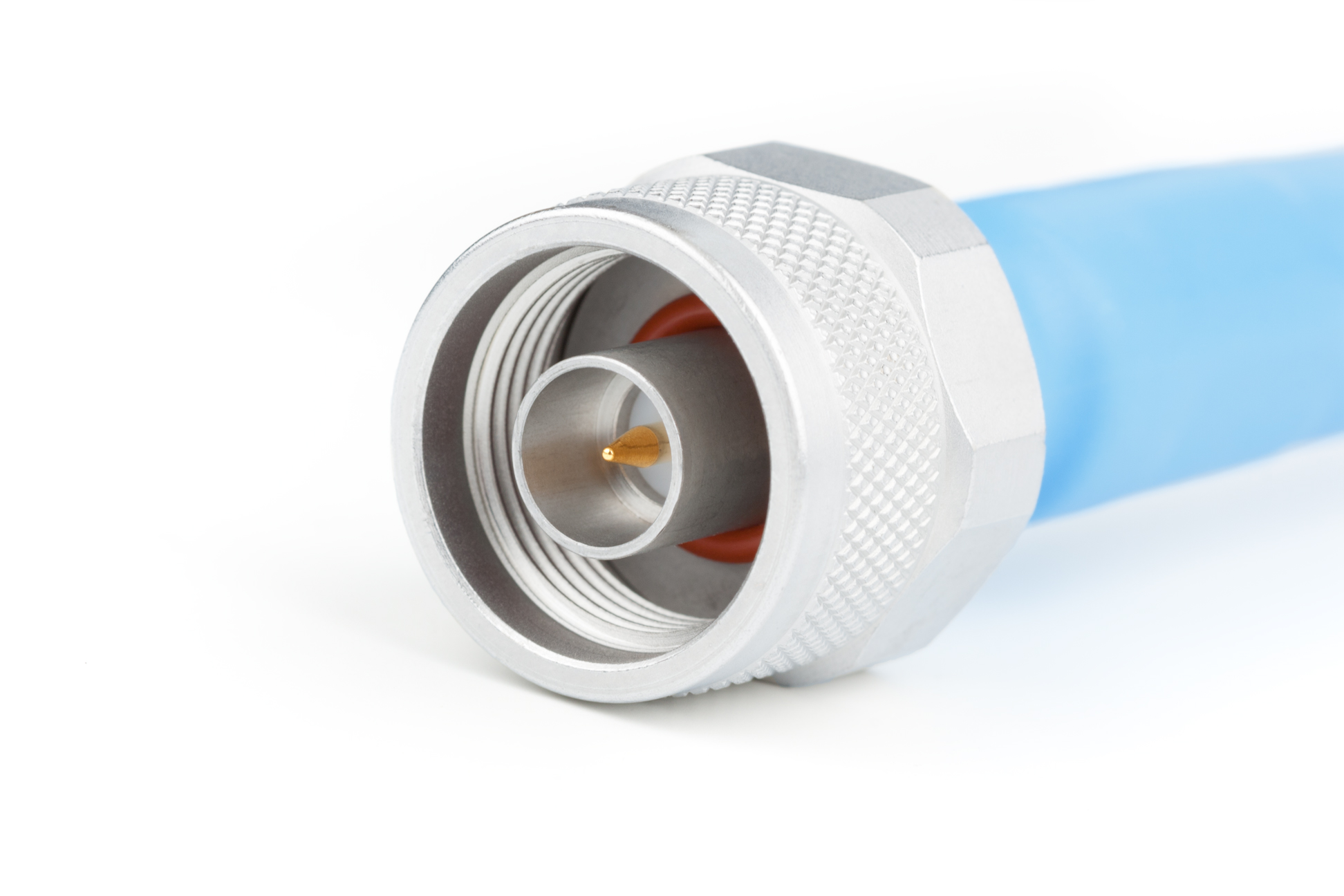
N Connector
The N connector (also, type-N connector) is a threaded, weatherproof, medium-size RF connector used to join coaxial cables. It was one of the first connectors capable of carrying microwave-frequency signals, and was invented in the 1940s by Paul Neill of Bell Labs, after whom the connector is named. Design The interface specifications for the N and many other connectors are referenced in MIL-STD-348. Originally, the connector was designed to carry signals at frequencies up to 1 GHz in military applications, but today's common Type N easily handles frequencies up to 11 GHz. More recent precision enhancements to the design by Julius Botka at Hewlett Packard have pushed this to 18 GHz. The male connector is hand-tightened (though versions with a hex nut are also available) and has an air gap between the center and outer conductors. The coupling has a -24 UNEF thread. Amphenol suggests tightening to a torque of , while Andrew Corporation suggest for their hex nut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RF Connector
A coaxial RF connector (radio frequency connector) is an electrical connector designed to work at radio frequencies in the multi-megahertz range. RF connectors are typically used with coaxial cables and are designed to maintain the shielding that the coaxial design offers. Better models also minimize the change in transmission line impedance at the connection in order to reduce signal reflection and power loss. As the frequency increases, transmission line effects become more important, with small impedance variations from connectors causing the signal to reflect rather than pass through. An RF connector must not allow external signals into the circuit through electromagnetic interference and capacitive pickup. Mechanically, RF connectors may provide a fastening mechanism ( thread, bayonet, braces, blind mate) and springs for a low ohmic electric contact while sparing the gold surface, thus allowing very high mating cycles and reducing the insertion force. Research activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ranges as microwaves; the above broad definition includes both UHF and EHF (millimeter wave) bands. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 0.3 m and 3 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire SHF band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. Frequencies in the microwave range are often referred to by their IEEE radar band designations: S, C, X, Ku, K, or Ka band, or by similar NATO or EU designations. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range. Rather, it indicates that microwaves are "small" (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used prior to microwave te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |