|
Patricia G. Spear
Patricia Gail Spear (born 1942) is an American Virology, virologist. She is a professor emeritus of microbiology and immunology at Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois. She is best known for her pioneering work studying the herpes simplex virus. Spear is a past president of the American Society for Virology and an elected member of the National Academy of Sciences. Education and early career Spear began her undergraduate education at Florida State University. She went to study nursing and ultimately switched her major to bacteriology with a minor in chemistry and graduated in 1964. One year later, she received her Master of Science from Florida State in bacteriology and then enrolled in a graduate program in virology at the University of Chicago. For her doctoral work, Spear joined the laboratory of Bernard Roizman to conduct research on herpes simplex virus (HSV). In an interview, she noted: "I thought it was mind-blowing how the virus could change the shape and behavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and '' Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are very common and contagious. They can be spread when an infected person begins shedding the virus. As of 2016, about 67% of the world population under the age of 50 had HSV-1. In the United States, about 47.8% and 11.9% are estimated to have HSV-1 and HSV-2, respectively, though actual prevalence may be much higher. Because it can be transmitted through any intimate contact, it is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Symptoms Many of those who are infected ''never'' develop symptoms. Symptoms, when they occur, may include watery blisters in the skin or mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, nose, genitals, or eyes (herpes simplex keratitis). Lesions heal with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nursing
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health care providers by their approach to patient care, training, and scope of practice. Nurses practice in many specialties with differing levels of prescription authority. Nurses comprise the largest component of most healthcare environments; but there is evidence of international shortages of qualified nurses. Many nurses provide care within the ordering scope of physicians, and this traditional role has shaped the public image of nurses as care providers. Nurse practitioners are nurses with a graduate degree in advanced practice nursing. They are however permitted by most jurisdictions to practice independently in a variety of settings. Since the postwar period, nurse education has undergone a process of diversification towards advanced a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. There are two distinct aspects of the immune response, the innate and the adaptive, which work together to protect against pathogens. The innate branch—the body's first reaction to an invader—is known to be a non-specific and quick response to any sort of pathogen. Components of the innate immune response include physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and monocytes, and soluble factors including cytokines and complement. On the other hand, the adaptive branch is the body's immune response which is catered against specific antigens and thus, it takes longer to activate the components involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Fusion
Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells (cells with a single nucleus) combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoclasts and trophoblasts, during embryogenesis, and morphogenesis. Cell fusion is a necessary event in the maturation of cells so that they maintain their specific functions throughout growth. History In 1847 Theodore Schwann expanded upon the theory that all living organisms are composed of cells when he added to it that discrete cells are the basis of life. Schwann observed that in certain cells the walls and cavities of the cells coalesce together. It was this observation that provided the first hint that cells fuse. It was not until 1960 that cell biologists deliberately fused cells for the first time. To fuse the cells, biologists combined isolated mouse cells, with the same kind of tissue, and induced fusion of their outer membrane using the Sendai v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated. In proteins that have segments extending extracellularly, the extracellular segments are also often glycosylated. Glycoproteins are also often important integral membrane proteins, where they play a role in cell–cell interactions. It is important to distinguish endoplasmic reticulum-based glycosylation of the secretory system from reversible cytosolic-nuclear glycosylation. Glycoproteins of the cytosol and nucleus can be modified through the reversible addition of a single GlcNAc residue that is considered reciprocal to phosphorylation and the functions of these are likely to be an additional regulatory mechanism that controls phosphorylation-based signalling. In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
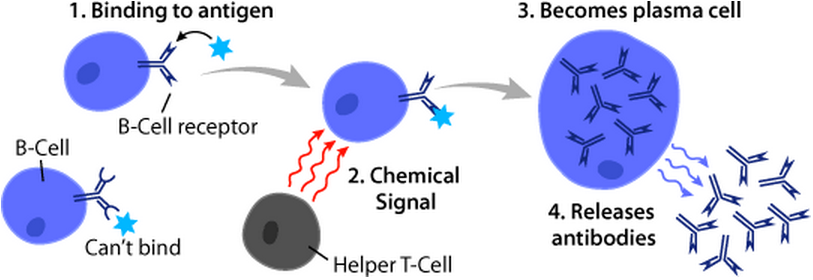
B Cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rockefeller University
The Rockefeller University is a private biomedical research and graduate-only university in New York City, New York. It focuses primarily on the biological and medical sciences and provides doctoral and postdoctoral education. It is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity." Rockefeller is the oldest biomedical research institute in the United States. In 2018, the faculty included 82 tenured and tenure-track members, including 37 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 17 members of the National Academy of Medicine, seven Lasker Award recipients, and five Nobel laureates. As of March 2022, a total of 26 Nobel laureates have been affiliated with Rockefeller University. The university is located on the Upper East Side of Manhattan, between 63rd and 68th streets on York Avenue. Richard P. Lifton became the university's eleventh president on September 1, 2016. The Rockefeller University Press publishes the ''Journal of Experimental Medicine' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoctoral Fellow
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). The ultimate goal of a postdoctoral research position is to pursue additional research, training, or teaching in order to have better skills to pursue a career in academia, research, or any other field. Postdocs often, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further formal qualificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron, "amber") and φόρησις (phórēsis, "the act of bearing"), is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis. The electrokinetic phenomenon of electrophoresis was observed for the first time in 1807 by Russian professors Peter Ivanovich Strakhov and Ferdinand Frederic Reuss at Moscow University, who noticed that the application of a constant electric field caused clay particles dispersed in water to migrate. It is ultimately caused by the presence of a charged interface between the particle surface and the surrounding fluid. It is the basis for analytical techniques used in chemistry for separating molecules by size, charge, or binding affinity. Electropho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid. Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the helical shape resembles the shape of a spring, taking the space of a cylinder but not being a cylinder itself. The capsid faces may consist of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virology
Virology is the Scientific method, scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host (biology), host cell (biology), cells for reproduction, their interaction with host organism physiology and immunity, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy. The identification of the causative agent of tobacco mosaic disease (TMV) as a novel pathogen by Martinus Beijerinck (1898) is now acknowledged as being the history of virology, official beginning of the field of virology as a discipline distinct from bacteriology. He realized the source was neither a bacterial nor a fungal infection, but something completely different. Beijerinck used the word "virus" to describe the mysterious agent in his 'contagium vivum fluidum' ('contagious living fluid'). Rosalind Franklin proposed the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




.gif)
