|
Password Authentication Protocol
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) is a password-based authentication protocol used by Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to validate users. PAP is specified in . Almost all network operating systems support PPP with PAP, as do most network access servers. PAP is also used in PPPoE, for authenticating DSL users. As the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) sends data unencrypted and "in the clear", PAP is vulnerable to any attacker who can observe the PPP session. An attacker can see the users name, password, and any other information associated with the PPP session. Some additional security can be gained on the PPP link by using CHAP or EAP. However, there are always tradeoffs when choosing an authentication method, and there is no single answer for which is more secure. When PAP is used in PPP, it is considered a weak authentication scheme. Weak schemes are simpler and have lighter computational overhead than more complex schemes such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), but they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password
A password, sometimes called a passcode (for example in Apple devices), is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary string of characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes called a personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RADIUS
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the spoke of a chariot wheel. as a function of axial position ../nowiki>" Spherical coordinates In a spherical coordinate system, the radius describes the distance of a point from a fixed origin. Its position if further defined by the polar angle measured between the radial direction and a fixed zenith direction, and the azimuth angle, the angle between the orthogonal projection of the radial direction on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, and a fixed reference direction in that plane. See also *Bend radius *Filling radius in Riemannian geometry *Radius of convergence *Radius of convexity * Radius of curvature *Radius of gyration ''Radius of gyration'' or gyradius of a body about the axis of ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
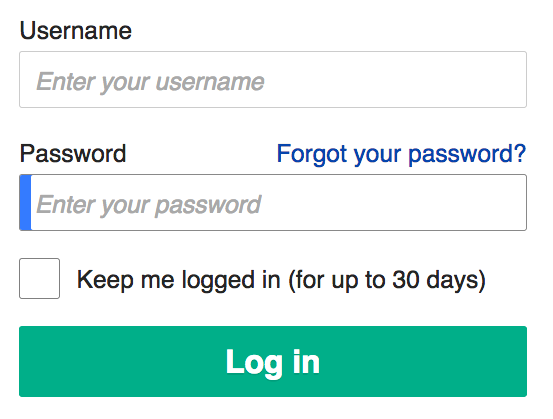
Password Authentication
A password, sometimes called a passcode (for example in Apple devices), is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary string of characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes called a personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Engineering Task Force
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and all its participants are volunteers. Their work is usually funded by employers or other sponsors. The IETF was initially supported by the federal government of the United States but since 1993 has operated under the auspices of the Internet Society, an international non-profit organization. Organization The IETF is organized into a large number of working groups and birds of a feather informal discussion groups, each dealing with a specific topic. The IETF operates in a bottom-up task creation mode, largely driven by these working groups. Each working group has an appointed chairperson (or sometimes several co-chairs); a charter that describes its focus; and what it is expected to produce, and when. It is open to all who want to partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Service Access Point
A Service Access Point (SAP) is an identifying label for network endpoints used in Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) networking. The SAP is a conceptual location at which one OSI layer can request the services of another OSI layer. As an example, PD-SAP or PLME-SAP in IEEE 802.15.4 can be mentioned, where the medium access control (MAC) layer requests certain services from the physical layer. Service access points are also used in IEEE 802.2 Logical Link Control in Ethernet and similar data link layer protocols. When using the OSI Network system (CONS or CLNS), the base for constructing an address for a network element is an NSAP address, similar in concept to an IP address. OSI protocols as well as Asynchronous Transfer Mode Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a telecommunications standard defined by American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and ITU-T (formerly CCITT) for digital transmission of multiple types of traffic. ATM was developed to meet the needs of ... ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handshake (computing)
In computing, a handshake is a signal between two devices or programs, used to, e.g., authenticate, coordinate. An example is the handshaking between a hypervisor and an application in a guest virtual machine. In telecommunications, a handshake is an automated process of negotiation between two participants (example "Alice and Bob") through the exchange of information that establishes the protocols of a communication link at the start of the communication, before full communication begins. The handshaking process usually takes place in order to establish rules for communication when a computer attempts to communicate with another device. Signals are usually exchanged between two devices to establish a communication link. For example, when a computer communicates with another device such as a modem, the two devices will signal each other that they are switched on and ready to work, as well as to agree to which protocols are being used. Handshaking can negotiate parameters that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challenge-handshake Authentication Protocol
In computing, the Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) is an authentication protocol originally used by Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to validate users. CHAP is also carried in other authentication protocols such as RADIUS and Diameter. Almost all network operating systems support PPP with CHAP, as do most network access servers. CHAP is also used in PPPoE, for authenticating DSL users. As the PPP sends data unencrypted and "in the clear", CHAP is vulnerable to any attacker who can observe the PPP session. An attacker can see the user's name, CHAP challenge, CHAP response, and any other information associated with the PPP session. The attacker can then mount an offline dictionary attack in order to obtain the original password. When used in PPP, CHAP also provides protection against replay attacks by the peer through the use of a challenge which is generated by the authenticator, which is typically a network access server. Where CHAP is used in other protocols, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password
A password, sometimes called a passcode (for example in Apple devices), is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary string of characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes called a personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter (protocol)
Diameter is an authentication, authorization, and accounting protocol for computer networks. It evolved from the earlier RADIUS protocol. It belongs to the application layer protocols in the internet protocol suite. ''Diameter Applications'' extend the base protocol by adding new commands and/or attributes, such as those for use with the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). Comparison with RADIUS The name is a play on words, derived from the RADIUS protocol, which is the predecessor (a diameter is twice the radius). Diameter is not directly backward compatible but provides an upgrade path for RADIUS. The main features provided by Diameter but lacking in RADIUS are: * Support for SCTP * Capability negotiation * Application layer acknowledgements; Diameter defines failover methods and state machines (RFC 3539) * Extensibility; new commands can be defined * Aligned on 32 bit boundaries Also: Like RADIUS, it is intended to work in both local and roaming AAA situ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPsec
In computing, Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a secure network protocol suite that authenticates and encrypts packets of data to provide secure encrypted communication between two computers over an Internet Protocol network. It is used in virtual private networks (VPNs). IPsec includes protocols for establishing mutual authentication between agents at the beginning of a session and negotiation of cryptographic keys to use during the session. IPsec can protect data flows between a pair of hosts (''host-to-host''), between a pair of security gateways (''network-to-network''), or between a security gateway and a host (''network-to-host''). IPsec uses cryptographic security services to protect communications over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It supports network-level peer authentication, data origin authentication, data integrity, data confidentiality (encryption), and replay protection (protection from replay attacks). The initial IPv4 suite was developed with few s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authentication Protocol
An authentication protocol is a type of computer communications protocol or cryptographic protocol specifically designed for transfer of authentication data between two entities. It allows the receiving entity to authenticate the connecting entity (e.g. Client connecting to a Server) as well as authenticate itself to the connecting entity (Server to a client) by declaring the type of information needed for authentication as well as syntax. It is the most important layer of protection needed for secure communication within computer networks. Purpose With the increasing amount of trustworthy information being accessible over the network, the need for keeping unauthorized persons from access to this data emerged. Stealing someone's identity is easy in the computing world - special verification methods had to be invented to find out whether the person/computer requesting data is really who he says he is. The task of the authentication protocol is to specify the exact series of steps n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide communications security over a computer network. The protocol is widely used in applications such as email, instant messaging, and voice over IP, but its use in securing HTTPS remains the most publicly visible. The TLS protocol aims primarily to provide security, including privacy (confidentiality), integrity, and authenticity through the use of cryptography, such as the use of certificates, between two or more communicating computer applications. It runs in the presentation layer and is itself composed of two layers: the TLS record and the TLS handshake protocols. The closely related Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a communications protocol providing security to datagram-based applications. In technical writing you often you will see references to (D)TLS when it applies to both versions. TLS is a proposed Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard, first defined in 1999, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |