|
Passerini Reaction
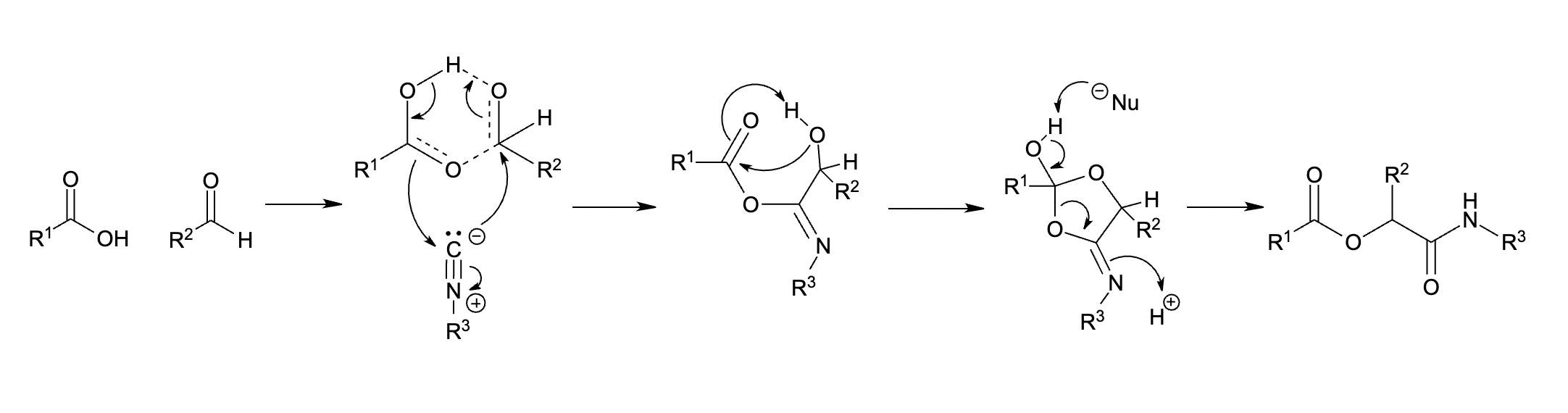
The Passerini reaction is a chemical reaction involving an isocyanide, an aldehyde (or ketone), and a carboxylic acid to form a α- acyloxy amide. This addition reaction is one of the oldest isocyanide-based multicomponent reactions (IMCR) and was first described in 1921 by Mario Passerini in Florence, Italy. It is typically carried out in aprotic solvents but can also be performed in ionic liquids such as water or Deep Eutectic solvents (DESs). It is a third order reaction; first order in each of the reactants. The Passerini reaction is often used in combinatorial and medicinal chemistry with recent utility in green chemistry and polymer chemistry. As isocyanides exhibit high functional group tolerance, chemoselectivity, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity, the Passerini reaction has a wide range of synthetic applications.''The Passirini Reaction'' L. Banfi, R.Riva in Organic Reactions vol. 65 L.E. Overman Ed. Wiley 2005 Mechanism The Passerini reaction has been hypothesiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passerini Reaction
The Passerini reaction is a chemical reaction involving an isocyanide, an aldehyde (or ketone), and a carboxylic acid to form a α- acyloxy amide. This addition reaction is one of the oldest isocyanide-based multicomponent reactions (IMCR) and was first described in 1921 by Mario Passerini in Florence, Italy. It is typically carried out in aprotic solvents but can also be performed in ionic liquids such as water or Deep Eutectic solvents (DESs). It is a third order reaction; first order in each of the reactants. The Passerini reaction is often used in combinatorial and medicinal chemistry with recent utility in green chemistry and polymer chemistry. As isocyanides exhibit high functional group tolerance, chemoselectivity, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity, the Passerini reaction has a wide range of synthetic applications.''The Passirini Reaction'' L. Banfi, R.Riva in Organic Reactions vol. 65 L.E. Overman Ed. Wiley 2005 Mechanism The Passerini reaction has been hypothesiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water (molecule)
Water () is a Chemical polarity, polar inorganic compound that is at room temperature a tasteless and odorless liquid, which is nearly colorless apart from Color of water, an inherent hint of blue. It is by far the most studied chemical compound and is described as the "universal solvent" and the "solvent of life". It is the most abundant substance on the surface of Earth and the only common substance to exist as a ice, solid, liquid, and water vapor, gas on Earth's surface. It is also the third most abundant molecule in the universe (behind Hydrogen, molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide). Water molecules form hydrogen bonds with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids, thus dissolving them. Its hydrogen bonding causes its many unique properties, such as having a solid form less dense than its liquid form, a relatively high boiling point of 100 °C for its molar m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical and the simplest aliphatic alcohol, with the formula C H3 O H (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, volatile, colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odour similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol). A polar solvent, methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced chiefly by the destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, as well as a host of more specialised chemicals. Occurrence Small amounts of methanol are present in normal, healthy hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passerini Ionic Mechanism
{{surname ...
Passerini is a surname, and may refer to: * Carlo Passerini, Italian entomologist * Giovanni Passerini, Italian botanist and entomologist * Ilario Passerini, Italian sprint canoer * Lorenzo Passerini (born 1991), Italian conductor * Silvio Passerini, Italian cardinal, the "Cardinal of Cortona" See also * Passerini's tanager * Passerini reaction * Carlo Gambacorti-Passerini * Elachista passerini * Terranova dei Passerini Terranova dei Passerini ( Lodigiano: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Lodi in the Italian region Lombardy, located about southeast of Milan and about southeast of Lodi. Terranova dei Passerini borders the following municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organocatalysis
In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an organic catalyst. This "organocatalyst" consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds.Special Issue: Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a misnomer for enzymes due to their comparable effects on reaction rates and forms of catalysis involved. Organocatalysts which display secondary amine functionality can be described as performing either enamine catalysis (by forming catalytic quantities of an active enamine nucleophile) or iminium catalysis (by forming catalytic quantities of an activated iminium electrophile). This mechanism is typical for covalent organocatalysis. Covalent binding of substrate normally requires high catalyst loading (for proline-catalysis typically 20–30 mol%). Noncovalent interactions such as hydrogen-bonding facilitates low catalyst l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mumm Rearrangement
The Mumm rearrangement is an organic reaction and a rearrangement reaction. It describes a 1,3(O-N) acyl transfer of an acyl imidate or isoimide group to an imide. The reaction is of relevance as part of the Ugi reaction The Ugi reaction is a multi-component reaction in organic chemistry involving a ketone or aldehyde, an amine, an isocyanide and a carboxylic acid to form a bis-amide. The reaction is named after Ivar Karl Ugi, who first reported this reaction in 1 .... References {{Reflist, 30em Rearrangement reactions Name reactions Carboximidates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imidate
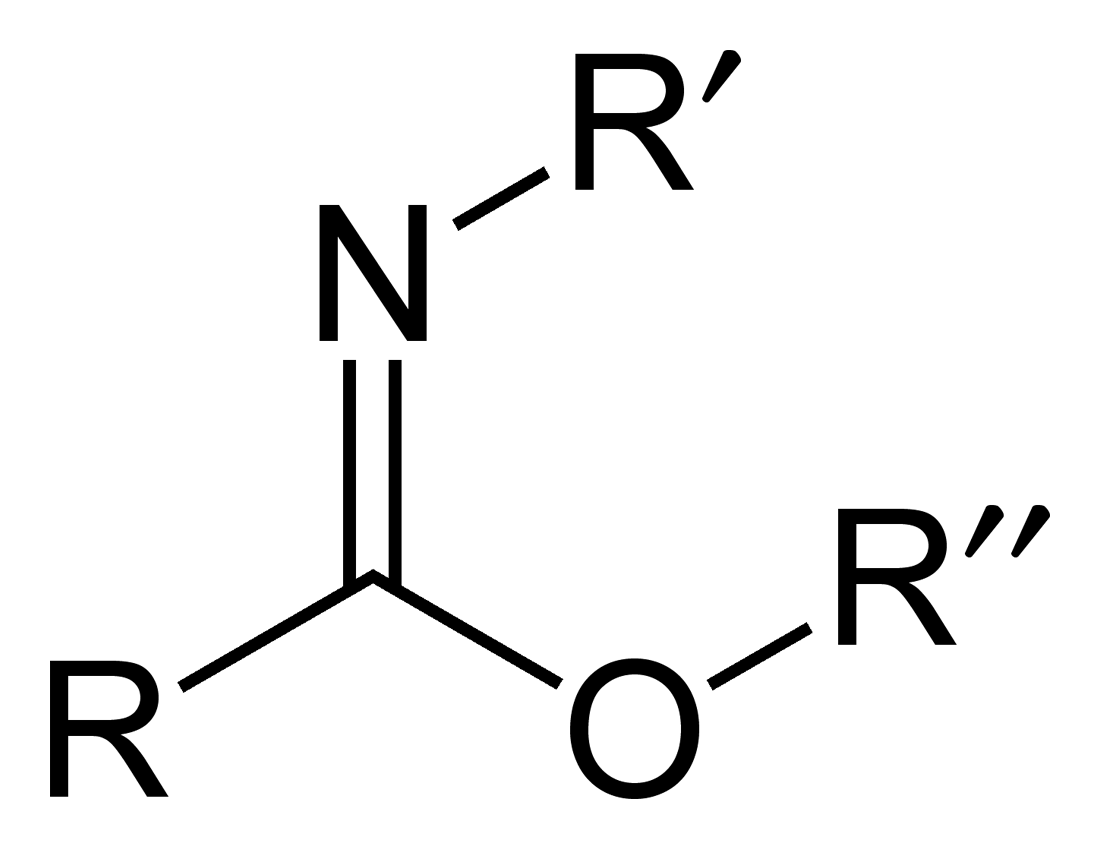
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as esters formed between a carboximidic acid (R-C(=NR')OH) and an alcohol, with the general formula R-C(=NR')OR". They are also known as imino ethers, since they resemble imines (>C=N-) with an oxygen atom connected to the carbon atom of the C=N double bond. Synthesis Imidates may be generated by a number of synthetic routes, but are in general formed by the Pinner reaction. This proceeds via the acid catalyzed attack of nitriles by alcohols. Imidates produced in this manner are formed as their hydrochloride salts, which are sometimes referred to as Pinner salts. Carboximidates are also formed as intermediates in the Mumm rearrangement and the Overman rearrangement. Imidate/amidate anions An amidate/imidate anion is formed upon deprotonation of an amide or imidic acid. Since amides and imidic acids are tautomers, they form the same anion upon deprotonation. The two names are thus syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions differ from electrophilic additions in that the former reactions involve the group to which atoms are added accepting electron pairs, whereas the latter reactions involve the group donating electron pairs. Addition to carbon–heteroatom double bonds Nucleophilic addition reactions of nucleophiles with electrophilic double or triple bond (π bonds) create a new carbon center with two additional single, or σ, bonds.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Addition of a nucleophile to carbon–heteroatom double or triple bonds such as >C=O or -C≡N show great variety. These types of bonds are polar (have a large difference in electronegativity betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimolecular Reaction
In chemistry, molecularity is the number of molecules that come together to react in an elementary (single-step) reactionAtkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical Chemistry. Oxford University Press, 2014 and is equal to the sum of stoichiometric coefficients of reactants in the elementary reaction with effective collision ( sufficient energy) and correct orientation. Depending on how many molecules come together, a reaction can be unimolecular, bimolecular or even trimolecular. The kinetic order of any elementary reaction or reaction step is ''equal'' to its molecularity, and the rate equation of an elementary reaction can therefore be determined by inspection, from the molecularity. The kinetic order of a complex (multistep) reaction, however, is not necessarily equal to the number of molecules involved. The concept of molecularity is only useful to describe elementary reactions or steps. Unimolecular reactions In a unimolecular reaction, a single molecule rearranges atoms, forming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passerini Concerted Mechanism
{{surname ...
Passerini is a surname, and may refer to: * Carlo Passerini, Italian entomologist * Giovanni Passerini, Italian botanist and entomologist * Ilario Passerini, Italian sprint canoer * Lorenzo Passerini (born 1991), Italian conductor * Silvio Passerini, Italian cardinal, the "Cardinal of Cortona" See also * Passerini's tanager * Passerini reaction * Carlo Gambacorti-Passerini * Elachista passerini * Terranova dei Passerini Terranova dei Passerini ( Lodigiano: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Lodi in the Italian region Lombardy, located about southeast of Milan and about southeast of Lodi. Terranova dei Passerini borders the following municipal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aprotic
A polar aprotic solvent is a solvent that lacks an acidic proton and is polar. Such solvents lack hydroxyl and amine groups. In contrast to protic solvents, these solvents do not serve as proton donors in hydrogen bonding In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a l ..., although they can be proton acceptors. Many solvents, including chlorocarbons and hydrocarbons, are classifiable as aprotic, but polar aprotic solvents are of particular interest for their ability to dissolve salts. Methods for purification of common solvents are available. References {{Chemical solutions Solvents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |