|
Paschen Breakdown Voltage
Paschen's law is an equation that gives the breakdown voltage, that is, the voltage necessary to start a discharge or electric arc, between two electrodes in a gas as a function of pressure and gap length. It is named after Friedrich Paschen who discovered it empirically in 1889. Paschen studied the breakdown voltage of various gases between parallel metal plates as the gas pressure and gap distance were varied: * With a constant gap length, the voltage necessary to Electric arc, arc across the gap decreased as the pressure was reduced and then increased gradually, exceeding its original value. * With a constant pressure, the voltage needed to cause an arc reduced as the gap size was reduced but only to a point. As the gap was reduced further, the voltage required to cause an arc began to rise and again exceeded its original value. For a given gas, the voltage is a function only of the product of the pressure and gap length. The curve he found of voltage versus the pressure-gap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paschen Curves
Paschen may refer to: * Friedrich Paschen (1865–1947), German physicist ** Paschen (crater), a lunar crater on the far side of the Moon ** Paschen-Back effect, the splitting of atomic energy levels in the presence of a strong magnetic field ** Paschen series, a Hydrogen spectral series in the infrared band ** Paschen's law, an equation that gives the breakdown voltage, that is the voltage necessary to start a discharge or electric arc, between two electrodes in a gas as a function of pressure and gap length {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's crust, comprising 0.00015% of the crust. Nearly all of the argon in Earth's atmosphere is radiogenic argon-40, derived from the decay of potassium-40 in Earth's crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, as it is the most easily produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas. The name "argon" is derived from the Greek word , neuter singular form of meaning 'lazy' or 'inactive', as a reference to the fact that the element undergoes almost no chemical reactions. The complete octe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Ionization
Impact ionization is the process in a material by which one energetic charge carrier can lose energy by the creation of other charge carriers. For example, in semiconductors, an electron (or hole) with enough kinetic energy can knock a bound electron out of its bound state (in the valence band) and promote it to a state in the conduction band, creating an electron-hole pair. For carriers to have sufficient kinetic energy a sufficiently large electric field must be applied, in essence requiring a sufficiently large voltage but not necessarily a large current. If this occurs in a region of high electrical field then it can result in avalanche breakdown. This process is exploited in avalanche diodes, by which a small optical signal is amplified before entering an external electronic circuit. In an avalanche photodiode the original charge carrier is created by the absorption of a photon. The impact ionization process is used in modern cosmic dust detectors like the ''G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Avalanche
An electron avalanche is a process in which a number of free electrons in a transmission medium are subjected to strong acceleration by an electric field and subsequently collide with other atoms of the medium, thereby ionizing them (impact ionization). This releases additional electrons which accelerate and collide with further atoms, releasing more electrons—a chain reaction. In a gas, this causes the affected region to become an Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrically conductive plasma (physics), plasma. The avalanche effect was discovered by John Sealy Townsend in his work between 1897 and 1901, and is also known as the Townsend discharge. Electron avalanches are essential to the dielectric breakdown process within gases. The process can culminate in corona discharges, streamer discharge , streamers, leader (spark), leaders, or in a electric spark, spark or continuous electric arc, arc that completely bridges the gap between the electrical conductors that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townsend Discharge
The Townsend discharge or Townsend avalanche is a gas ionisation process where free electrons are accelerated by an electric field, collide with gas molecules, and consequently free additional electrons. Those electrons are in turn accelerated and free additional electrons. The result is an avalanche breakdown, avalanche multiplication that permits electrical conduction through the gas. The discharge requires a source of free electrons and a significant electric field; without both, the phenomenon does not occur. The Townsend discharge is named after John Sealy Townsend, who discovered the fundamental ionisation mechanism by his work circa 1897 at the Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge. General description of the phenomenon The avalanche occurs in a gaseous medium that can be ionization, ionised (such as air). The electric field and the mean free path of the electron must allow free electrons to acquire an energy level (velocity) that can cause impact ionisation. If the electric fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Reaction
A chain reaction is a sequence of reactions where a reactive product or by-product causes additional reactions to take place. In a chain reaction, positive feedback leads to a self-amplifying chain of events. Chain reactions are one way that systems which are not in thermodynamic equilibrium can release energy or increase entropy in order to reach a state of higher entropy. For example, a system may not be able to reach a lower energy state by releasing energy into the environment, because it is hindered or prevented in some way from taking the path that will result in the energy release. If a reaction results in a small energy release making way for more energy releases in an expanding chain, then the system will typically collapse explosively until much or all of the stored energy has been released. A macroscopic metaphor for chain reactions is thus a snowball causing a larger snowball until finally an avalanche results ("snowball effect"). This is a result of stored gravitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionization Energy
Ionization, or Ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with electromagnetic radiation. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected. Uses Everyday examples of gas ionization are such as within a fluorescent lamp or other electrical discharge lamps. It is also used in radiation detectors such as the Geiger-Müller counter or the ionization chamber. The ionizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronvolt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV, also written electron-volt and electron volt) is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acc ... gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an Voltage, electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a Units of energy, unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equivalent to the numerical value of the Electric charge, charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in Particle accelerator#Electrostatic particle accelerators, electrostatic particle accel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Free Path
In physics, mean free path is the average distance over which a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, or a photon) travels before substantially changing its direction or energy (or, in a specific context, other properties), typically as a result of one or more successive collisions with other particles. Scattering theory Imagine a beam of particles being shot through a target, and consider an infinitesimally thin slab of the target (see the figure). The atoms (or particles) that might stop a beam particle are shown in red. The magnitude of the mean free path depends on the characteristics of the system. Assuming that all the target particles are at rest but only the beam particle is moving, that gives an expression for the mean free path: :\ell = (\sigma n)^, where is the mean free path, is the number of target particles per unit volume, and is the effective cross-sectional area for collision. The area of the slab is , and its volume is . The typical number of st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
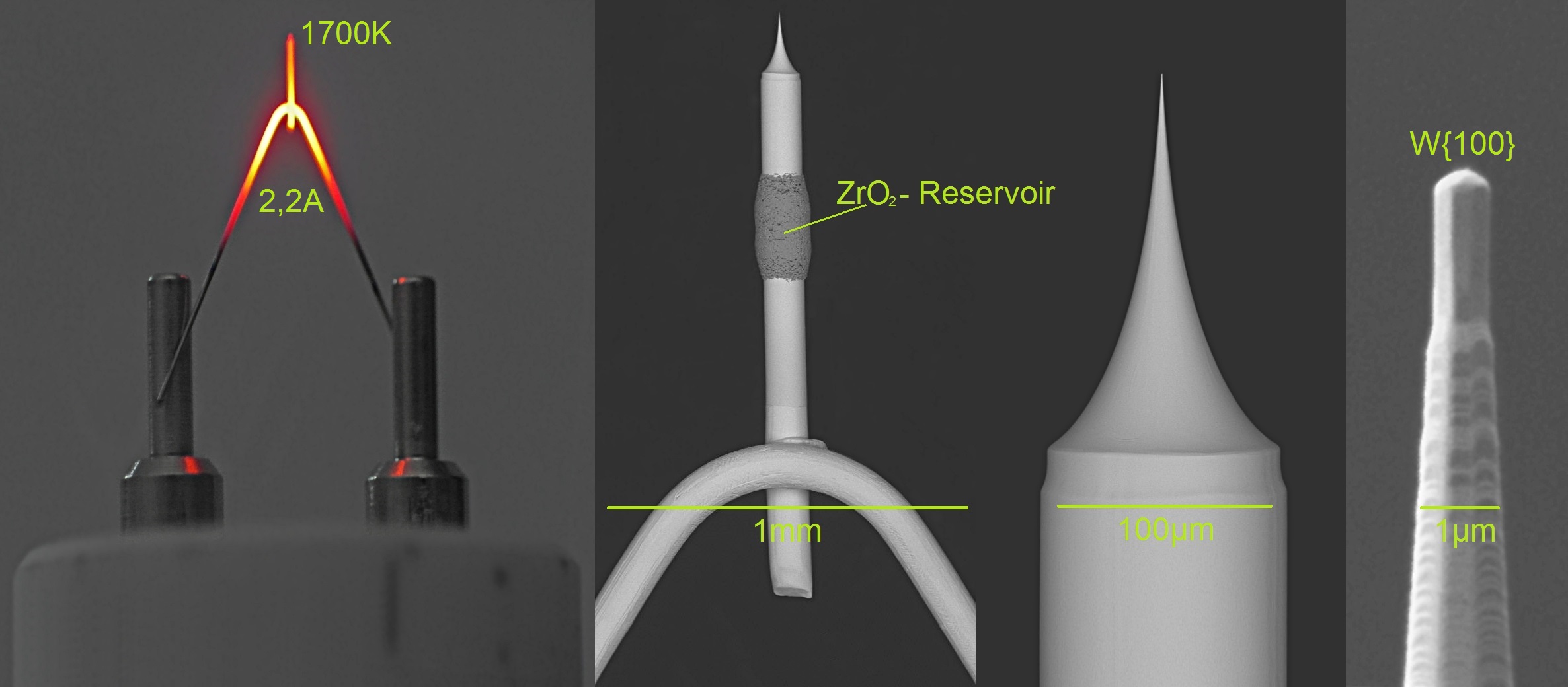
Field Electron Emission
Field electron emission, also known as field emission (FE) and electron field emission, is emission of electrons induced by an electrostatic field. The most common context is field emission from a solid surface into a vacuum. However, field emission can take place from solid or liquid surfaces, into a vacuum, a fluid (e.g. air), or any non-conducting or weakly conducting dielectric. The field-induced promotion of electrons from the valence (chemistry), valence to conduction band of semiconductors (the Zener effect) can also be regarded as a form of field emission. The terminology is historical because related phenomena of surface photoeffect, thermionic emission (or Richardson–Dushman effect) and "cold electronic emission", i.e. the emission of electrons in strong static (or quasi-static) electric fields, were discovered and studied independently from the 1880s to 1930s. When field emission is used without qualifiers it typically means "cold emission". Field emission in pure metal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)