|
Partitions
Partition may refer to: Computing Hardware * Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive * Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job Software * Partition (database), the division of a database * Logical partition (LPAR), a subset of a computer's resources, virtualized as a separate computer Problems * Binary space partitioning * Partition problem, an NP-complete problem in computer science Mathematics * Partition (number theory), a way to write a number as a sum of other numbers * Multiplicative partition, a way to write a number as a product of other numbers * Partition of an interval * Partition of a set * Partition of unity, a certain kind of set of functions on a topological space * Plane partition * Graph partition Natural science * Partition function (quantum field theory) * Partition function (statistical mechanics) * Partition coefficient, a concept in organic chemistry Law and politics * Partition (law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772 after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792 when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition took place on October 24, 1795, in reaction to the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising the previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Partition
In mathematics and especially in combinatorics, a plane partition is a two-dimensional array of nonnegative integers \pi_ (with positive number, positive integer indices ''i'' and ''j'') that is nonincreasing in both indices. This means that : \pi_ \ge \pi_ and \pi_ \ge \pi_ for all ''i'' and ''j''. Moreover, only finitely many of the \pi_ may be nonzero. Plane partitions are a generalization of Partition (number theory), partitions of an integer. A plane partition may be represented visually by the placement of a stack of \pi_ unit cubes above the point (''i'', ''j'') in the plane, giving a three-dimensional solid as shown in the picture. The image has matrix form : \begin 4 & 4 & 3 & 2 & 1\\ 4 & 3 & 1 & 1\\ 3 & 2 & 1\\ 1 \end Plane partitions are also often described by the positions of the unit cubes. From this point of view, a plane partition can be defined as a finite subset \mathcal of positive integer lattice points (''i'', ''j'', ''k'') in \mathbb^3, such that if (''r'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition (number Theory)
In number theory and combinatorics, a partition of a positive integer , also called an integer partition, is a way of writing as a sum of positive integers. Two sums that differ only in the order of their summands are considered the same partition. (If order matters, the sum becomes a composition.) For example, can be partitioned in five distinct ways: : : : : : The order-dependent composition is the same partition as , and the two distinct compositions and represent the same partition as . A summand in a partition is also called a part. The number of partitions of is given by the partition function . So . The notation means that is a partition of . Partitions can be graphically visualized with Young diagrams or Ferrers diagrams. They occur in a number of branches of mathematics and physics, including the study of symmetric polynomials and of the symmetric group and in group representation theory in general. Examples The seven partitions of 5 are: * 5 * 4 + 1 * 3 + ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Partition
In mathematics, a graph partition is the reduction of a graph to a smaller graph by partitioning its set of nodes into mutually exclusive groups. Edges of the original graph that cross between the groups will produce edges in the partitioned graph. If the number of resulting edges is small compared to the original graph, then the partitioned graph may be better suited for analysis and problem-solving than the original. Finding a partition that simplifies graph analysis is a hard problem, but one that has applications to scientific computing, VLSI circuit design, and task scheduling in multiprocessor computers, among others. Recently, the graph partition problem has gained importance due to its application for clustering and detection of cliques in social, pathological and biological networks. For a survey on recent trends in computational methods and applications see . Two common examples of graph partitioning are minimum cut and maximum cut problems. Problem complexity Typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of Unity
In mathematics, a partition of unity of a topological space is a set of continuous functions from to the unit interval ,1such that for every point x\in X: * there is a neighbourhood of where all but a finite number of the functions of are 0, and * the sum of all the function values at is 1, i.e., \sum_ \rho(x) = 1. Partitions of unity are useful because they often allow one to extend local constructions to the whole space. They are also important in the interpolation of data, in signal processing, and the theory of spline functions. Existence The existence of partitions of unity assumes two distinct forms: # Given any open cover \_ of a space, there exists a partition \_ indexed ''over the same set'' such that supp \rho_i \subseteq U_i. Such a partition is said to be subordinate to the open cover \_i. # If the space is locally-compact, given any open cover \_ of a space, there exists a partition \_ indexed over a possibly distinct index set such that each has co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of A Set
In mathematics, a partition of a set is a grouping of its elements into non-empty subsets, in such a way that every element is included in exactly one subset. Every equivalence relation on a set defines a partition of this set, and every partition defines an equivalence relation. A set equipped with an equivalence relation or a partition is sometimes called a setoid, typically in type theory and proof theory. Definition and Notation A partition of a set ''X'' is a set of non-empty subsets of ''X'' such that every element ''x'' in ''X'' is in exactly one of these subsets (i.e., ''X'' is a disjoint union of the subsets). Equivalently, a family of sets ''P'' is a partition of ''X'' if and only if all of the following conditions hold: *The family ''P'' does not contain the empty set (that is \emptyset \notin P). *The union of the sets in ''P'' is equal to ''X'' (that is \textstyle\bigcup_ A = X). The sets in ''P'' are said to exhaust or cover ''X''. See also collectively exhaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
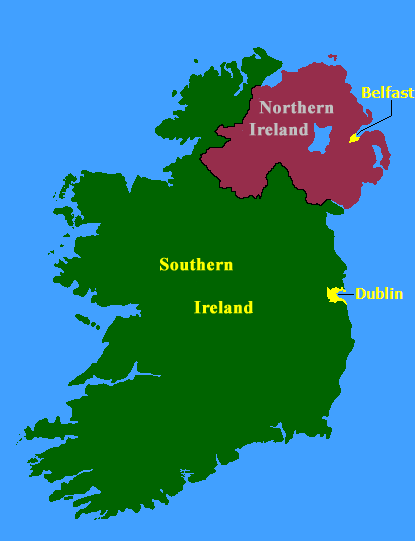
Partition (politics)
In politics, a partition is a change of political borders cutting through at least one territory considered a homeland by some community.Brendan O'LearyDEBATING PARTITION: JUSTIFICATIONS AND CRITIQUES Arguments for *historicist – that partition is inevitable, or already in progress * last resort – that partition should be pursued to avoid the worst outcomes (genocide or large-scale ethnic expulsion), if all other means fail * cost–benefit – that partition offers a better prospect of conflict reduction than the if existing borders are not changed * better tomorrow – that partition will reduce current violence and conflict, and that the new more homogenized states will be more stable * rigorous end – heterogeneity leads to problems, hence homogeneous states should be the goal of any policy Arguments against * national territorial unity will be lost * bi-nationalism and multi-nationalism are not undesirable * the impossibility of a just partition * difficult in de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Management (operating Systems)
In operating systems, memory management is the function responsible for managing the computer's primary memory. The memory management function keeps track of the status of each memory location, either ''allocated'' or ''free''. It determines how memory is allocated among competing processes, deciding which gets memory, when they receive it, and how much they are allowed. When memory is allocated it determines which memory locations will be assigned. It tracks when memory is freed or ''unallocated'' and updates the status. This is distinct from application memory management, which is how a process manages the memory assigned to it by the operating system. Memory management techniques Single contiguous allocation ''Single allocation'' is the simplest memory management technique. All the computer's memory, usually with the exception of a small portion reserved for the operating system, is available to a single application. MS-DOS is an example of a system that allocates memory i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Partition
A logical partition (LPAR) is a subset of a computer's hardware resources, virtualized as a separate computer. In effect, a physical machine can be partitioned into multiple logical partitions, each hosting a separate instance of an operating system. PR/SM Although the terms ''PR/SM'' and ''LPAR'' are often used interchangeably in IBM Z, including in IBM documentation, ''PR/SM'' was not present in the IBM 370/168's Virtual Machine Facility/370; it came in with the IBM 3090, years later. Formally, LPAR designates the mode of operation or an individual logical partition, whereas PR/SM is the commercial designation of the feature. In mainframe computing PR/SM (Processor Resource/System Manager) is a type-1 Hypervisor (a virtual machine monitor) that allows multiple logical partitions to share physical resources such as CPUs, I/O channels and LAN interfaces; when sharing channels, the LPARs can share I/O devices such as direct access storage devices (DASD). PR/SM is integrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Space Partitioning
In computer science, binary space partitioning (BSP) is a method for space partitioning which recursively subdivides a Euclidean space into two convex sets by using hyperplanes as partitions. This process of subdividing gives rise to a representation of objects within the space in the form of a tree data structure known as a BSP tree. Binary space partitioning was developed in the context of 3D computer graphics in 1969. The structure of a BSP tree is useful in rendering because it can efficiently give spatial information about the objects in a scene, such as objects being ordered from front-to-back with respect to a viewer at a given location. Other applications of BSP include: performing geometrical operations with shapes (constructive solid geometry) in CAD, collision detection in robotics and 3D video games, ray tracing, and other applications that involve the handling of complex spatial scenes. Overview Binary space partitioning is a generic process of recursively dividi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplicative Partition
In number theory, a multiplicative partition or unordered factorization of an integer ''n'' is a way of writing ''n'' as a product of integers greater than 1, treating two products as equivalent if they differ only in the ordering of the factors. The number ''n'' is itself considered one of these products. Multiplicative partitions closely parallel the study of multipartite partitions, discussed in , which are additive partitions of finite sequences of positive integers, with the addition made pointwise. Although the study of multiplicative partitions has been ongoing since at least 1923, the name "multiplicative partition" appears to have been introduced by . The Latin name "factorisatio numerorum" had been used previously. MathWorld uses the term unordered factorization. Examples *The number 20 has four multiplicative partitions: 2 × 2 × 5, 2 × 10, 4 × 5, and 20. *3 × 3 × 3 × ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of An Interval
In mathematics, a partition of an interval on the real line is a finite sequence of real numbers such that :. In other terms, a partition of a compact interval is a strictly increasing sequence of numbers (belonging to the interval itself) starting from the initial point of and arriving at the final point of . Every interval of the form is referred to as a subinterval of the partition ''x''. Refinement of a partition Another partition of the given interval , bis defined as a refinement of the partition , if contains all the points of and possibly some other points as well; the partition is said to be “finer” than . Given two partitions, and , one can always form their common refinement, denoted , which consists of all the points of and , in increasing order. Norm of a partition The norm (or mesh) of the partition : is the length of the longest of these subintervals : . Applications Partitions are used in the theory of the Riemann integral, the Riemann–St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |