|
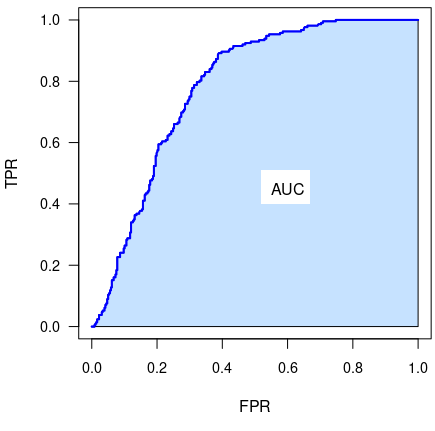
Partial Area Under The ROC Curve (pAUC)
The Partial Area Under the ROC Curve (pAUC) is a metric for the performance of binary classifier. It is computed based on the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve that illustrates the diagnostic ability of a given binary classifier system as its discrimination threshold is varied. The ROC curve is created by plotting the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR) at various threshold settings.The area under the ROC curve (AUC) is often used to summarize in a single number the diagnostic ability of the classifier. The AUC is simply defined as the area of the ROC space that lies below the ROC curve. However, in the ROC space there are regions where the values of FPR or TPR are unacceptable or not viable in practice. For instance, the region where FPR is greater than 0.8 involves that more than 80% of negative subjects are incorrectly classified as positives: this is unacceptable in many real cases. As a consequence, the AUC computed in the entire ROC sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receiver Operating Characteristic
A receiver operating characteristic curve, or ROC curve, is a graphical plot that illustrates the diagnostic ability of a binary classifier system as its discrimination threshold is varied. The method was originally developed for operators of military radar receivers starting in 1941, which led to its name. The ROC curve is created by plotting the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR) at various threshold settings. The true-positive rate is also known as sensitivity, recall or ''probability of detection''. The false-positive rate is also known as ''probability of false alarm'' and can be calculated as (1 − specificity). The ROC can also be thought of as a plot of the power as a function of the Type I Error of the decision rule (when the performance is calculated from just a sample of the population, it can be thought of as estimators of these quantities). The ROC curve is thus the sensitivity or recall as a function of fall-out. In general, if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Positive Rate
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives: * Sensitivity (true positive rate) is the probability of a positive test result, conditioned on the individual truly being positive. * Specificity (true negative rate) is the probability of a negative test result, conditioned on the individual truly being negative. If the true status of the condition cannot be known, sensitivity and specificity can be defined relative to a " gold standard test" which is assumed correct. For all testing, both diagnoses and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Positive Rate
In statistics, when performing multiple comparisons, a false positive ratio (also known as fall-out or false alarm ratio) is the probability of falsely rejecting the null hypothesis for a particular test. The false positive rate is calculated as the ratio between the number of negative events wrongly categorized as positive (false positives) and the total number of actual negative events (regardless of classification). The false positive rate (or "false alarm rate") usually refers to the expectancy of the false positive ratio. Definition The false positive rate is FPR=\frac where \mathrm is the number of false positives, \mathrm is the number of true negatives and N=\mathrm+\mathrm is the total number of ground truth negatives. The level of significance that is used to test each hypothesis is set based on the form of inference ( simultaneous inference vs. selective inference) and its supporting criteria (for example FWER or FDR), that were pre-determined by the researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic AUC Annotated
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. Dartmouth BASIC, The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two ROC AUC
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Evolution Arabic digit The digit used in the modern Western world to represent the number 2 traces its roots back to the Indic Brahmic script, where "2" was written as two horizontal lines. The modern Chinese and Japanese languages (and Korean Hanja) still use this method. The Gupta script rotated the two lines 45 degrees, making them diagonal. The top line was sometimes also shortened and had its bottom end curve towards the center of the bottom line. In the Nagari script, the top line was written more like a curve connecting to the bottom line. In the Arabic Ghubar writing, the bottom line was completely vertical, and the digit looked like a dotless closing question mark. Restoring the bottom line to its original horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McClish 1
Edward Ernest McClish (1909-1993) was an American military officer in the Philippines in World War II. During the Japanese occupation of the Philippines, Lt. Colonel McClish commanded a division of Filipino guerrillas on Mindanao island. Early life Ernest E. McClish was the son of Ross Enzire McClish, a Choctaw Nation citizen listed as "full blood" on the Dawes Rolls, and Minnie Lee Mosteller. McClish graduated from Haskell Institute in 1929 and Bacone College in 1931 and became an army officer. He entered on active duty with the National Guard in 1940 and in 1941 commanded a company of Philippine Scouts. He became a battalion commander in August 1941 and was on the island of Negros when World War II began in the Philippines on 8 December 1941. Contemporaries described McClish as a handsome, soft-spoken Oklahoman and a "colorful guerrilla leader" with a quiet manner who dealt with problems in a methodical manner rather than barking out orders. He suffered from malaria and got o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang , in Shanxi, China
{{disambig ...
Jiang may refer to: * ''Jiang'' (rank), rank held by general officers in the military of China *Jiang (surname), several Chinese surnames **Jiang Zemin (1926–2022), as general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party *Jiang River, an ancient river of China *Jiang County Jiang County or Jiangxian () is a county in the south of Shanxi Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Way PAUC
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Evolution Arabic digit The digit used in the modern Western world to represent the number 2 traces its roots back to the Indic Brahmic script, where "2" was written as two horizontal lines. The modern Chinese and Japanese languages (and Korean Hanja) still use this method. The Gupta script rotated the two lines 45 degrees, making them diagonal. The top line was sometimes also shortened and had its bottom end curve towards the center of the bottom line. In the Nagari script, the top line was written more like a curve connecting to the bottom line. In the Arabic Ghubar writing, the bottom line was completely vertical, and the digit looked like a dotless closing question mark. Restoring the bottom line to its original horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi Coefficient
In statistics, the phi coefficient (or mean square contingency coefficient and denoted by φ or rφ) is a measure of association for two binary variables. In machine learning, it is known as the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) and used as a measure of the quality of binary (two-class) classifications, introduced by biochemist Brian W. Matthews in 1975. Introduced by Karl Pearson, and also known as the ''Yule phi coefficient'' from its introduction by Udny Yule in 1912 this measure is similar to the Pearson correlation coefficient in its interpretation. In fact, a Pearson correlation coefficient estimated for two binary variables will return the phi coefficient. Two binary variables are considered positively associated if most of the data falls along the diagonal cells. In contrast, two binary variables are considered negatively associated if most of the data falls off the diagonal. If we have a 2×2 table for two random variables ''x'' and ''y'' where ''n''11, ''n'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |