|
Paris–Brest–Paris
Paris–Brest–Paris (PBP) is a long-distance cycling event. It was originally a 1,200 km () bicycle race from Paris to Brest and back to Paris in 1891. The last time it was run as a race was 1951. The most recent edition of PBP was held on 18–22 August 2019. In 1931 amateur cyclists were separated from professionals. There are two independent long distance bicycle tours. One is the ''brevet'' (also called ''randonnée''), in which cyclists ride individually. The goal is to make it within 90 hours, but with no competition. This is held every four years. The other is an '' audax'' where cyclists ride in a group, held every five years. So in 1931 there were three independent cycling events, sharing the same route. The ''audax'' is organised by the Union des Audax Françaises, while the ''brevet'' is organised by the Audax Club Parisien. The ''brevet'' As in all ''brevet'' events, there is emphasis on self-sufficiency. Riders buy supplies anywhere along the course, but su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Giffard
Pierre Giffard (1 May 1853 – 21 January 1922) was a French journalist, a pioneer of modern political reporting, a newspaper publisher and a prolific sports organiser. In 1892, he was appointed ''Chevalier'' (Knight) of the Légion d'Honneur and in 1900 he was appointed an ''Officier'' (Officer) of the Légion d'Honneur. Parisian newspapers used sporting events as circulation aids, and Giffard created the Paris–Brest–Paris cycle race in 1891, the 380 kilometre Paris–Belfort running race in 1892, the world's first car race from Paris to Rouen in 1894, the Paris marathon in 1896, and a foot-race from Bordeaux to Paris in 1903. Giffard served as the editor of '' Le Petit Journal'' and then the sports daily '' Le Vélo'', where his passionate support for Alfred Dreyfus and thus his opposition to the car-maker Comte Jules-Albert de Dion over the whole Dreyfus affair led de Dion to create a rival daily, '' L'Auto'', which in turn created the Tour de France cycle race. Early l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Terront
Charles Terront (9 April 1857 – 31 October 1932) was the first major French cycling star. He won sprint, middle distance and endurance events in Europe and the United States. In September 1891 he won the first Paris–Brest–Paris cycle race, which at was more than double the length of any previous event. He rode a Humber bicycle fitted with prototype removable pneumatic tyres made by Michelin. He won 54 major events over his 15-year career, was 'Champion of France' twice and 'Champion of Great Britain' twice. Early life and career Terront was born in Saint-Ouen, Seine-Saint-Denis. He took up cycle racing in 1876 along with his brother Jules. Charles excelled at both endurance and speed events, and also won many events on a tandem with Jules. He won 54 major solo events over his 15-year career, including being Champion of France twice and Champion of Great Britain twice. In 1879 he covered in 24 hours. On 27 September 1893 he left Saint Petersburg in Russia to cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevet (cycling)
Randonneuring (also known as Audax in the UK, Australia and Brazil) is a long-distance cycling sport with its origins in audax cycling. In randonneuring, riders attempt courses of 200 km or more, passing through predetermined "controls" (checkpoints) every few tens of kilometres. Riders aim to complete the course within specified time limits, and receive equal recognition regardless of their finishing order. Riders may travel in groups or alone as they wish, and are expected to be self-sufficient between controls. A randonneuring event is called a randonnée or brevet, and a rider who has completed a 200 km event is called a randonneur. The international governing body for randonneuring is Audax Club Parisien (ACP), which works with other randonneuring organisations worldwide through Les Randonneurs Mondiaux (RM). Randonneuring is popular in France, and has a following in The Netherlands, Belgium, United Kingdom, Italy, Australia, United States, Canada, Brazil, Ire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Petit Journal (newspaper)
''Le Petit Journal'' was a conservative daily Parisian newspaper founded by Moïse Polydore Millaud; published from 1863 to 1944. Together with ''Le Petit Parisien'', ''Le Matin (France), Le Matin'', and ''Le Journal'', it was one of the four major French dailies. In 1890, during the Boulangiste crisis, its circulation first reached one million copies. Five years later, it had a circulation of two million copies, making it the world's largest newspaper.Ivan Chupin, Nicolas Hubé and Nicolas Kaciaf, ''Histoire politique et économique des médias en France'', La Découverte, 2009 History Early years The first issue of the Journal appeared on 1 February 1863 with a printing of 83,000 copies. Its founder, Millaud, was originally from Bordeaux and had begun as a publisher of financial and legal newsletters. For a few years, he was the owner of ''La Presse (France), La Presse'', an early Penny press, penny paper. The first printing ran to 83,000 copies; a large printing compared to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Doriot
Auguste Frédéric Doriot (24 October 1863 – 1955) was a French motoring pioneer who developed, built and raced cars for Peugeot before founding his own manufacturing company D.F.P. in combination with Ludovic Flandrin and the Parant brothers. In 1891, Doriot and his Peugeot colleague Louis Rigoulot completed the longest trip by a petrol powered vehicle when their self-designed and built Daimler powered Peugeot Type 3 completed 2,100 kilometres (1375 miles) from Valentigney to Paris and Brest and back again. They were attached to the first Paris-Brest-Paris bicycle race, but the duo reached Brest one day after the winning cyclist, Charles Terront, finished in Paris, and they then finished six days after him. Doriot's son, Georges Doriot, emigrated to the United States and became a professor at the Harvard Business School, where he later became known as the ''father of Venture Capitalism''. He also served as a brigadier general during World War II and was known for founding IN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelin
Michelin (; ; full name: ) is a French multinational tyre manufacturing company based in Clermont-Ferrand in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes '' région'' of France. It is the second largest tyre manufacturer in the world behind Bridgestone and larger than both Goodyear and Continental. In addition to the Michelin brand, it also owns the Kléber tyres company, Uniroyal-Goodrich Tire Company, SASCAR, Bookatable and Camso brands. Michelin is also notable for its Red and Green travel guides, its roadmaps, the Michelin stars that the Red Guide awards to restaurants for their cooking, and for its company mascot '' Bibendum'', colloquially known as the Michelin Man. Michelin's numerous inventions include the removable tyre, the pneurail (a tyre for rubber-tyred metros) and the radial tyre. Michelin manufactures tyres for Space Shuttles, aircraft, automobiles, heavy equipment, motorcycles, and bicycles. In 2012, the group produced 166 million tyres at 69 facilities loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
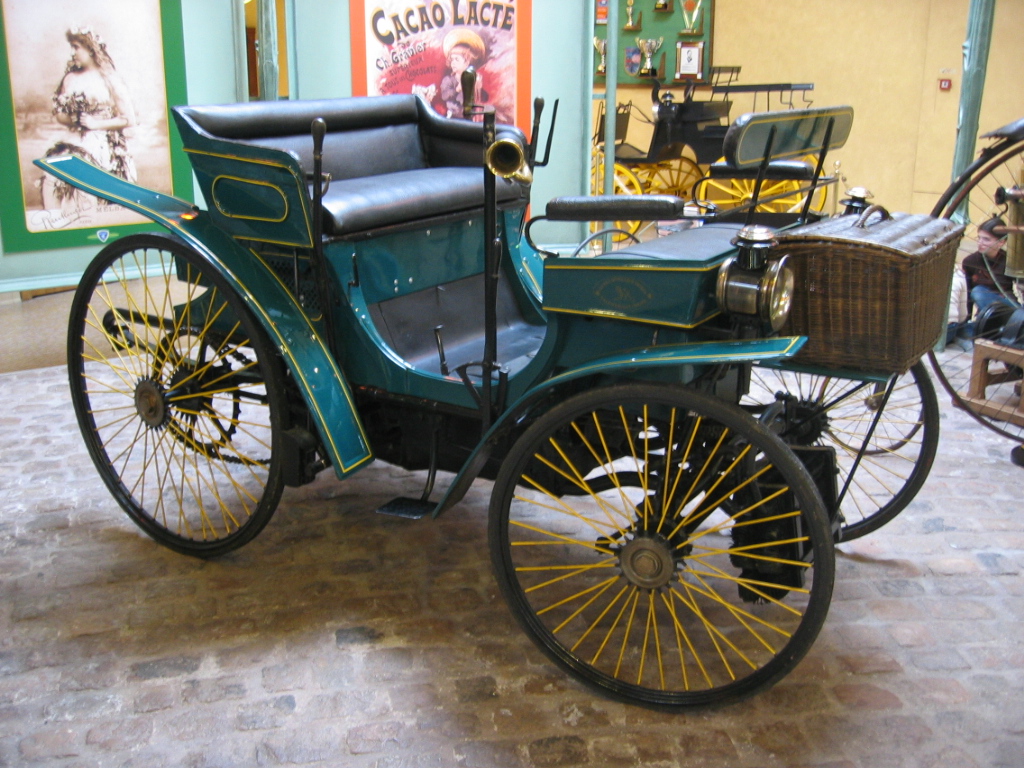
Peugeot Type 3
Background The earliest Peugeot models from 1889 were steam-powered tricycles, built in collaboration with Léon Serpollet. In 1890, Armand Peugeot met with car technology innovators Gottlieb Daimler and Émile Levassor and became convinced that reliable, practical, lightweight vehicles would have to be powered by petrol and have four wheels. The Type 2 was the first such model. Peugeot's one-time partner, Serpollet, continued with steam technology under the brand name Gardner-Serpollet until Serpollet's death in 1907. Performance The engine was a German design by Daimler but was licensed for production in France by Panhard et Levassor and then sold to Peugeot. It was a 15° V-twin and produced 2 bhp, sufficient for a top speed of approximately . World record Peugeot decided to show the quality of the Type 3 by running a demonstration model alongside the cyclists in the inaugural Paris–Brest–Paris cycle race in September 1891, thus gaining official confirmation of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fougères
Fougères (; br, Felger; Gallo: ''Foujerr'') is a commune and a sub-prefecture of the Ille-et-Vilaine department in the region of Brittany in northwestern France. As of 2017, Fougères had 20,418 inhabitants. The Fougères area comprises approximately 88,000 inhabitants and is currently growing, unlike the town centre. History Toponymy Fougères is a town on the edge of Brittany, Maine and Normandy and is named after a fern (see also '' fougère''), or from ''fous'' which means ''fossé'' ("gap"). The town of Fougères is mentioned in the chorus of the song La Blanche Hermine by Gilles Servat. The author uses it as a symbol of the Breton resistance where it is adjacent to the town of Clisson in the Loire-Atlantique. Fougères is historically, since the arrival of Latin in Armorica, a region where Gallo is spoken. In Gallo, Fougères translates to ''Foujerr'' while its Breton name is ''Felger''. Entry signs to the agglomeration have carried the Breton name fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
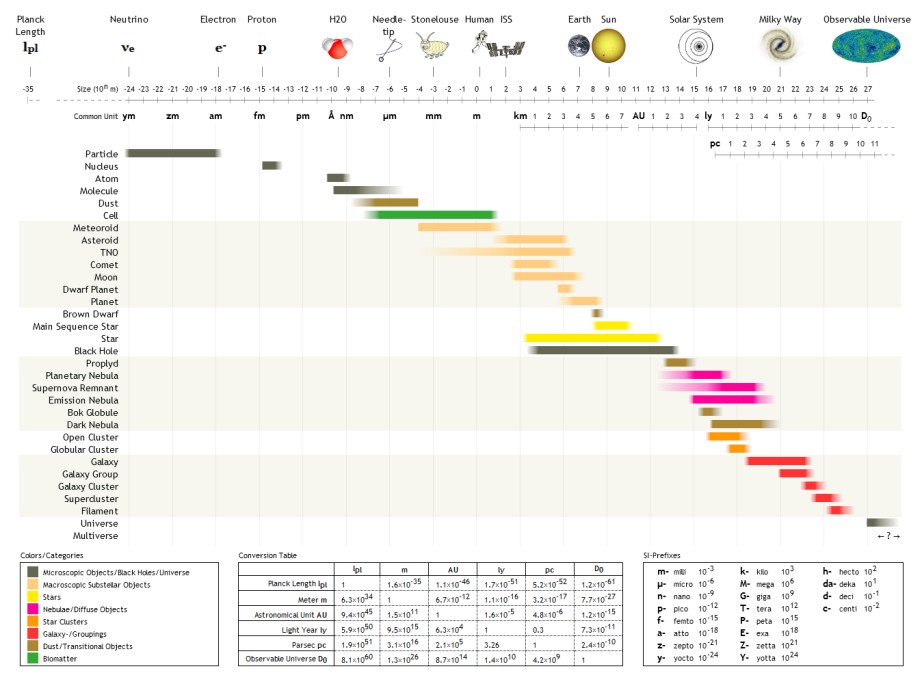
1 E6 M
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' ( SI symbol: ') is a unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one octilliont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest, France
Brest (; ) is a port city in the Finistère department, Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of the peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon. The city is located on the western edge of continental France. With 142,722 inhabitants in a 2007 census, Brest forms Western Brittany's largest metropolitan area (with a population of 300,300 in total), ranking third behind only Nantes and Rennes in the whole of historic Brittany, and the 19th most populous city in France; moreover, Brest provides services to the one million inhabitants of Western Brittany. Although Brest is by far the largest city in Finistère, the ''préfecture'' (regional capital) of the department is the much smaller Quimper. During the Middle Ages, the history of Brest was the history of its castle. Then Richelieu made it a military harbour in 1631. Brest grew around its arsenal un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines
Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines () is a new town and an agglomeration community in the French department of Yvelines. It is one of the original five villes nouvelles (new towns) of Paris and was named after the Saint Quentin Pond, which was chosen to become the town's centre. The town was built from a greenfield site starting in the 1960s. Its area is 119.2 km2. In 2018, Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines had a population of 228,312.Comparateur de territoire INSEE, accessed 6 April 2022. It is part of the much larger metropolitan area, and is around west of the centre of Paris. Administrative divisions The ''communauté d'agglomération'' comprises 12[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armand Peugeot
Armand Peugeot (; 18 February 1849 – 4 February 1915) was an industrialist in France, pioneer of the automobile industry and the man who transformed Peugeot into a manufacturer of bicycles and, later, of automobiles. He was accepted into the Automotive Hall of Fame in 1999. Family Born in 1849 into a Protestant family at Herimoncourt, in eastern France, Armand Peugeot was the son of Emile Peugeot and grandson of Jean-Pierre Peugeot. The family had a metal working business, producing a range of practical goods such as springs, saws, spectacle frames and coffee grinders. In 1872, he married Sophie Leonie Fallot (1852–1930) and they had five children, but their only son, Raymond, died in 1896. Armand Peugeot died on 2 January 1915 in Neuilly-sur-Seine, near Paris. Education He was a graduate of the École Centrale Paris, a prestigious engineering school in France. In 1881, Peugeot travelled to England where he saw the potential of bicycles and their manufacture. Business ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |