|
Pardubice Airport
Pardubice Airport ( cs, Letiště Pardubice) is both military and civilian international airport in the city of Pardubice, Czech Republic. Apart from the military purpose, it is used for scheduled services, charter flights to Southern Europe during the summer season and cargo flights. After the construction of a new terminal building, apron and ground handling facilities in 2017, Pardubice Airport opened up to serve more passengers and handle standard commercial aircraft such as Boeing 737 or Airbus A320 providing better and faster services. The new terminal building bears the name of Jan Kašpar, a Czech aviation pioneer. Airport's 2017 refurbishment and construction costed 256 million CZK and was fully funded by the Pardubice City Council and Pardubice Region through their shared subsidiary company East Bohemian Airport, a.s. that runs the airport. History Early years In 1910 Jan Kašpar, an engineer and aviation enthusiast, and his cousin Eugen Čihák, bought a Bleriot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pardubice
Pardubice (; german: Pardubitz) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 89,000 inhabitants. It is the capital city of the Pardubice Region and lies on the Elbe River. The historic centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument reservations, urban monument reservation. Pardubice is known as the centre of industry, which represents by an oil refinery or an electronic equipment plant. The city is well known for its sport events, which include the Great Pardubice Steeplechase in horse racing, the Golden Helmet of Pardubice in motorcycle racing, and the Czech Open international chess and games festival. Administrative division Pardubice is divided into eight boroughs, which are further divided into 27 administrative parts (in brackets): *Pardubice I (Bílé Předměstí (partly), Pardubice-Staré Město, Zámek, Zelené Předměstí (partly)); *Pardubice II (Cihelna, Polabiny, Rosice (partly)); *Pardubice III (Bílé Předměstí (part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glider Aircraft
A glider is a fixed-wing aircraft that is supported in flight by the dynamic reaction of the air against its lifting surfaces, and whose free flight does not depend on an engine. Most gliders do not have an engine, although motor-gliders have small engines for extending their flight when necessary by sustaining the altitude (normally a sailplane relies on rising air to maintain altitude) with some being powerful enough to take off by self-launch. There are a wide variety of types differing in the construction of their wings, aerodynamic efficiency, location of the pilot, controls and intended purpose. Most exploit meteorological phenomena to maintain or gain height. Gliders are principally used for the air sports of gliding, hang gliding and paragliding. However some spacecraft have been designed to descend as gliders and in the past military gliders have been used in warfare. Some simple and familiar types of glider are toys such as paper planes and balsa wood gliders. Etym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
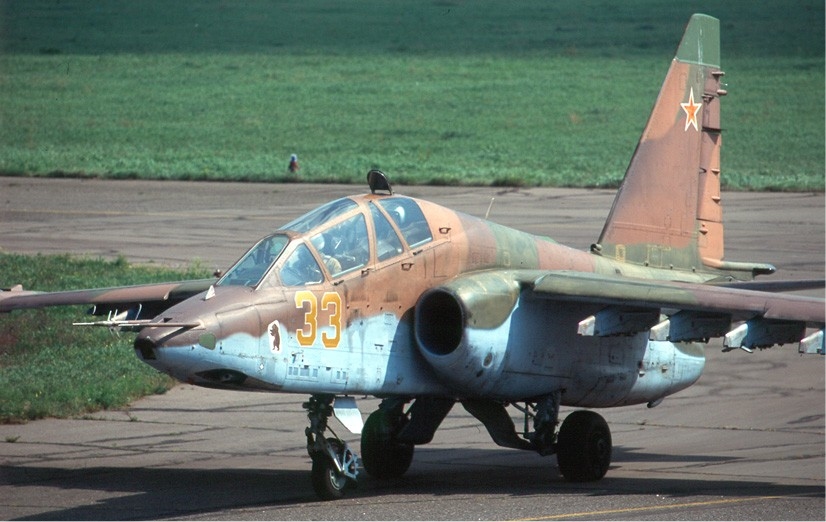
Su-25
The Sukhoi Su-25 ''Grach'' (russian: Грач (''rook''); NATO reporting name: Frogfoot) is a subsonic, single-seat, twin-engine jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Sukhoi. It was designed to provide close air support for Soviet Ground Forces. The first prototype made its maiden flight on 22 February 1975. After testing, the aircraft went into series production in 1978 in Tbilisi in the Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic. Early variants included the Su-25UB two-seat Trainer aircraft, trainer, the Su-25BM for Target tug, target-towing, and the Su-25K for export customers. Some aircraft were upgraded to the Su-25SM standard in 2012. The Su-25T and the Su-25TM (also known as the Su-39) were further developments, not produced in significant numbers. The Su-25, and the Sukhoi Su-34, Su-34, were the only armoured, Fixed-wing aircraft, fixed-wing aircraft in production in 2007.Gordon and Dawes 2004. Su-25s are in service with Russia, other Commonwealth of Independent States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su-22
The Sukhoi Su-17 (''izdeliye'' S-32) is a variable-sweep wing fighter-bomber developed for the Soviet military. Its NATO reporting name is "Fitter". Developed from the Sukhoi Su-7, the Su-17 was the first variable-sweep wing aircraft to enter Soviet service. Two subsequent Sukhoi aircraft, the Su-20 and Su-22, have usually been regarded as variants of the Su-17. The Su-17/20/22 series has had a long career and has been operated by many other air forces of including the Russian Federation, other former Soviet republics, the former Warsaw Pact, countries in the Arab world, Angola and Peru. Development Shortly after the Su-7 fighter-bomber was put into service, the Sukhoi Design Bureau was ordered to develop a deep modernization program for the aircraft in the early 1960s. The program would be aimed primarily at updating on-board avionics and the takeoff/landing performance characteristics. The concept of variable-geometry wings - something gaining wider attention at that time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyushin Il-14
The Ilyushin Il-14 (NATO reporting name: Crate) was a Soviet twin-engine commercial and military personnel and cargo transport aircraft that first flew in 1950, and entered service in 1954. The Il-14 was also manufactured in East Germany by VEB Flugzeugwerke as the VEB 14 and in Czechoslovakia as the Avia 14. The Ilyushin Il-14 was typically replaced by the Antonov An-24 and Yakovlev Yak-40. Design and development The Il-14 was developed as a replacement for the widespread Douglas DC-3 and its Soviet built version, the Lisunov Li-2. A development of the earlier Ilyushin Il-12, (that first flew in 1945), the Il-14 was intended for use in both military and civil applications. The Il-12 had major problems with poor engine-out behaviour. Also, it had less payload capability than was originally planned (although the Il-12 was intended to carry 32 passengers, in service it only carried 18, which was uneconomical). The development into the Il-14 was a vast improvement over the Il-12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyushin Il-28
The Ilyushin Il-28 (russian: Илью́шин Ил-28; NATO reporting name: Beagle) is a jet aircraft, jet bomber of the immediate postwar period that was originally manufactured for the Soviet Air Forces. It was the Soviet Union's first such aircraft to enter large-scale production. It was also licence-built in China as the Harbin H-5. Total production in the USSR was 6,316 aircraft, and over 319 H-5s were built. Only 187 examples of the HJ-5 training variant were manufactured. In the 1990s hundreds remained in service with various air forces over 50 years after the Il-28 first appeared. The only H-5s in service currently are approximately 80 aircraft which operate with the Korean People's Air Force. The Il-28 has the USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 27"Parsch, Andreas and Aleksey V. Martynov"Designations of Soviet and Russian Military Aircraft and Missiles." ''designation-systems.net,'' 2008. Retrieved: 22 August 2011. and NATO reporting name "Beagle", while the Il-28U trainer var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mil Mi-1
The Mil Mi-1 (USAF/DoD reporting name "Type 32", NATO reporting name "Hare") was a Soviet three- or four-seat light utility helicopter. It was the first Soviet helicopter to enter serial production. It is powered by one Ivchenko AI-26V radial piston engine. It entered service in 1950 and was first seen on the 1951 Soviet Aviation Day, Tushino and was produced for 16 years. More than 1,000 were built in the USSR and 1,594 in Poland, as SM-1. Development Mikhail Mil began work on rotary-winged aircraft before 1930, but the Mi-1, his first production helicopter, was begun in 1946, under a designation EG-1. In 1947 Mil became a head of OKB-4 design bureau in Tushino, and works were intensified. A final design was named GM-1 (for ''Gyelikopter Mila'', Mil's Helicopter). Soviet engineers tried to create a completely original design. So, they made a rotor hub with spaced vertical and horizontal hinges. This design increased the efficiency of helicopter control and was much simpler t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
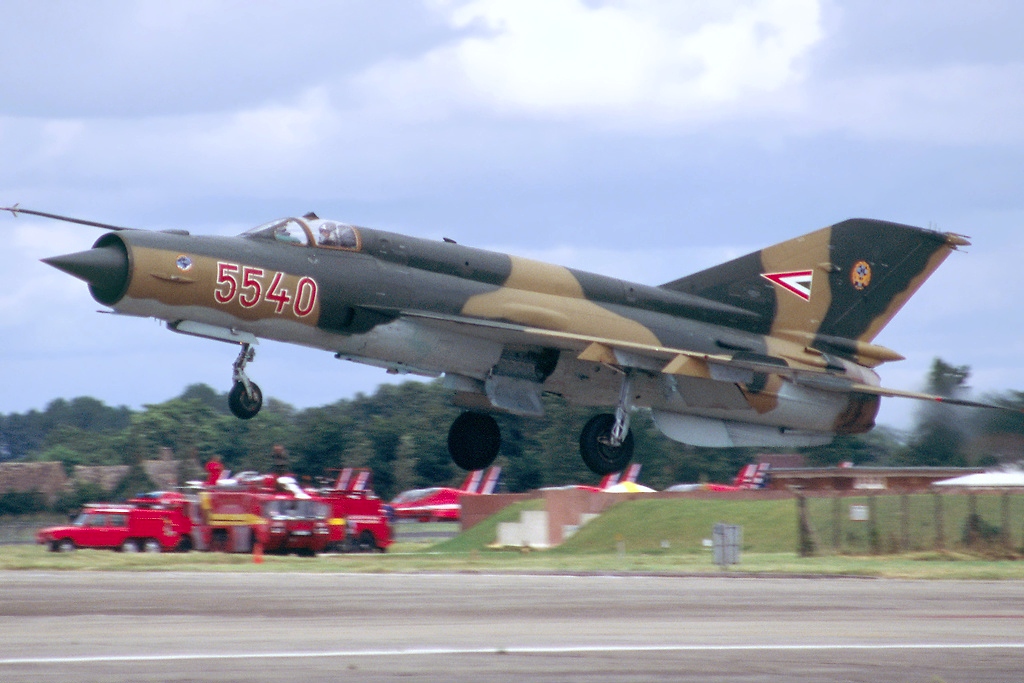
MiG-21
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-21 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-21; NATO reporting name: Fishbed) is a supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft, designed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich Design Bureau in the Soviet Union. Its nicknames include: "balalaika", because its planform resembles the stringed musical instrument of the same name; "''Ołówek''", Polish for "pencil", due to the shape of its fuselage, and "''Én Bạc''", meaning "silver swallow", in Vietnamese. Approximately 60 countries across four continents have flown the MiG-21, and it still serves many nations six decades after its maiden flight. It set aviation records, becoming the most-produced supersonic jet aircraft in aviation history, the most-produced combat aircraft since the Korean War and, previously, the longest production run of any combat aircraft (now exceeded by both the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle and General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon). Development Origins The MiG-21 jet fight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiG-19
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-19 (russian: Микоян и Гуревич МиГ-19; NATO reporting name: Farmer) is a Soviet second generation, single-seat, twinjet fighter aircraft, the world's first mass-produced supersonic aircraft. It was the first Soviet production aircraft capable of supersonic speeds in level flight. A comparable U.S. "Century Series" fighter was the North American F-100 Super Sabre, although the MiG-19 primarily fought against the more modern McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II and Republic F-105 Thunderchief over North Vietnam. This aircraft was originally used by the Soviet Union but it was later used by the People's Liberation Army Air Force. Design and development In 1950 the Mikoyan-Gurevich (MiG) design bureau (also known as OKB-155) began work on a new fighter aircraft, intended to have a greater range than the existing MiG-15 and MiG-17 aircraft, and capable of reaching supersonic speeds in level flight. MiG chose to use two of the new Mikulin AM-5 axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MiG-15
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 (russian: Микоя́н и Гуре́вич МиГ-15; USAF/DoD designation: Type 14; NATO reporting name: Fagot) is a jet fighter aircraft developed by Mikoyan-Gurevich for the Soviet Union. The MiG-15 was one of the first successful jet fighters to incorporate swept wings to achieve high transonic speeds. In aerial combat during the Korean War, it outclassed straight-winged jet day fighters, which were largely relegated to ground-attack roles. In response to the MiG-15’s appearance and in order to counter it, the United States Air Force rushed the North American F-86 Sabre to Korea.Thompson, Warren"Sabre: The F-86 in Korea."''Flight Journal'', December 2002. Retrieved: 30 June 2011. When refined into the more advanced MiG-17, the basic design would again surprise the West when it proved effective against supersonic fighters such as the Republic F-105 Thunderchief and McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II in the Vietnam War of the 1960s. The MiG-15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avia S-199
The Avia S-199 is a propeller-driven Messerschmitt Bf 109G-based fighter aircraft built after World War II utilizing the Bf 109G airframe and a Junkers Jumo 211F engine in place of the original and unavailable Daimler-Benz DB 605 engine. It is notable as the first fighter obtained by the Israeli Air Force, and used during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. Constructed in Czechoslovakia, with parts and plans left over from Luftwaffe aircraft production, the aircraft had numerous problems and was generally unpopular with its pilots. Czechoslovak pilots nicknamed it ''Mezek'' ("Mule"), while in Israel it was officially known as the ''Sakeen'' ("knife" in Hebrew). In practice, the aircraft was more often called Messerschmitt or ''Messer'' (which also means "knife", in German and Yiddish). Design and development Avia continued building Messerschmitt Bf 109G-6s after the war under the Avia S-99 name, at two aircraft factories in Czechoslovakia: one of them officially called ''závod Avi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing (air Force Unit)
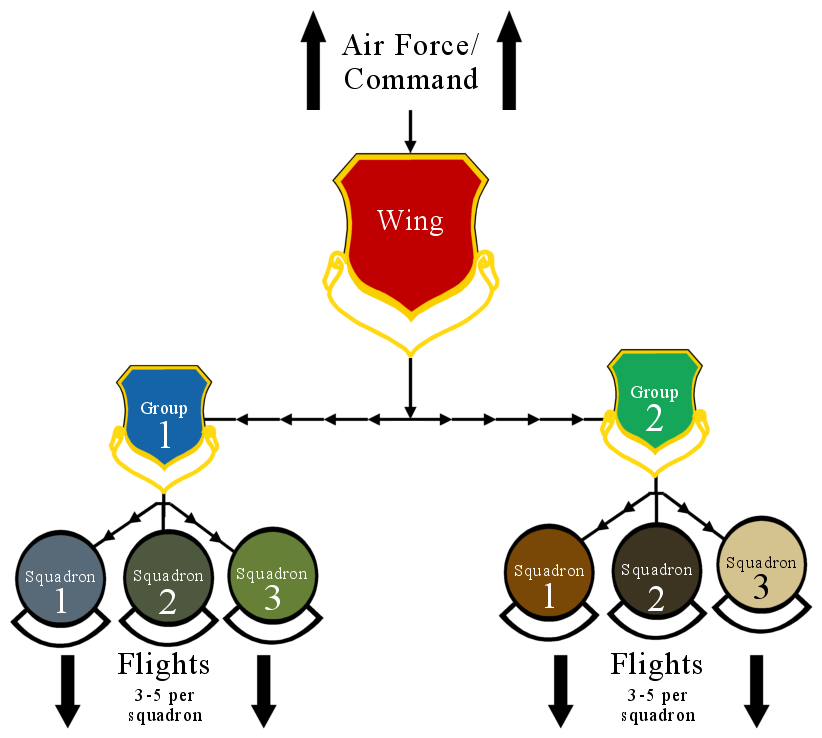
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three Squadron (aviation), squadrons, with several wings forming a group (air force unit), group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the United Kingdom, British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the Interservice rivalry, rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While Cavalry wing, the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)