|
Paramesotriton Hongkongensis
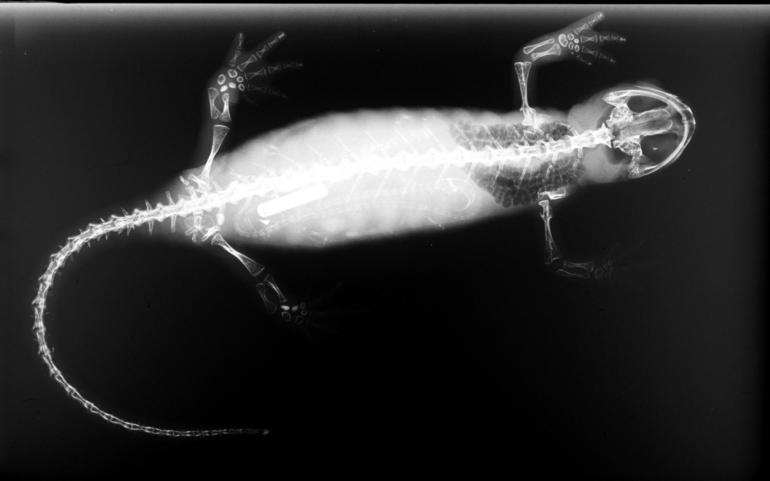
The Hong Kong warty newt or Hong Kong newt (''Paramesotriton hongkongensis'', see alsthe synonyms is a species of salamander found in Hong Kong. Once thought to be endemic to the territory, the species has also been found in the coastal parts of Guangdong Province. It is the only Urodela living in Hong Kong. This newt is considered by some naturalists as a subspecies of '' Paramesotriton chinensis''. However, some disagree with such a classification based on the disjunctive distribution of the two, and the differences in their physical appearance and habitat preference. Description The snout-to-tail length of the newt is about 11 to 15 cm. Its body colour ranges from light to dark brown, with patches of orange markings scattered on the ventral side. The patterns of the patches are unique for each individual, resembling the fingerprints of humans. Small granules can be found throughout the body. A mid-dorsal skin ridge extends backwards from the neck through the anterior t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta in South China. With 7.5 million residents of various nationalities in a territory, Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated places in the world. Hong Kong is also a major global financial centre and one of the most developed cities in the world. Hong Kong was established as a colony of the British Empire after the Qing Empire ceded Hong Kong Island from Xin'an County at the end of the First Opium War in 1841 then again in 1842.. The colony expanded to the Kowloon Peninsula in 1860 after the Second Opium War and was further extended when Britain obtained a 99-year lease of the New Territories in 1898... British Hong Kong was occupied by Imperial Japan from 1941 to 1945 during World War II; British administration resume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong Province
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) across a total area of about , Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world (after Uttar Pradesh in India). Its economy is larger than that of any other province in the nation and the fifth largest sub-national economy in the world with a GDP (nominal) of 1.95 trillion USD (12.4 trillion CNY) in 2021. The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, a Chinese megalopolis, is a core for high technology, manufacturing and foreign trade. Located in this zone are two of the four top Chinese cities and the top two Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP; Guangzhou, the capital of the province, and Shenzhen, the first special economic zone in the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urodela
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramesotriton Chinensis
The Chinese warty newt (''Paramesotriton chinensis'') is a species of salamander in the family Salamandridae. It is found only in China, with a range extending from Chongqing to Hunan, Anhui, Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong, and Guangxi Provinces in Central China. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, rivers, and freshwater marshes. It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby .... Female Chinese warty newts reach total length of , males are slightly shorter. References Paramesotriton Endemic fauna of China Amphibians of China Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Amphibians described in 1859 Taxa named by John Edward Gray {{Salamandridae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, nearly unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or deceased and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadpole
A tadpole is the larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial. Tadpoles have some fish-like features that may not be found in adult amphibians such as a lateral line, gills and swimming tails. As they undergo metamorphosis, they start to develop functional lungs for breathing air, and the diet of tadpoles changes drastically. A few amphibians, such as some members of the frog family Brevicipitidae, undergo direct development i.e., they do not undergo a free-living larval stage as tadpoles instead emerging from eggs as fully formed "froglet" miniatures of the adult morphology. Some other species hatch into tadpoles underneath the skin of the female adult or are kept in a pouch until after metamorphosis. Having no hard skeletons, it might be expected that tadpole fossils would not exist. However, traces of biofilms have been preserved and fossil tadpoles have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphosis (biology)
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some insects, fish, amphibians, mollusks, crustaceans, cnidarians, echinoderms, and tunicates undergo metamorphosis, which is often accompanied by a change of nutrition source or behavior. Animals can be divided into species that undergo complete metamorphosis (" holometaboly"), incomplete metamorphosis ("hemimetaboly"), or no metamorphosis (" ametaboly"). Scientific usage of the term is technically precise, and it is not applied to general aspects of cell growth, including rapid growth spurts. Generally organisms with a larva stage undergo metamorphosis, and during metamorphosis the organism loses larval characteristics. References to "metamorphosis" in mammals are imprecise and only colloquial, but historically idealist ideas of transformation an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Protected Species In Hong Kong
List of protected species in Hong Kong. Plants Protected Species under Forestry Regulations Cap. 96A Animals Protected species undeWild Animals Protection Ordinance Cap 170 See also {{portal, Hong Kong *Environment of Hong Kong External links ReferencesHong Kong Reptile & Amphibian Society Environment of Hong Kong Biota of Hong Kong [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






