|
Paramakanda Raja Maha Vihara
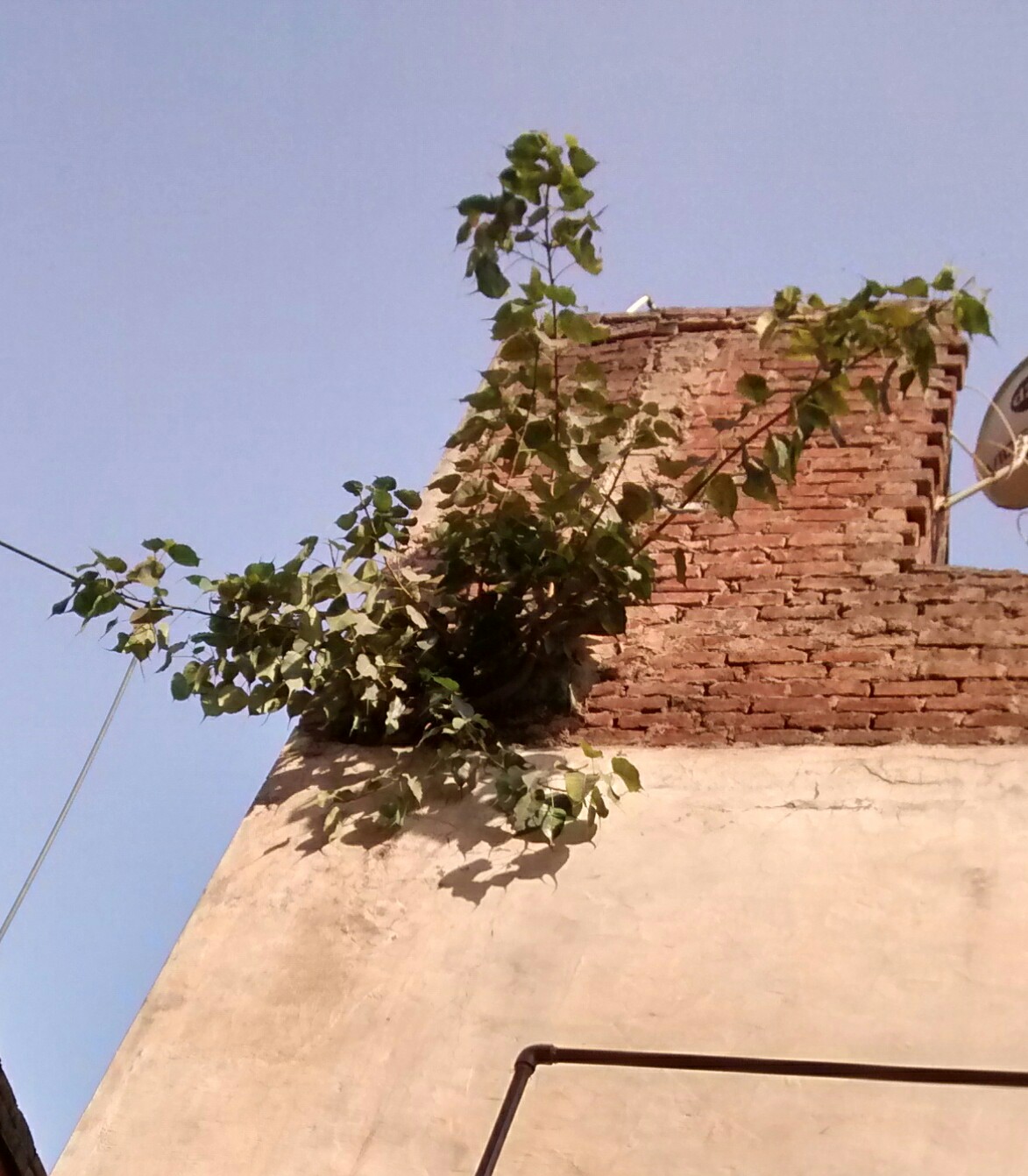
Paramakanda Raja Maha Vihara ( si, පරමාකන්ද රජ මහා විහාරය) is an ancient Buddhist temple in Puttalam District, Sri Lanka. The temple is located in Paramakanda village approximately distance from the Anamaduwa town. The site has been formally recognised by the Government as an archaeological site in Sri Lanka. The designations were declared on 1 November 1996 and 6 June 2008 under the government Gazette numbers 948 and 1586. The temple It is believed that the history of Paramakanda temple goes back to the reign of king Walagamba (103 BC and c. 89–77 BC). The Vihara complex mainly consists of two terraces. The lower terrace includes the Stupa, Bodhi tree, dripledged rock caves, Bikkhu dwellings, the main image house and the bell tower. Another small image house, a Stupa and a rock carved foot print of Buddha are found in the upper temple premises. The main image house of the lower terrace is adorned with paintings and sculptures belonging t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anamaduwa
Anamaduwa (Sinhala: ආණමඩුව) is a town in Puttalam District, North Western Province, Sri Lanka. It is located about away from Puttalam. Etymology There are few stories around the name of Anamaduwa. According to one such story, after uniting the country King Dutugemunu had given precious gifts to Nandimitra, one of the ten giant warriors belonged to the king. Nandimitra was given an area in the south-west region of Anuradhapura and he settled himself there with his battalion of Elephants. It is believed that the elephants were housed in an elephant kraal ( In Sinhalaː ''Ali Maduwa'') where in the present day Anamaduwa is situated. As the time went and the influence brought in by the Tamil language to the area, Ali Maduwa had become to ''Anei Madam'' and then evolved to current name of Anamaduwa. Tourist attractions * Paramakanda Vihara, is an ancient Buddhist temple A Buddhist temple or Buddhist monastery is the place of worship for Buddhists, the followers of Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Caves In Sri Lanka
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Puttalam District
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in History of India, northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a Bhavana, training of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thonigala Rock Inscription, Anamaduwa
Thonigala Rock Inscriptions ( si, තෝනිගල සෙල් ලිපිය) are two inscriptions engraved on a rock situated in Anamaduwa, in Sri Lanka. Each inscription is about 100 feet long and each letter is about one feet in height and engraved about one inch deep in to the rock. Also it is said to be the largest rock inscription found in Sri Lanka. History Thonigala rock inscriptions are dated back to the first century BC to the period of King Mahaculi Mahathissa (76-62 BC), who was a son of King Walagamba. The inscriptions reveal details about a grant of a lake and village to a Buddhist Monastery named Achagirika Tissa Pabbata. Today this Monastery is believed to be the Paramakanda Raja Maha Vihara, which is located about from Thonigala. Folklore There is folklore that describe how the name of Thonigala formed. The most popular story is associated with Kuveni, the first consort of King Vijaya. According to the story, Vijaya had to marry a princess from India i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
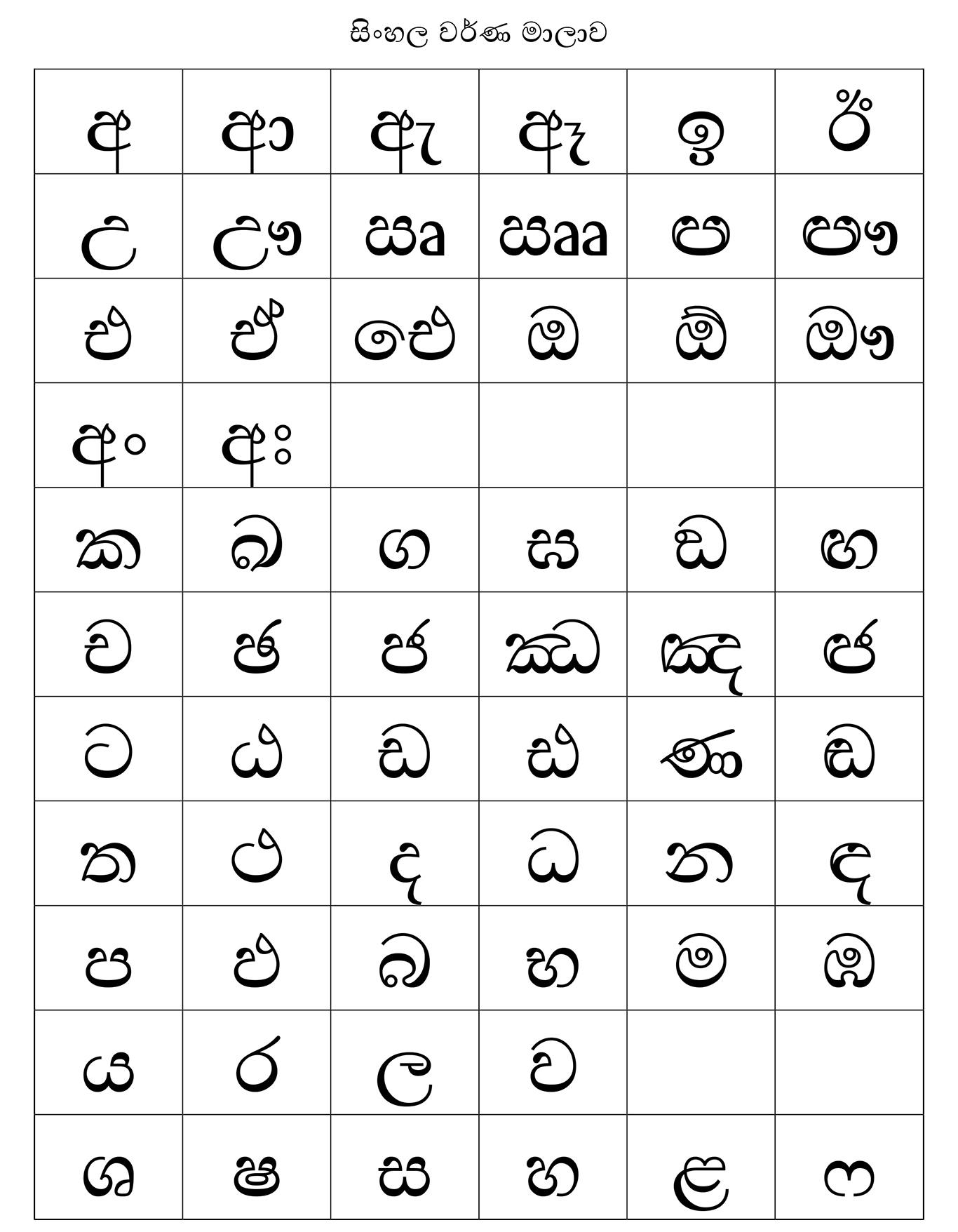
Sinhala Language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 2 million people as of 2001. It is written using the Sinhala script, which is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada, Theravada Buddhist literature. The early form of the Sinhala language, is attested as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions with long vowels and aspirated consonants is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle Indian Prakrits that has been used during the time of the Buddha. The closest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmi
Brahmi (; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi [''sc. lipi''], which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T[errien] de Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bo Tree
''Ficus religiosa'' or sacred fig is a species of fig native to the Indian subcontinent and Indochina that belongs to Moraceae, the fig or mulberry family. It is also known as the bodhi tree, pippala tree, peepul tree, peepal tree, pipal tree, or ashvattha tree (in India and Nepal). The sacred fig is considered to have a religious significance in three major religions that originated on the Indian subcontinent, Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. Hindu and Jain ascetics consider the species to be sacred and often meditate under it. This is the tree under which Gautama Buddha is believed to have attained enlightenment. The sacred fig is the state tree of the Indian states of Odisha, Bihar and Haryana. Description ''Ficus religiosa'' is a large dry season-deciduous or semi-evergreen tree up to tall and with a trunk diameter of up to . The leaves are cordate in shape with a distinctive extended drip tip; they are long and broad, with a petiole. The fruits are small figs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandyan Era Frescoes
Kandyan era frescoes are mural paintings created during the Kingdom of Kandy (1469–1815) in Sri Lanka, a time when kings gave a special place to arts and literature. As there was a political instability in Sri Lanka after the Anuradhapura Era, which lasted more than 500 years, kings didn't take much effort to build up the religious side of the people. Therefore there were no monks with Upasampada and people didn't have much education about Buddhism. Therefore at the beginning of Kandyan Kingdom, the monks got Upasampada, and started to preach Buddism to people. As people didn't know many things, monks (Specially Sangaraja Maha Nahimi) advised the kings to paint the walls of the temples with Jataka Stories so that anyone could understand even without knowing how to read. This marked the beginning of frescoes of the Kandyan Era. Special features of Kandyan era frescoes The walls of the Kandyan Era were built by clay which was stuck in between sticks. Then after they used Mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha Footprint
Buddha's footprints ( sa, Buddhapada) are Buddhist icons shaped like an imprint of Gautama Buddha's foot or both feet. There are two forms: natural, as found in stone or rock, and those made artificially. Many of the "natural" ones are acknowledged not to be genuine footprints of the Buddha, but rather replicas or representations of them, which can be considered ''cetiya'' (Buddhist relics) and also an early aniconic and symbolic representation of the Buddha. Symbolism Footprints of the Buddha abound throughout Asia, dating from various periods. Japanese author , who spent years tracking down the footprints in many Asian countries, estimates that he found more than 3,000 such footprints, among them about 300 in Japan and more than 1,000 in Sri Lanka. They often bear distinguishing marks, such as a Dharmachakra at the centre of the sole, or the 32, 108 or 132 auspicious signs of the Buddha, engraved or painted on the sole. A depression atop Sri padaya in Sri Lanka is among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or ''pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spreadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Associated Newspapers Of Ceylon Limited
Associated Newspapers of Ceylon Limited (ANCL), also known as Lake House. It publishes three daily, three weekend, five weekly, two monthly and three annual publications in Sinhala, English and Tamil. Associated Newspapers of Ceylon Limited is a public limited liability company incorporated in Sri Lanka in 1926 by its founder D. R. Wijewardena. 75% of its shares were Nationalized under the Associated Newspapers of Ceylon Limited (Special Provisions) Law No. 28 of 1973 and this stake is held by the Public Trustee of Sri Lanka on behalf of the Government. Lake House is Sri Lanka's oldest publication company. Its '' Daily News'' English daily was the first Sri Lankan newspaper to be published on-line. At present ''Dinamina'', Resa, ''Daily News'', ''Thinakaran'', ''Sunday Observer'', . '' |