|
Paraje De Fray Cristóbal
Paraje was a populated place along the east bank of the Rio Grande, in Socorro County, New Mexico, United States, now a ghost town. It is located north northeast of the Fra Cristobal Range. History Paraje de Fray Cristóbal The site of Paraje was originally an area known to the first Spanish colonists of New Mexico as Paraje de Fray Cristóbal. It was a paraje, an unpopulated stopping place along the old Camino Real de Tierra Adentro from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It was the first watering and grazing place along the Rio Grande available, after the crossing of the Jornada del Muerto from the south or the last such stop before entering it from the north. Travelers passed through the north northwest/south southeast trending Lava Gate between the difficult terrain of the Jornada del Muerto Volcano ''malpaís'' (lava field) to the northeast of it and the foothills of the mountain range to the southwest which funneled travelers to the paraje on the Rio Grande. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socorro County, New Mexico
Socorro County is a county in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 census, the population was 17,866. The county seat is Socorro. The county was formed in 1852 as one of the original nine counties of New Mexico Territory. Socorro was originally the name given to a Native American village (''see'': Puebloan peoples) by Don Juan de Oñate in 1598. Having received vitally needed food and assistance from the native population, Oñate named the pueblo ''Socorro'' ("succor" in English). Socorro County is home to multiple scientific research institutions including New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, the National Radio Astronomy Observatory and its associated Very Large Array, the Magdalena Ridge Observatory, and the Langmuir Laboratory for Atmospheric Research. Federal public lands in Socorro County include parts of the Cibola National Forest, the Bosque del Apache National Wildlife Refuge, the Sevilleta National Wildlife Refuge, the Bureau of Land Management ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Oñate
Juan de Oñate y Salazar (; 1550–1626) was a Spanish conquistador from New Spain, explorer, and colonial governor of the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México in the viceroyalty of New Spain. He led early Spanish expeditions to the Great Plains and Lower Colorado River Valley, encountering numerous indigenous tribes in their homelands there. Oñate founded settlements in the province, now in the Southwestern United States. Oñate is notorious for the 1599 Acoma Massacre. Following a dispute that led to the ambush and death of thirteen Spaniards at the hands of the Ácoma, including Oñate's nephew, Juan de Zaldívar, Oñate ordered a brutal retaliation against Acoma Pueblo. The Pueblo was destroyed. Around 800–1000 Ácoma were killed. Today, Oñate remains a controversial figure in New Mexican history: in 1998, the right foot was cut off a statue of the conquistador that stands in Alcalde, New Mexico, in protest of the massacre, and significant controversy arose when a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Socorro County, New Mexico
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
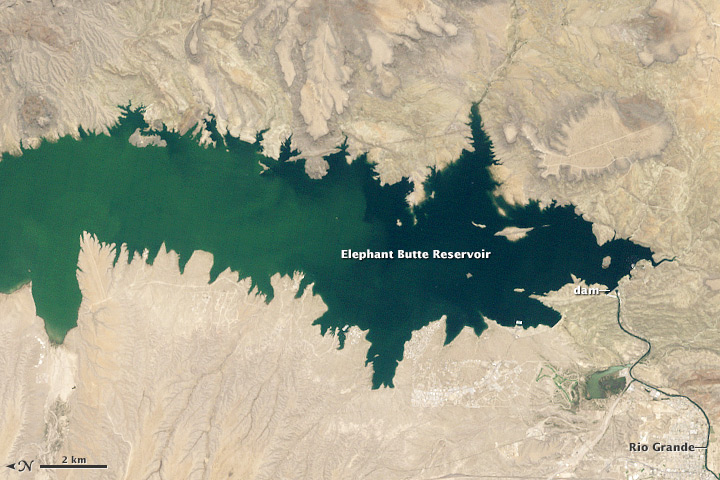
Elephant Butte Reservoir
Elephant Butte Reservoir is a reservoir on the southern part of the Rio Grande in the U.S. state of New Mexico, north of Truth or Consequences. The reservoir is the 84th largest man-made lake in the United States and the largest in New Mexico by total surface area and peak volume. It is the only place in New Mexico that one can find pelicans perched on or alongside the lake. There are also temporary US Coast Guard bases stationed at Elephant Butte. It is impounded by Elephant Butte Dam and is part of the largest state park in New Mexico, Elephant Butte Lake State Park. The reservoir is part of the Rio Grande Project to provide power and irrigation to south-central New Mexico and western Texas. It began to be filled in 1915 and 1916 and at highstand was the largest man-made lake in the world. The reservoir can hold of water from a drainage of 28,900 square miles (74,850 km2). It provides irrigation to 178,000 acres (720 km2) of land. Fishing is a popular recreational a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skirmish Near Fort Thorn, New Mexico Territory
The Skirmish near Fort Thorn, New Mexico Territory, also known as the Fight at E Company Grove, was a skirmish of the American Civil War on the morning of September 26, 1861. It followed the Battle of Canada Alamosa one of several small battles that occurred near the border between Confederate Arizona and Union New Mexico Territory. This one being an attempt by detachments of three companies of the Union Regiment of Mounted Rifles to pursue the Confederate cavalry force of Captain Bethel Coopwood's San Elizario Spy Company, and detachments of Company B and E, Second Texas Mounted Rifles, that was retiring from their victory at Canada Alamosa toward their base at Camp Robledo, 12 miles north of Dona Ana, New Mexico. Background Following his victory at Alamosa, Captain Bethel Coopwood paroled and released all the captured men without arms, only retaining as prisoners Captain John H. Minks, the wounded Second Lieutenant Matias Medina, and John Morrin, a wounded teamster, as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate Arizona
Arizona Territory, Colloquialism, colloquially referred to as Confederate Arizona, was an Constitution of the Confederate States, organized incorporated territory of the Confederate States that existed from August 1, 1861 to May 26, 1865, when the Confederate States Army Trans-Mississippi Department, commanded by General Edmund Kirby Smith, was conclusion of the American Civil War, surrendered at Shreveport, Louisiana. However, after the Battle of Glorieta Pass, the Confederates had to retreat from the territory, and by July 1862, effective Confederate control of the territory had ended. Delegates to the secession convention had voted in March 1861 to secede from the New Mexico Territory and the Union (American Civil War), Union, and seek to join the Confederacy. It consisted of the portion of the New Mexico Territory south of the 34th parallel north, 34th parallel, including parts of the modern states of New Mexico and Arizona. The capital was Mesilla, New Mexico, Mesilla, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Lawrence Hubbell
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thomas the Tank En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Craig
Fort Craig was a U.S. Army fort located along El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro, near Elephant Butte Lake State Park and the Rio Grande in Socorro County, New Mexico. The Fort Craig site was approximately 1,050 feet east-west by 600 feet north-south (320 by 180 m) and was located on 40 acres (16 hectares). History Before Fort Craig The 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo called for the construction of a series of forts along the new boundaries between Mexico and the United States. Apaches and other Native American groups were reportedly harassing settlers and travelers on both sides of the border. The attacks by the tribes from U.S. territory into Mexico was a problem the U.S. government was obligated to address under the treaty. In 1849, an initial garrison was established at Socorro, New Mexico, whose name can be translated as "safety." A fort called Fort Conrad was then established in 1851 on the west bank of the Rio Grande near Valverde Creek. This was near the north end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Conrad
Fort Conrad was a U.S. Army fort established in Socorro County, New Mexico Territory in 1851. Fort Conrad was located near modern Tiffany, New Mexico. It was on the west side of the Rio Grande. Because of its location, it was later abandoned for Fort Craig Fort Craig was a U.S. Army fort located along El Camino Real de Tierra Adentro, near Elephant Butte Lake State Park and the Rio Grande in Socorro County, New Mexico. The Fort Craig site was approximately 1,050 feet east-west by 600 feet north-so ... in 1854. References Geography of Socorro County, New Mexico Conrad History of Socorro County, New Mexico 1851 establishments in New Mexico Territory 1854 disestablishments in New Mexico Territory Military installations established in 1851 Military installations closed in 1854 {{NewMexico-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpaís (landform)
Malpaís, in the Southwestern United States, Spain, Mexico, and other Spanish-speaking regions, are rough and barren landscapes that consist of relict and largely uneroded lava fields exhibiting recognizable lava flows, volcanic cones, and other volcanic landforms. This type of volcanic landscape is extremely rough and difficult to traverse. It is characteristic of arid environments because in more humid climates, such rough terrains are smoothed by erosion and vegetation. While the term describes many xeric places, it is strongly associated with Spanish-speaking countries and the Southwestern United States, where Spanish settlers named this landform.Strahler, A. N., 1970, ''Introduction to Physical Geography'', 2nd ed. John Wiley and Sopns. New York, New York. 486 pp. Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. Jackson, eds. (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' (5th ed.). Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. Badlands landform The word 'malpaís' in Spanish t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Time Zone
The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time ( UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time ( UTC−06:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time at the 105th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In the United States, the exact specification for the location of time zones and the dividing lines between zones is set forth in the Code of Federal Regulations at 49 CFR 71. In the United States and Canada, this time zone is generically called Mountain Time (MT). Specifically, it is Mountain Standard Time (MST) when observing standard time, and Mountain Daylight Time (MDT) when observing daylight saving time. The term refers to the Rocky Mountains, which range from British Columbia to New Mexico. In Mexico, this time zone is known as the or ("Pacific Zone"). In the US and Canada, the Mountain Time Zone is to the east of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |