|
Paracoccidioidomycosis
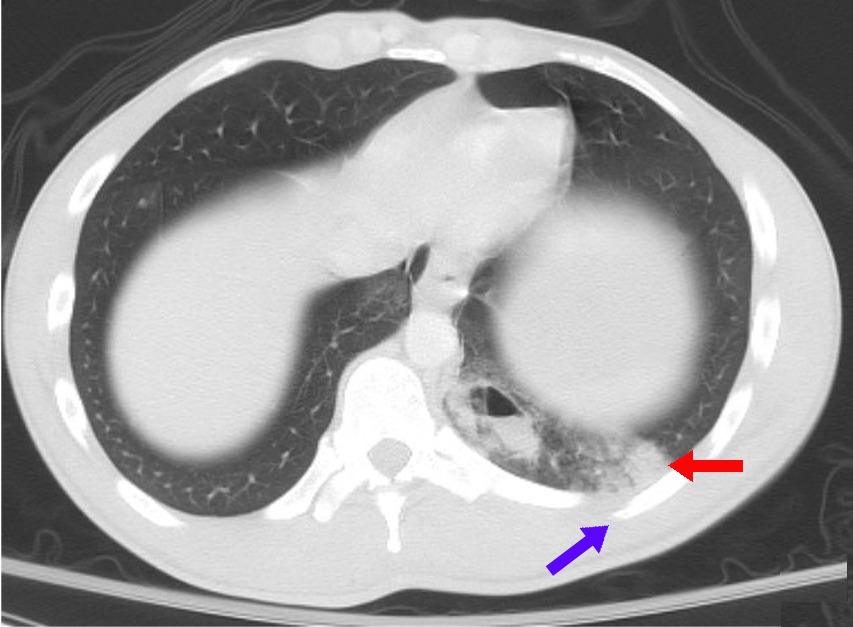
Paracoccidioidomycosis (PCM), also known as South American blastomycosis, is a fungal infection that can occur as a mouth and skin type, lymphangitic type, multi-organ involvement type (particularly lungs), or mixed type. If there are mouth ulcers or skin lesions, the disease is likely to be widespread. There may be no symptoms, or it may present with fever, sepsis, weight loss, large glands, or a large liver and spleen. The cause is fungi in the genus '' Paracoccidioides'', including '' Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' and '' Paracoccidioides lutzii'', acquired by breathing in fungal spores. Diagnosis is by sampling of blood, sputum, or skin. The disease can appear similar to tuberculosis, leukaemia, and lymphoma Treatment is with antifungals; itraconazole. For severe disease, treatment is with amphotericin B followed by itraconazole, or trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole as an alternative. It is endemic to Central and South America, and is considered a type of neglected tropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracoccidioides Brasiliensis
''Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' is a dimorphic fungus and one of the two species that cause paracoccidioidomycosis (the other being '' Paracoccidioides lutzii).'' The fungus has been affiliated with the family Ajellomycetaceae (division Ascomycota) although a sexual state or teleomorph has not yet been found. History ''Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' was first discovered by Adolfo Lutz in 1908 in Brazil. Although Lutz did not suggest a name for the disease caused by this fungus, he made note of structures he called "pseudococcidica" together with mycelium in cultures grown at 25 °C. In 1912, Alfonse Splendore proposed the name ''Zymonema brasiliense'' and described the features of the fungus in culture. Finally in 1930, Floriano de Almeida created the genus ''Paracoccidioides'' to accommodate the species, noting its distinction from ''Coccidioides immitis''. Physiology ''Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' is a nonphotosynthetic eukaryote with a rigid cell wall and organell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracoccidioides Lutzii
''Paracoccidioides lutzii'' is a dimorphic fungus that is one of the causal agents of paracoccidioidomycosis, together with ''Paracoccidioides brasiliensis''. Unlike ''P. brasiliensis,'' which is found throughout Central and South America, ''P. lutzii'' is found only in Brazil and Ecuador. It is less virulent than ''P. brasiliensis.'' History ''Paracoccidioides'' species were discovered by Adolfo Lutz in 1908 in Brazil. ''P. lutzii'' was formerly classified "PB-01 like", and proposed as a new species in 2014, being discovered in the Central-West region of Brazil. The infection it causes is considered to be a neglected endemic mycosis, a type of neglected tropical disease. Ecology ''P. lutzii'' occurs in nature as a filamentous structure. It forms conidia as part of its life cycle, which cause infection when inhaled into the respiratory tract of humans. Epidemiology Little is known about the epidemiology of the new species, as most previous epidemiological reports have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula. Lymphadenopathy is a common and nonspecific sign. Common causes include infections (from minor causes such as the common cold and post-vaccination swelling to serious ones such as HIV/AIDS), autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Lymphadenopathy is frequently idiopathic and self-limiting. Causes Lymph node enlargement is recognized as a common sign of infectious, autoimmune, or malignant disease. Examples may include: * Reactive: acute infection (''e.g.,'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycosis
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection. Fungi are everywhere, but only some cause disease. Fungal infection occurs after spores a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected Tropical Diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms ( helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. Some treatments for NTDs are relatively inexpensive. For example, the treatment for schistosomiasis is US$0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, in 2010 it was estimated that control of neglected diseases would require funding of between US$2 billion and $3 billion over the subsequent five to seven years. Some ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracoccidioides
The Ajellomycetaceae are a family of fungi in the Ascomycota, class Eurotiomycetes. The family contains eight genera Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat .... References Onygenales Ascomycota families Taxa described in 2004 {{Eurotiomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotes that it is of short duration and, as a corollary of that, of recent onset. The quantification of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core denotation of "acute" is always qualitatively in contrast with " chronic", which denotes long-lasting disease (for example, in acute leukaemia and chronic leukaemia). In addition, "acute" also often connotes two other meanings: sudden onset and severity, such as in acute myocardial infarction (AMI), where suddenness and severity are both established aspects of the meaning. It thus often connotes that the condition is fulminant (as in the AMI example), but not always (as in acute rhinitis, which is usually synonymous with the common cold). The one thing that acute MI and acute rhinitis have in common is that they are not chronic. They can happen again (as in recurrent pneumonia, that is, multiple acute pneumonia episodes), but they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asymptomatic. Infections of this kind are usually called subclinical infections. Diseases such as mental illnesses or psychosomatic conditions are considered subclinical if they present some individual symptoms but not all those normally required for a clinical diagnosis. The term clinically silent is also found. Producing only a few, mild symptoms, disease is paucisymptomatic. Symptoms appearing later, after an asymptomatic incubation period, mean a pre-symptomatic period has existed. Importance Knowing that a condition is asymptomatic is important because: * It may develop symptoms later and only then require treatment. * It may resolve itself or become benign. * It may be contagious, and the contribution of asymptomatic and pre-sympto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic (epidemiology)
In epidemiology, an infection is said to be endemic in a specific population or populated place when that infection is constantly maintained at a baseline level without extra infections being brought into the group as a result of travel or similar means. An endemic disease always has a steady, predictable number of people getting sick, but that number can be high ('' hyperendemic'') or low (''hypoendemic''), and the disease can be severe or mild. Also, a disease that is usually endemic can become epidemic. For example, chickenpox is endemic (steady state) in the United Kingdom, but malaria is not. Every year, there are a few cases of malaria reported in the UK, but these do not lead to sustained transmission in the population due to the lack of a suitable vector (mosquitoes of the genus '' Anopheles''). Consequently, the number of people infected by malaria is too variable to be called endemic. However, the number of people who get chickenpox in the UK varies little from y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given by mouth or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, rash, and headache. Severe side effects may include liver problems, heart failure, Stevens–Johnson syndrome and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. It is in the triazole family of medications. It stops fungal growth by affecting the cell membrane or affecting their metabolism. Itraconazole was patented in 1978 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1992. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Recent research works suggest itraconazole (ITZ) could also be used in the treatment of cancer by inhibiting the hedgehog pathway in a similar way t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungals
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Virus_PHIL_1878_lores.jpg)