|
Pappenheim (state)
Pappenheim was a German county in western Bavaria, Germany, located on the AltmĂĽhl river between Treuchtlingen and Solnhofen, and south of WeiĂźenburg. As former sovereign family, mediatized to Bavaria in 1806, the family which ruled the state belongs to High nobility. History Pappenheim originated as a Lordship around 1030, and was raised to a county in 1628. The first member of the House of Pappenheim was ''Henricus Caput'', mentioned in 1111 as vassal of Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor. From about 1100 until 1806 the Lords and Counts of Pappenheim held the position of hereditary marshals of the Holy Roman Empire, a court office that made them deputies of the Empire's arch marshals, the Electors of Saxony, with certain ceremonial tasks at the Coronation of the Holy Roman Emperor. Being immediate to the Emperor, Pappenheim was a member of the Swabian bench of Imperial Counts with one collective vote in the Imperial Diet. Pappenheim was partitioned twice: between itself, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FĂĽrstenberg (princely Family)
Fürstenberg (also Fuerstenberg and Furstenberg) may refer to: Historical states * Fürstenberg-Baar, county (1441–1559) * Fürstenberg-Blumberg, county (1559–1614) * Fürstenberg-Donaueschingen, county (1617–1698) * Fürstenberg-Fürstenberg, county (1408–1441, 1704–1716) and principality (1716–1804) * Fürstenberg-Geisingen, county (1441–1483) * Fürstenberg-Heiligenberg, county (1559–1664) and principality (1664–1716) * Fürstenberg-Messkirch, county (1614–1716) and principality (1716–1744) * Fürstenberg-Möhringen, county (1599–1641) * Fürstenberg-Pürglitz, principality (1762–1806) * Fürstenberg-Stühlingen, county (1614–1704) * Fürstenberg-Taikowitz, county (1759–1806) * Fürstenberg-Weitra, county (1705–1806) * Fürstenberg-Wolfach, county (1408–1490) * Principality of Fürstenberg, county (1250–1408) and principality Cities and municipalities * Fürstenberg/Havel, a city in the district of Oberhavel, Brandenburg, Germany * Fürste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire)
The Imperial Diet ( la, Dieta Imperii Comitium Imperiale; german: Reichstag) was the deliberative body of the Holy Roman Empire. It was not a legislative body in the contemporary sense; its members envisioned it more like a central forum where it was more important to negotiate than to decide. Its members were the Imperial Estates, divided into three colleges. The diet as a permanent, regularized institution evolved from the ''Hoftage'' (court assemblies) of the Middle Ages. From 1663 until the end of the empire in 1806, it was in permanent session at Regensburg. All Imperial Estates enjoyed immediacy and, therefore, they had no authority above them besides the Holy Roman Emperor himself. While all the estates were entitled to a seat and vote, only the higher temporal and spiritual princes of the College of Princes enjoyed an individual vote (''Virilstimme''), while lesser estates such as imperial counts and imperial abbots, were merely entitled to a collective vote (''Kuriats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Heinrich Von Pappenheim
Gottfried is a masculine German given name. It is derived from the Old High German name , recorded since the 7th century. The name is composed of the elements (conflated from the etyma for 'God' and 'good', and possibly further conflated with ) and ('peace, protection'). The German name was commonly hypocoristically abbreviated as ''Götz'' from the late medieval period. ''Götz'' and variants (including '' Göthe, Göthke'' and ''Göpfert'') also came into use as German surnames. Gottfried is a common Jewish surname as well. Given name The given name ''Gottfried'' became extremely frequent in Germany in the High Middle Ages, to the point of eclipsing most other names in ''God-'' (such as ''Godabert, Gotahard, Godohelm, Godomar, Goduin, Gotrat, Godulf'', etc.) The name was Latinised as ''Godefridus''. Medieval bearers of the name include: *Gotfrid, Duke of Alemannia and Raetia (d. 709) *Godefrid (d. c. 720), son of Drogo of Champagne, Frankish nobleman. *Godfrid Haraldsson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry V, Lord Of Pappenheim
Henry may refer to: People *Henry (given name) *Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany **Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: **Henry I of Castile **Henry II of Castile **Henry III of Castile **Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the name and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CoA Marschall Von Pappenheim
Coa may refer to: Places * Coa, County Fermanagh, a rural community in County Fermanagh, Northern Ireland * CĂ´a River, a tributary of the Douro, Portugal ** Battle of Coa, part of the Peninsular War period of the Napoleonic Wars ** CĂ´a Valley Paleolithic Art, one of the biggest open air Paleolithic art sites * QuwĂŞ (or Coa), an Assyrian vassal state or province from the 9th century BC to around 627 BCE in the lowlands of eastern Cilicia ** Adana, the ancient capital of QuwĂŞ, also called QuwĂŞ or Coa * CĂ´a (Mozambique), central Mozambique People * Eibar Coa (born 1971) Other uses * Coa de jima, or coa, a specialized tool for harvesting agave cactus * Continental Airlines, major US airline * c.o.a., coat of arms * Coa (argot) ( es), criminal slang used in Chile See also * COA (other) * ''Coea'', a genus of butterflies * ''Coua Couas are large, mostly terrestrial birds of the cuckoo family, endemic to the island of Madagascar. Couas are reminiscent of African ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
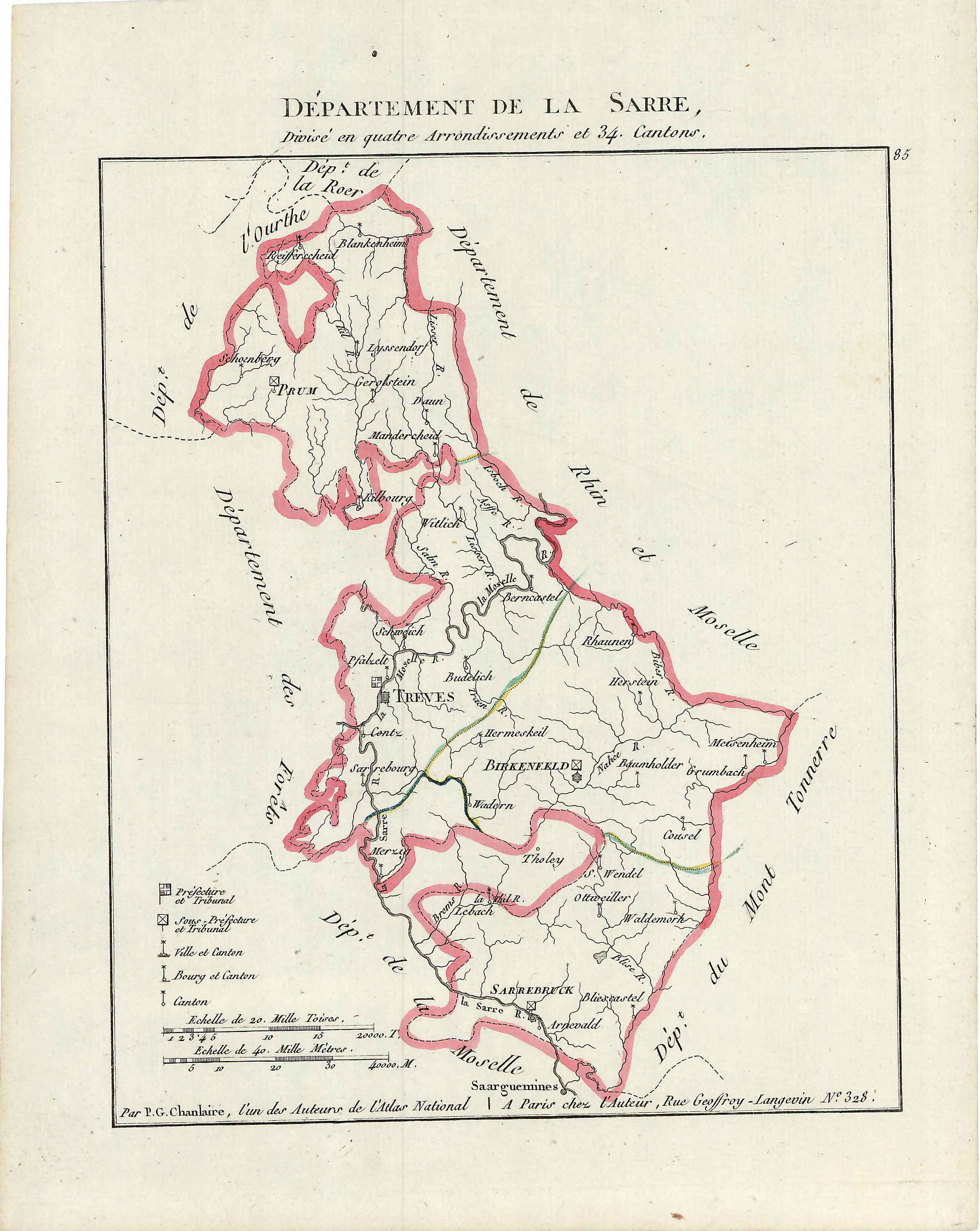
Sarre (department)
Sarre was a department in the First French Republic and First French Empire. Its territory is now part of Germany and Belgium. Named after the river Saar (french: Sarre), it was created in 1798 in the aftermath of the Treaty of Campo Formio of 18 October 1797 which ceded the left bank of the Rhine to France. Despite its name it covered a much larger area than the historical area known as the Saarland. Prior to the French occupation of the area from 1793 onward, its territory had been divided between the Electorate of Trier, Nassau-Saarbrücken and the Electorate of the Palatinate (the Duchy of Zweibrücken and the County of Veldenz). Its territory is now part of the German states Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland as well as a tiny adjacent section of the Belgian province of Liège. Its capital was Trier. The department was subdivided into the following arrondissements and cantons (situation in 1812): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congress Of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Participants were representatives of all European powers and other stakeholders, chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September 1814 to June 1815. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars without the use of (military) violence. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries, but to resize the main powers so they could balance each other and remain at peace, being at the same time shepherds for the smaller powers. More fundamentally, strongly generalising, conservative thinking leaders like Von Metternich also sought to restrain or eliminate republicanism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Ansbach
The Principality or Margraviate of (Brandenburg-)Ansbach (german: FĂĽrstentum Ansbach or ) was a principality in the Holy Roman Empire centered on the Franconian city of Ansbach. The ruling Hohenzollern princes of the land were known as margraves, as their ancestors were margraves (so the principality was a margraviate but not a march). History The principality was established at the death of Frederick V, Burgrave of Nuremberg, on 21 January 1398, when his lands were partitioned between his two sons. The younger son, Frederick VI, received Ansbach and the elder, John III, received Bayreuth. After John III's death on 11 June 1420, the two principalities were reunited under Frederick VI, who had become Elector Frederick I of Brandenburg in 1415. Upon Frederick I's death on 21 September 1440, his territories were divided between his sons; John received the principality of Bayreuth (Brandenburg-Kulmbach), Frederick received Brandenburg, and Albert received Ansbach. Thereafter An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |