|
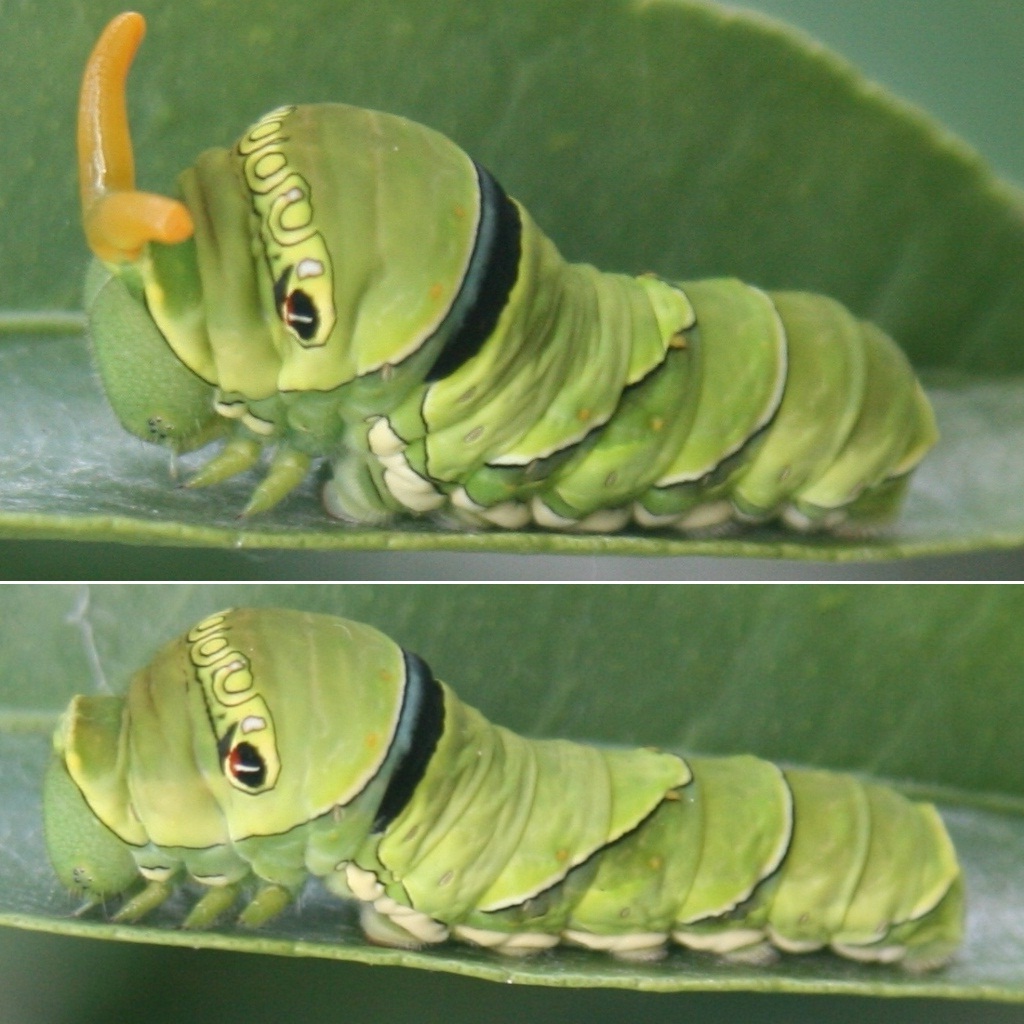
Papilio Aegeus
''Papilio aegeus'', the orchard swallowtail butterfly or large citrus butterfly is a species of butterfly from the family Papilionidae, that is found in eastern Australia and Papua New Guinea. The larvae of this species are sometimes considered a pest, due to their feeding on citrus leaves in suburban gardens. Description Both male and female have black forewings with a white stripe, though there is more white overall on the female forewing. The hindwing is again black, and there is a white swath through the middle. Here the markings differ in that the female has chains of red to orange and blue crescents toward the edge. The markings on the underside are similar to those on top. The body is black. The wingspan is about in females and in males, making it rather large overall and the largest butterfly commonly seen in at least part of its range. Despite being a swallowtail, which group derives its name from the distinctive tails on the hindwing, this characteristic is entirely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairns
Cairns (, ) is a city in Queensland, Australia, on the tropical north east coast of Far North Queensland. The population in June 2019 was 153,952, having grown on average 1.02% annually over the preceding five years. The city is the 5th-most-populous in Queensland, and 15th in Australia. The city was founded in 1876 and named after Sir William Wellington Cairns, following the discovery of gold in the Hodgkinson river. Throughout the late 19th century, Cairns prospered from the settlement of Chinese immigrants who helped develop the region's agriculture. Cairns also served as a port for blackbirding ships, bringing slaves and indentured labourers to the sugar plantations of Innisfail. During World War II, the city became a staging ground for the Allied Forces in the Battle of the Coral Sea. By the late 20th century the city had become a centre of international tourism, and in the early 21st century has developed into a major metropolitan city. Cairns is a popular tourist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thursday Island
Thursday Island, colloquially known as TI, or in the Kawrareg dialect, Waiben or Waibene, is an island of the Torres Strait Islands, an archipelago of at least 274 small islands in the Torres Strait. TI is located approximately north of Cape York Peninsula in Far North Queensland, Australia. Thursday Island is also the name of the town in the south and west of the island and also the name of the locality which contains the island within the Shire of Torres. The town of Rose Hill (known as Abednego until 7 September 1991) is located on the north-eastern tip of the island (). In the , Thursday Island had a population of 2,938 people. Geography Thursday Island has an area of about . The highest point on Thursday Island, standing at above sea level, is Milman Hill, a World War II defence facility. While Thursday Island is within the Shire of Torres and is the administrative centre for that shire, it is also the administrative and commercial centre of the local government area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an animal or a plant to avoid observation or detection by other animals. It may be a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation. Methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle and mimicry. Crypsis can involve visual, olfactory (with pheromones) or auditory concealment. When it is visual, the term cryptic coloration, effectively a synonym for animal camouflage, is sometimes used, but many different methods of camouflage are employed by animals or plants. Overview There is a strong evolutionary pressure for animals to blend into their environment or conceal their shape, for prey animals to avoid predators and for predators to be able to avoid detection by prey. Exceptions include large herbivores without natural enemies, brilliantly colored birds that rely on flight to escape predators, and venomous or otherwise powerfully armed animals with warning coloration. Cryptic animals include the tawny frogmouth (feather pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmeterium
The osmeterium is a defensive organ found in all papilionid larvae, in all stages. The organ is situated in the prothoracic segment and can be everted when the larva feels threatened. The everted organ resembles a fleshy forked tongue (not unlike a snake tongue), and this along with the large eye-like spots on the body might be used to startle birds and small reptiles. The osmeterial organ remains inside the body in the thoracic region in an inverted position and is everted when the larva is disturbed in any way emitting a foul, disagreeable odor which serves to repel ants, small spiders and mantids. To humans, this odour is rather strong but pleasant, usually smelling like a concentrated scent of the caterpillar’s food plant and pineapple. The constitution of the osmeterial secretion varies from species to species and contains monoterpene hydrocarbons, sesquiterpenic compounds or a mixture of aliphatic acids and esters The fine structure of the osmeterium of '' Papilio dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes and one pair of antennae. Their blood is not totally contained in vessels; some circulates in an open cavity known as the haemocoel. Insects are the most diverse group of animals; they include more than a million described species and represent more than half of all known living organisms. The total number of extant species is estimated at between six and ten million; In: potentially over 90% of the animal life forms on Earth are insects. Insects may be found in nearly all environments, although only a small number of species reside in the oceans, which are dominated by another arthropod group, crustaceans, which recent research has indicated insects are nested within. Nearly all insects hatch from eggs. Inse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male Orchard Swallowtail
Male ( symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. Not all species share a common sex-determination system. In most animals, including humans, sex is determined genetically; however, species such as '' Cymothoa exigua'' change sex depending on the number of females present in the vicinity. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineages, an exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
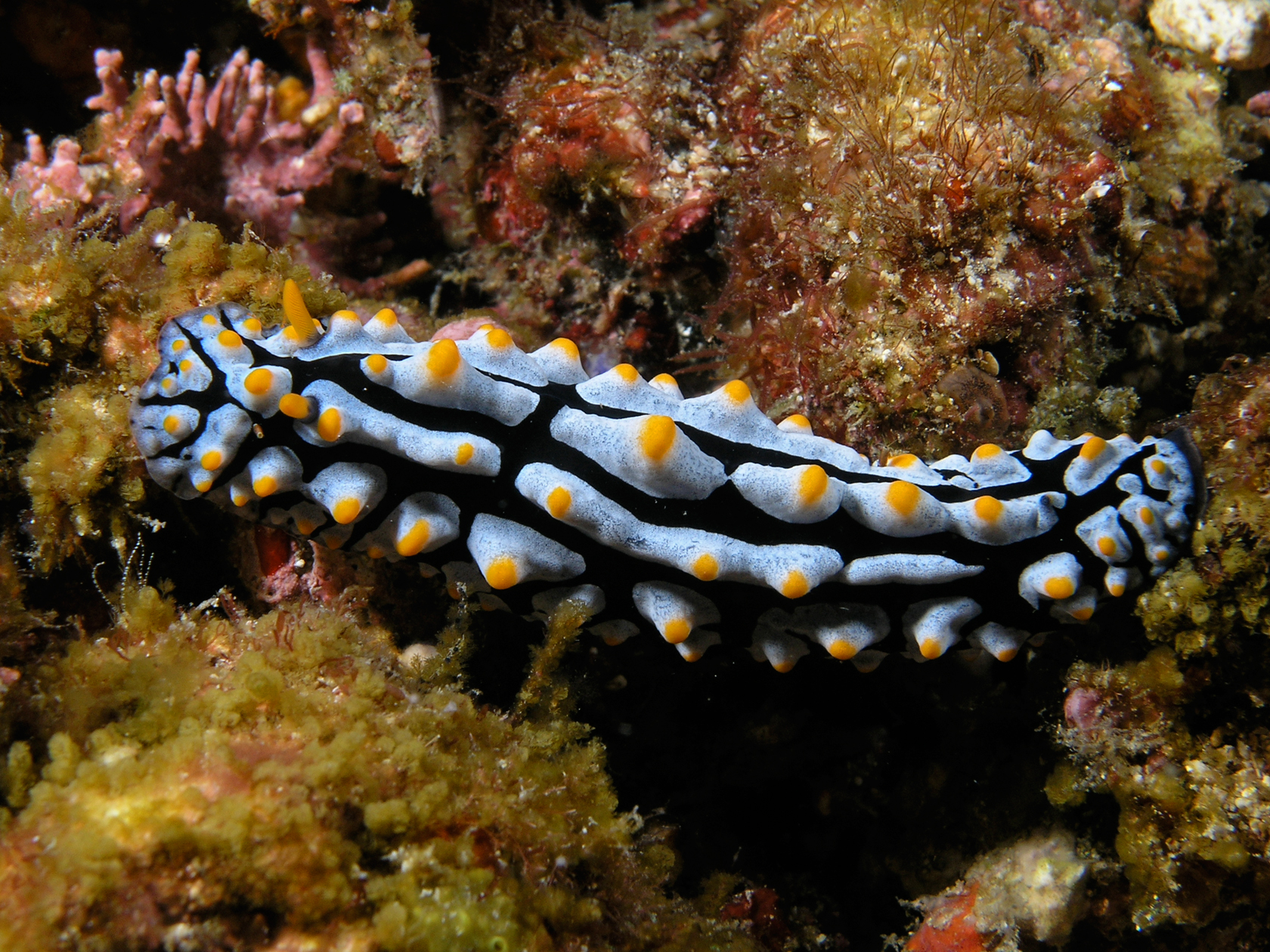
Tubercles
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal. In plants A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection, but it has slightly different meaning depending on which family of plants or animals it is used to refer to. In the case of certain orchids and cacti, it denotes a round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on the lip. They are also known as podaria (singular ''podarium''). When referring to some members of the pea family, it is used to refer to the wart-like excrescences that are found on the roots. In fungi In mycology, a tubercle is used to refer to a mass of hyphae from which a mushroom is made. In animals When it is used in relation to certain dorid nudibranchs such as '' Peltodoris nobilis'', it means the nodules on the dorsum of the animal. The tubercles in nudibranchs can present themselves in different ways: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolegs
A proleg is a small, fleshy, stub structure found on the ventral surface of the abdomen of most larval forms of insects of the order Lepidoptera, though they can also be found on other larval insects such as sawflies and a few other types of insects. In all the orders in which they appear, mainly Hymenoptera and Lepidoptera, prolegs of any form evolved independently of each other by convergent evolution. Prolegs of lepidopteran larvae have a small circle of gripping hooks, called "crochets". The arrangement of the crochets can be helpful in identification to family level. Although the point has been debated, prolegs are not widely regarded as true legs, derived from the primitive uniramous limbs. Certainly in their morphology they are not jointed, and so lack the five segments (coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, tarsus) of thoracic insect legs. Prolegs do have limited musculature, but much of their movement is hydraulically powered. See also * Terrestrial locomotion in animals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'', "form", "likeness") is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, between each moult (''ecdysis''), until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to grow or assume a new form. Differences between instars can often be seen in altered body proportions, colors, patterns, changes in the number of body segments or head width. After shedding their exoskeleton (moulting), the juvenile arthropods continue in their life cycle until they either pupate or moult again. The instar period of growth is fixed; however, in some insects, like the salvinia stem-borer moth, the number of instars depends on early larval nutrition. Some arthropods can continue to moult after sexual maturity, but the stages between these subsequent moults are generally not called instars. For most insect species, an ''instar'' is the developmental stage of the larval forms of holometabolous (complete metamorphism) or nymphal forms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |