|
Papadoplaka
Papadoplaka ( el, Παπαδόπλακα) is a natural reef islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan Sea. The islet is in a bay between cape Lithino and cape Kefalas, at Kommos, and close to Gortyn which was the ancient capital of Crete. The name can be loosely translated as the ''priest's rock''. Reconstructing Murex Royal Purple and Biblical Blue in the Aegean by Deborah Ruscillo. It is administered within Heraklion (regional unit), Heraklion regional unit. Group of islets [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trafos
Trafos ( el, Τράφος) is an islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan sea. The islet is in a bay between the capes of Lithino and Kefalas, at Kommos, and close to Gortyn which was the ancient capital of Crete. It is administered within Heraklion regional unit. In 2000, the marine area around Trafos was established as an archaeological zone. Group of islets There are a group of four islets in the bay including Papadoplaka (to the west), Megalonisi (with the lighthouse), Mikronisi Mikronisi ( el, Μικρονήσι, "small island", also known as ''Agios Pavlos'' el, Άγιος Παύλος, "St Paul") is an islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan Sea. The islet is in a bay between the capes ... (also known as Agios Pavlos), and Trafos. References Landforms of Heraklion (regional unit) Uninhabited islands of Crete Islands of Greece {{Greece-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalonisi (Crete)
Megalonisi ( el, Μεγαλονήσι, "big island") is an uninhabited islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan Sea that hosts a lighthouse. The islet is in a bay between the capes of Lithino and Kefalas, at Kommos, and close to Gortyn which was the ancient capital of Crete. It is administered within Heraklion regional unit. Group of islets There is a group of four islets in the bay including Papadoplaka (to the west), Megalonisi (with the lighthouse), Mikronisi (also known as Agios Pavlos), and Trafos Trafos ( el, Τράφος) is an islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan sea. The islet is in a bay between the capes of Lithino and Kefalas, at Kommos, and close to Gortyn which was the ancient capital of Crete. .... References {{Cretan islands Landforms of Heraklion (regional unit) Mediterranean islands Uninhabited islands of Crete Islands of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kommos (Crete)
Kommos ( el, Κομμός) is a Greek prehistoric Bronze Age port and archaeological site in southern Crete, 5 km north of Matala. It was a busy port with connections to the Near East that continued into historic periods; the rich finds and elaborate buildings reflect the importance of foreign trade for the Cretan economy.Shaw, ''Kommos''. Its ancient name was probably Amyklaion ( el, Αμύκλαιον), which would reflect a link with Amyclae; Robin Lane Fox speculates that it is referred to in Odyssey 3.296: "a small rock holds back the great waves." That small rock is likely to have been the natural reef of Papadoplaka and a submerged sandy shore stretching to the coast would have formed a natural harbor. This breakwater was partially degraded by aerial bombing during the Second World War as part of a campaign to deny safe harbours for the Nazis' enemies. Kommos was the harbour firstly for the nearby larger ruined Minoan settlement and palace of Phaistos, which was o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikronisi
Mikronisi ( el, Μικρονήσι, "small island", also known as ''Agios Pavlos'' el, Άγιος Παύλος, "St Paul") is an islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan Sea. The islet is in a bay between the capes of Lithino and Kefalas, at Kommos, and close to Gortyn which was the ancient capital of Crete. It is administered within Heraklion regional unit. Group of islets There are a group of four islets in the bay including Papadoplaka (to the west), Megalonisi (with the lighthouse), Mikronisi, and Trafos Trafos ( el, Τράφος) is an islet off the southern coast of the Greek island of Crete in the Libyan sea. The islet is in a bay between the capes of Lithino and Kefalas, at Kommos, and close to Gortyn which was the ancient capital of Crete. .... References {{Cretan islands Landforms of Heraklion (regional unit) Mediterranean islands Uninhabited islands of Crete Islands of Greece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
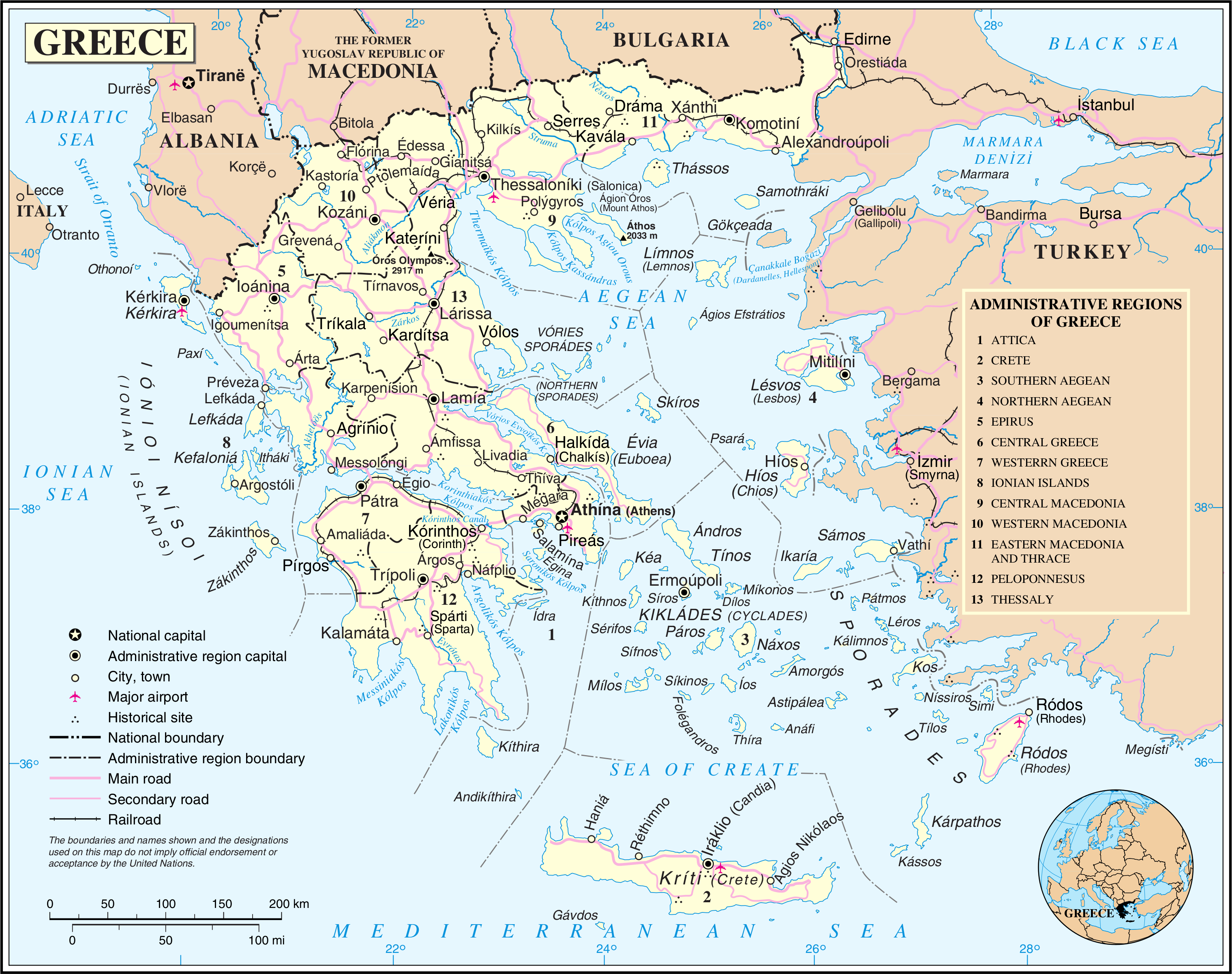
Modern Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece ( el, περιφέρειες, translit=periféries) are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was often arbitrary; not all of the pre-1986 traditional historical-geographic regions had official administrative bodie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Islands
The following is a list of islands in the Mediterranean Sea. The two main island countries in the region are Malta and Cyprus, while other countries with islands in the Mediterranean Sea include Italy, France, Greece, Spain, Tunisia, Croatia, and Turkey. By area By population (above 200,000) By country Albania * Sazan * Kunë * Ksamil Islands * Franz Joseph Island * Zvërnec Islands * Tongo Island * Stil Island Croatia France *Corsica ** Lavezzi Islands ** Cavallo Island *Frioul archipelago *Lérins Islands *Îles d'Hyères Greece * Crete * Euboea * Gavdos Cyclades Dodecanese Islands Ionian Islands North Aegean islands Saronic Islands Sporades Islands Italy Notable Italian islands include: * Calabria **Coreca Reefs ** Isola di Dino **San Nicola Arcella * Campanian Archipelago ** Capri ** Gaiola Island ** Ischia ** Nisida ** Procida ** Sirenuse * Cheradi Islands ** Gallipoli ** San Paolo Island ** Sant'Andrea Island ** Vivara * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Heraklion (regional Unit)
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnisos
Amnisos, also Amnissos and Amnisus (Greek: or ; Linear B: 𐀀𐀖𐀛𐀰 ''A-mi-ni-so''), is the current but unattested name given to a Bronze Age settlement on the north shore of Crete that was used as a port to the palace city of Knossos. It appears in Greek literature and mythology from the earliest times, but its origin is far earlier, in prehistory. The historic settlement belonged to a civilization now called Minoan. Excavations at Amnissos in 1932 uncovered a villa that included the "House of the Lilies", which was named for the lily theme that was depicted in a wall fresco. Geography Amnisos is 7 km east of Heraklion (Iraklio) on a beach used for recreation by the citizens of the modern city. The current sea level is three meters higher than the bronze-aged sea level. The walls of submerged houses are visible from the shore. The ancient settlement bears the same name as the river exiting there. Currently called the Karteros, from the iron-aged name of Caerat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minoan Civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450BC until it ended around 1100BC, during the early Greek Dark Ages, part of a wider bronze age collapse around the Mediterranean. It represents the first advanced civilization in Europe, leaving behind a number of massive building complexes, Minoan art, sophisticated art, and writing systems. Its economy benefited from a network of trade around much of the Mediterranean. The civilization was rediscovered at the beginning of the 20th century through the work of British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans. The name "Minoan" derives from the mythical Minos, King Minos and was coined by Evans, who identified the site at Knossos with the labyrinth of the Minotaur. The Minoan civilization has been described as the earliest of its kind in Europe, and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komos 09
The Kōmos ( grc, κῶμος; pl. kōmoi) was a ritualistic drunken procession performed by revelers in ancient Greece, whose participants were known as komasts (κωμασταί, ''kōmastaí''). Its precise nature has been difficult to reconstruct from the diverse literary sources and evidence derived from vase painting. The earliest reference to the komos is in Hesiod's '' Shield of Herakles'', which indicates it took place as part of wedding festivities (line 281). And famously Alcibiades gate-crashes the ''Symposium'' while carousing in a komos. However, no one kind of event is associated with the komos: Pindar describes them taking place at the city festivals (Pythian 5.21, 8.20, Olympian 4.9), while Demosthenes mentions them taking place after the '' ''pompe'''' and '' choregoi'' on the first day of the Greater Dionysia (Speeches 21.10), which may indicate the komos might have been a competitive event. The komos must be distinguished from the '' pompe'', or ritual pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gortyn
Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna ( el, Γόρτυν, , or , ) is a municipality, and an archaeological site, on the Mediterranean island of Crete away from the island's capital, Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka. Gortyn was the Roman capital of Creta et Cyrenaica. The area was first inhabited around 7000 BC. It is located in the valley of Messara in the south of the Psiloritis mountain, in the current position of the settlements of Metropolis and Agioi Deka, and near the Libyan Sea. Municipality The municipality Gortyna was formed as part of Greece's 2011 local government reform by merging the following four former municipalities, each of which became municipal units: * Agia Varvara *Gortyna * Kofinas *Rouvas The municipality has an area of , the municipal unit . Geography Climate History There is evidence of human occupation in Gortyn as far back as the Neolithic era (7000 BC). Many artifacts have been found from the Minoan period (2600–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
