|
Paola Malatesta
{{Infobox noble , name = Paola Agnese Malatesta , title = Marquesa of Mantua , image = File:Paola Malatesta.jpg , caption = , alt = , CoA = 100px , more = no , succession = , spouse = Gianfrancesco , spouse-type = , issue =Ludovico III Gonzaga, Marquis of MantuaCecilia Gonzaga , issue-link = , issue-pipe = , full name = , native_name = , styles = , titles = , noble family = Malatesta , house-type = , father = Malatesta IV Malatesta , mother = Elisabetta da Varano , birth_name = , birth_date = {{Birth year, 1393 , birth_place = Pesaro , christening_date = , christening_place = , death_date = {{Death date, 1449, 02, 28 , death_place = Mantua , burial_date = , burial_place = , religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arms Of The House Of Malatesta
Arms or ARMS may refer to: *Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to: People * Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader Coat of arms or weapons *Armaments or weapons **Firearm **Small arms *Coat of arms **In this sense, "arms" is a common element in pub names Enterprises *Amherst Regional Middle School *Arms Corporation, originally named Dandelion, a defunct Japanese animation studio who operated from 1996 to 2020 *TRIN (finance) or Arms Index, a short-term stock trading index *Australian Relief & Mercy Services, a part of Youth With A Mission Arts and entertainment *ARMS (band), an American indie rock band formed in 2004 * ''Arms'' (album), a 2016 album by Bell X1 * "Arms" (song), a 2011 song by Christina Perri from the album ''lovestrong'' * ''Arms'' (video game), a 2017 fighting video game for the Nintendo Switch *ARMS Charity Concerts, a series of charitable rock concerts in support of Action into Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vittorino Da Feltre
Vittorino da Feltre (1378February 2, 1446) was an Italian humanist and teacher. He was born in Feltre, Belluno, Republic of Venice and died in Mantua. His real name was Vittorino Rambaldoni. It was in Vittorino that the Renaissance idea of the complete man, or ''l'uomo universale'' — health of body, strength of character, wealth of mind — reached its first formulation. Biography He studied under John of Ravenna and at Padua under Gasparino da Barzizza. He later taught there, but after a few years he was invited by Gianfrancesco I Gonzaga, the marquis of Mantua, to educate his children. At Mantua, Vittorino set up a school at which he taught the marquis's children and the children of other prominent families — both sons and daughters — together with many poor children whom he charged no fee, treating them all on an equal footing. He not only taught the humanistic subjects, but placed special emphasis on religious and physical education. Vittorino’s lessons in Greek and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility Of Mantua
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic of Genoa (1005–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1449 Deaths
Year 1449 ( MCDXLIX) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * January 6 – Constantine XI Palaiologos is crowned Byzantine Emperor at Mistra; he will be the last in a line of rulers that can be traced to the founding of Rome. * February – Alexăndrel seizes the throne of Moldavia, with the support of the boyars. * March 24 – Hundred Years' War: English capture Fougères in Brittany. * April 7 – The last Antipope, Felix V, abdicates. * April 19 – Pope Nicholas V is elected by the Council of Basel. * April 25 – The Council of Basel dissolves itself. * May – An English privateering fleet led by Robert Wennington challenges ships of the Hanseatic League. * May 14 – Second Siege of Sfetigrad (1449): The Albanian garrison surrenders and the Ottomans seize the fortress. * May 20 – Battle of Alfarrobeira: King Afonso V of Portugal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1393 Births
Year 1393 ( MCCCXCIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events * January 28 – Bal des Ardents: Four members of the court of Charles VI of France die in a fire, at a masquerade ball. Date unknown * In central Persia, the Muzzafarid Empire, led by Shah Mansur, rebels against their Timurid occupiers. The rebellion is squashed and the Muzaffarid nobility are executed, ending the Muzaffarid Dynasty in Persia. * George VII succeeds his popular father, Bagrat V, as King of Georgia. * Abdul Aziz II becomes Sultan of the Marinid Dynasty in present-day Morocco, after the death of Sultan Abu Al-Abbas. * Raimondo Del Balzo Orsini succeeds Otto, Duke of Brunswick-Grubenhagen, as Prince of Taranto (now southeastern Italy). * Samsenethai succeeds his father, Fa Ngum, as King of Lan Xang (now Laos). * King James I of Cyprus inherits the title of King of Armenia, after the death of his distant cousin Leo VI (although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Of Brandenburg, Marquise Of Mantua
Barbara of Brandenburg (1422 – 7 November 1481) was a Marchioness consort of Mantua, married in 1433 to Ludovico III Gonzaga, Marquis of Mantua. She was referred to as a ''virago'' because of her strong character and forceful nature, and served as Regent of Mantua several times during the absence of Ludivico III between 1445 and 1455.Ingeborg Walter. Barbara di Hohenzollern, marchesa di Mantova (итал.). Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani – Volume 6 (1964). Treccani. She is regarded as an important figure in the Italian Renaissance and was a student of Vittorino da Feltre. Life Barbara was the daughter of John, Margrave of Brandenburg-Kulmbach, and Barbara of Saxe-Wittenberg and a niece of Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund. Her engagement took place on 5 July and marriage took place on 12 November 1433 in Mantua, when she was only ten years old, and she spent the latter part of her childhood in Mantua. Her marriage had been arranged partially by her uncle the Emperor. Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Mantegna
Andrea Mantegna (, , ; September 13, 1506) was an Italian painter, a student of Roman archeology, and son-in-law of Jacopo Bellini. Like other artists of the time, Mantegna experimented with perspective, e.g. by lowering the horizon in order to create a sense of greater monumentality. His flinty, metallic landscapes and somewhat stony figures give evidence of a fundamentally sculptural approach to painting. He also led a workshop that was the leading producer of prints in Venice before 1500. Biography Youth and education Mantegna was born in Isola di Carturo, Venetian Republic close to Padua (now Italy), second son of a carpenter, Biagio. At the age of 11, he became the apprentice of Paduan painter Francesco Squarcione. Squarcione, whose original profession was tailoring, appears to have had a remarkable enthusiasm for ancient art, and a faculty for acting. Like his famous compatriot Petrarca, Squarcione was an ancient Rome enthusiast: he traveled in Italy, and perhaps a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martyrology
A martyrology is a catalogue or list of martyrs and other saints and beati arranged in the calendar order of their anniversaries or feasts. Local martyrologies record exclusively the custom of a particular Church. Local lists were enriched by names borrowed from neighbouring churches. Consolidation occurred, by the combination of several local martyrologies, with or without borrowings from literary sources. This is the now accepted meaning in the Latin Church. In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the nearest equivalent to the martyrology is the Synaxarion and the longer Menologion. As regards form, one should distinguish between simple martyrologies that simply enumerate names, and historical martyrologies, which also include stories or biographical details; for the latter, the term ''passionary'' is also used. Oldest examples The martyrology, or ''ferial'', of the Roman Church in the middle of the fourth century still exists. It comprises two distinct lists, the ''Depositio marty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include three independent orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor being the largest contemporary male order), orders for women religious such as the Order of Saint Clare, and the Third Order of Saint Francis open to male and female members. They adhere to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary. Several smaller Franciscan spirituality in Protestantism, Protestant Franciscan orders exist as well, notably in the Anglican and Lutheran traditions (e.g. the Community of Francis and Clare). Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval from Pope Innocent III in 1209 to form a new religious order. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poor Clare Nuns
The Poor Clares, officially the Order of Saint Clare ( la, Ordo sanctae Clarae) – originally referred to as the Order of Poor Ladies, and later the Clarisses, the Minoresses, the Franciscan Clarist Order, and the Second Order of Saint Francis – are members of a contemplative Order of nuns in the Catholic Church. The Poor Clares were the second Franciscan branch of the order to be established. Founded by Clare of Assisi and Francis of Assisi on Palm Sunday in the year 1212, they were organized after the Order of Friars Minor (the ''first Order''), and before the Third Order of Saint Francis for the laity. As of 2011, there were over 20,000 Poor Clare nuns in over 75 countries throughout the world. They follow several different observances and are organized into federations. The Poor Clares follow the '' Rule of St. Clare'', which was approved by Pope Innocent IV on the day before Clare's death in 1253. The main branch of the Order (O.S.C.) follows the observance of Pope Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardino Da Siena
Bernardino of Siena, OFM (8 September 138020 May 1444), also known as Bernardine, was an Italian priest and Franciscan missionary preacher in Italy. He was a systematizer of Scholastic economics. His preaching, his book burnings, and his " bonfires of the vanities" made him famous/infamous during his own lifetime because they were frequently directed against sorcery, gambling, infanticide, witchcraft, homosexuals, Jews, Romani "Gypsies", usury, etc. Bernardino was later canonised by the Catholic Church as a saint – where he is also referred to as "the Apostle of Italy" – for his efforts to revive the country's Catholicism during the 15th century. Sources Two hagiographies of Bernardino of Siena were written by two of his friends; the one the same year in which he died, by Barnaba of Siena; the other by the humanist Maffeo Vegio. Another important contemporary biographical source is that written by the Sienese diplomat Leonardo Benvoglienti, who was another personal acqua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
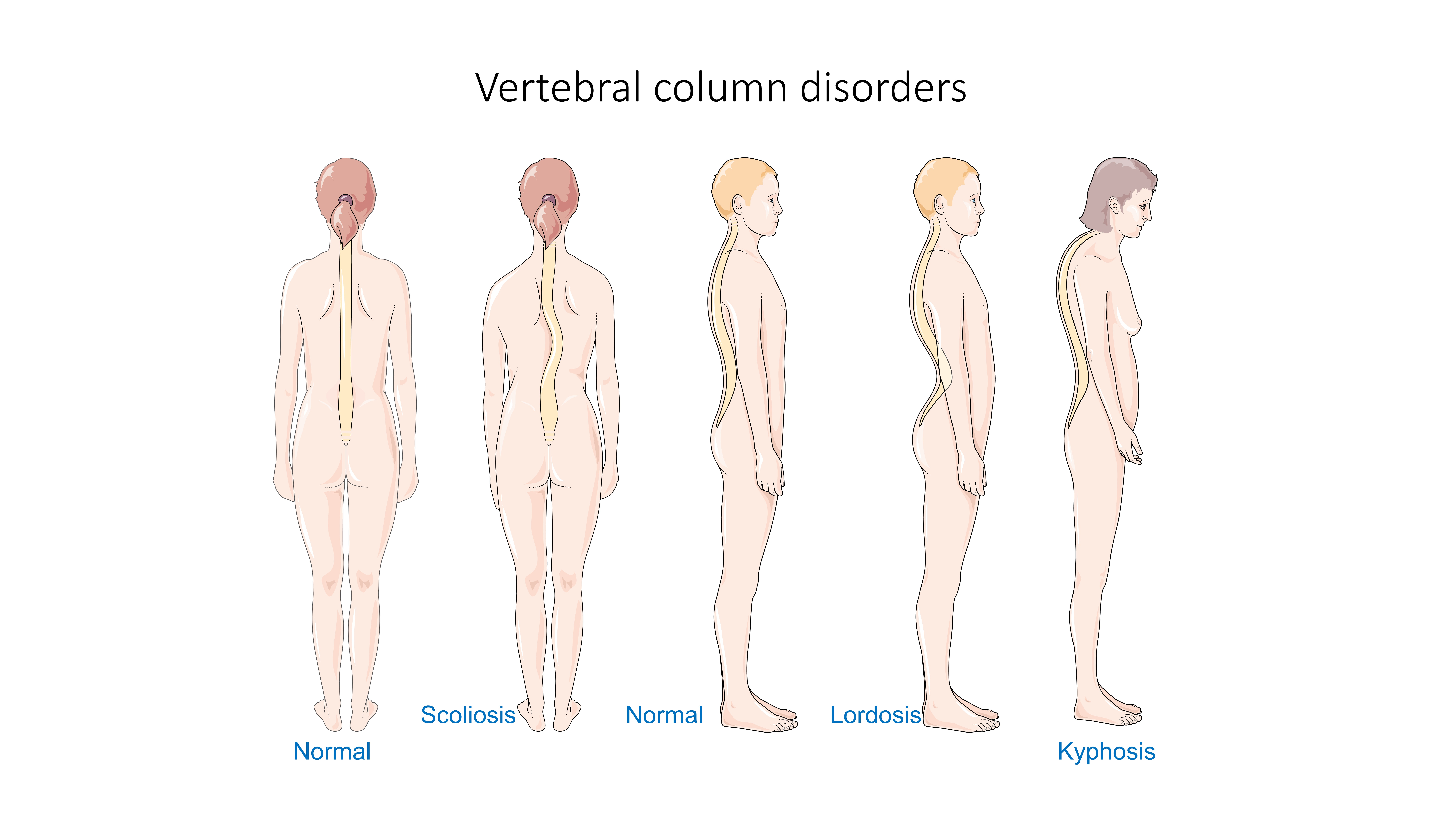
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females. In the sense of a deformit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |