|
Panicum Mosaic Virus
''Panicum mosaic virus'' (PMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA viral pathogen that infects plant species in the panicoid tribe of the grass family, ''Poaceae''. The pathogen was first identified in Kansas in 1953 and most commonly causes disease on select cultivars of turf grass, switchgrass, and millet. The disease most commonly associated with the panicum mosaic virus pathogen is St. Augustine Decline Syndrome, which infects species of turf grass and causes chlorotic mottling. In addition to St. Augustine Decline, panicum mosaic virus is responsible for chlorotic streaking and mild green mosaicking in select cultivars of switchgrass and millet. History PMV was first observed in Kansas in 1953. It was originally noted to infect switchgrass (''Panicum virgatum''), and was observed infecting St. Augustine grass (''Stenotaphrum secundatum'') in Texas in 1966. The strain specific to St. Augustine grass has since been observed in Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi and South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-sense Single-stranded RNA Virus
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome. Positive-strand RNA viruses are divided between the phyla ''Kitrinoviricota'', ''Lenarviricota'', and ''Pisuviricota'' (specifically classes ''Pisoniviricetes'' and '' Stelpavirictes'') all of which are in the kingdom '' Orthornavirae'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are monophyletic and descended from a common RNA virus ancestor. In the Baltimore classification system, +ssRNA viruses belong to Group IV. Positive-sense RNA viruses include pathogens s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centipedegrass
''Eremochloa ophiuroides'', or centipedegrass, is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. Used as a warm season lawn grass, it forms thick sods and spreads by stolons In biology, stolons (from Latin '' stolō'', genitive ''stolōnis'' – "branch"), also known as runners, are horizontal connections between organisms. They may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton; typically, animal stolons are external s .... It is medium to light green in color and has a coarse texture with short upright seedhead stems that grow to about 3-5 inches. Native to southern China, it was introduced to the United States in 1916 and has since become one of the common grasses in the southeastern states and Hawai'i. It can also be considered a weed. Cultivation Centipedegrass is a low maintenance grass. It requires infrequent mowing.Aaron Patton and John Boyd"Centipedegrass."FSA6120. University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture.Archivedon 23 March 2012.) Centipedegrass has medium shade to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense (molecular Biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript. DNA sense Because of the complementary nature of base-pairing between nucleic acid polymers, a double-stranded DNA molecule will be composed of two strands with sequences that are reverse complements of each other. To help molecular biologists specifically identify each strand individually, the two strands are usually differentiated as the "sense" strand and the "antisense" strand. An individual strand of DNA is referred to as positive-sense (also positive (+) or simply sense) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
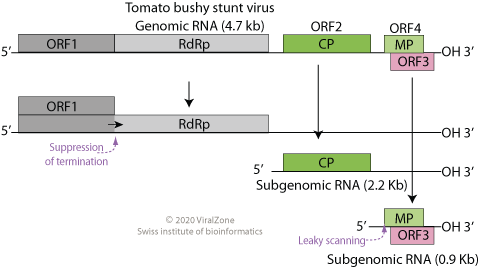
Tombusviridae
''Tombusviridae'' is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from ''Tomato bushy stunt virus'' (TBSV). Genome All viruses in the family have a non-segmented (monopartite) linear genome, with the exception of Dianthoviruses, whose genome is bipartite. The genome is approximately 4.6–4.8kb in length, lacks a 5' cap and a poly(A) tail, and it encodes 4–6 ORFs. The polymerase encodes an amber stop codon which is the site of a readthrough event within ORF1, producing two products necessary for replication. There is no helicase encoded by the virus. ICTVFamily - Tombusviridae in: Virus Taxonomy. Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses 2012, pp 1111-1138, 23 November 2011, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-384684-6.00096-3 Structure The RNA is encapsulated in an icosahedral (T=3) capsid, composed of 180 units of a single coat protein 27–42K in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Virus
Plant viruses are viruses that affect plants. Like all other viruses, plant viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that do not have the molecular machinery to replicate without a host. Plant viruses can be pathogenic to higher plants. Most plant viruses are rod-shaped, with protein discs forming a tube surrounding the viral genome; isometric particles are another common structure. They rarely have an envelope. The great majority have an RNA genome, which is usually small and single stranded (ss), but some viruses have double-stranded (ds) RNA, ssDNA or dsDNA genomes. Although plant viruses are not as well understood as their animal counterparts, one plant virus has become very recognizable: ''tobacco mosaic virus'' (TMV), the first virus to be discovered. This and other viruses cause an estimated US$60 billion loss in crop yields worldwide each year. Plant viruses are grouped into 73 genera and 49 families. However, these figures relate only to cultivated plants, which r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panicovirus
''Panicovirus'' is a genus of viruses, in the family '' Tombusviridae''. Panicae serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: systemic mosaic. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * '' Cocksfoot mild mosaic virus'' * ''Panicum mosaic virus ''Panicum mosaic virus'' (PMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA viral pathogen that infects plant species in the panicoid tribe of the grass family, ''Poaceae''. The pathogen was first identified in Kansas in 1953 and most commonly caus ...'' * '' Thin paspalum asymptomatic virus'' Structure Viruses in ''Panicovirus'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and Spherical geometries, and T=3 symmetry. The diameter is around 28-34 nm. Genomes are linear, around 4-5.4kb in length. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by penetration into the host cell. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus repli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Wheat
Common wheat (''Triticum aestivum''), also known as bread wheat, is a cultivated wheat species. About 95% of wheat produced worldwide is common wheat; it is the most widely grown of all crops and the cereal with the highest monetary yield. Taxonomy Numerous forms of wheat have evolved under human selection. This diversity has led to confusion in the naming of wheats, with names based on both genetic and morphological characteristics. List of common cultivars * Albimonte * Manital Phylogeny Bread wheat is an allohexaploid (an allopolyploid with six sets of chromosomes: two sets from each of three different species). Of the six sets of chromosomes, two come from ''Triticum urartu'' (einkorn wheat) and two from a species related to ''Aegilops speltoides''. This spontaneous hybridisation created the tetraploid species ''Triticum turgidum'' (an ancestor of wild emmer wheat and durum wheat) 580,000–820,000 years ago. The last two sets of chromosomes came from wild goat-gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The leafy stalk of the plant produces pollen inflorescences (or "tassels") and separate ovuliferous inflorescences called ears that when fertilized yield kernels or seeds, which are fruits. The term ''maize'' is preferred in formal, scientific, and international usage as a common name because it refers specifically to this one grain, unlike ''corn'', which has a complex variety of meanings that vary by context and geographic region. Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat or rice. In addition to being consumed directly by humans (often in the form of masa), maize is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panicum Mosaic Satellite Virus
Panicum mosaic satellite virus (SPMV) is a plant satellite virus in genus ''Papanivirus'', which is a member of realm ''Riboviria'' without assigned family or order. It only infects grasses which are infected by ''Panicum mosaic virus''. One study found that 72% of ''Stenotaphrum secundatum St. Augustine grass (''Stenotaphrum secundatum''), also known as buffalo turf in Australia and buffalo grass in South Africa, is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. It is a warm-season lawn grass that is popular for cultivation in tropica ...'' (St Augustine grass) infected with panicum mosaic virus was also infected with SPMV. In addition to SPMV, many plants infected with panicum mosaic virus are also infected with satellite RNAs. References External linksICTVdB—The Universal Virus Database: Panicum mosaic satellite virus *Mart Krupovic [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearl Millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum''; also known as 'Bajra' in Hindi, 'Sajje' in Kannada, 'Kambu' in Tamil, 'Bajeer' in Kumaoni and 'Maiwa' in Hausa, 'Mexoeira' in Mozambique) is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and suggested area of domestication, for the crop is in the Sahel zone of West Africa. Recent archaeobotanical research has confirmed the presence of domesticated pearl millet on the Sahel zone of northern Mali between 2500 and 2000 BC. Description Pearl millet has ovoid grains of 3 – 4 mm length, the largest kernels of all varieties of millet (not including sorghum). These can be nearly white, pale yellow, brown, grey, slate blue or purple. The 1000-seed weight can be anything from 2.5 to 14 g with a mean of 8 g. The height of the plant ranges from 0.5 – 4 m. Cultivation Pearl millet is well ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |