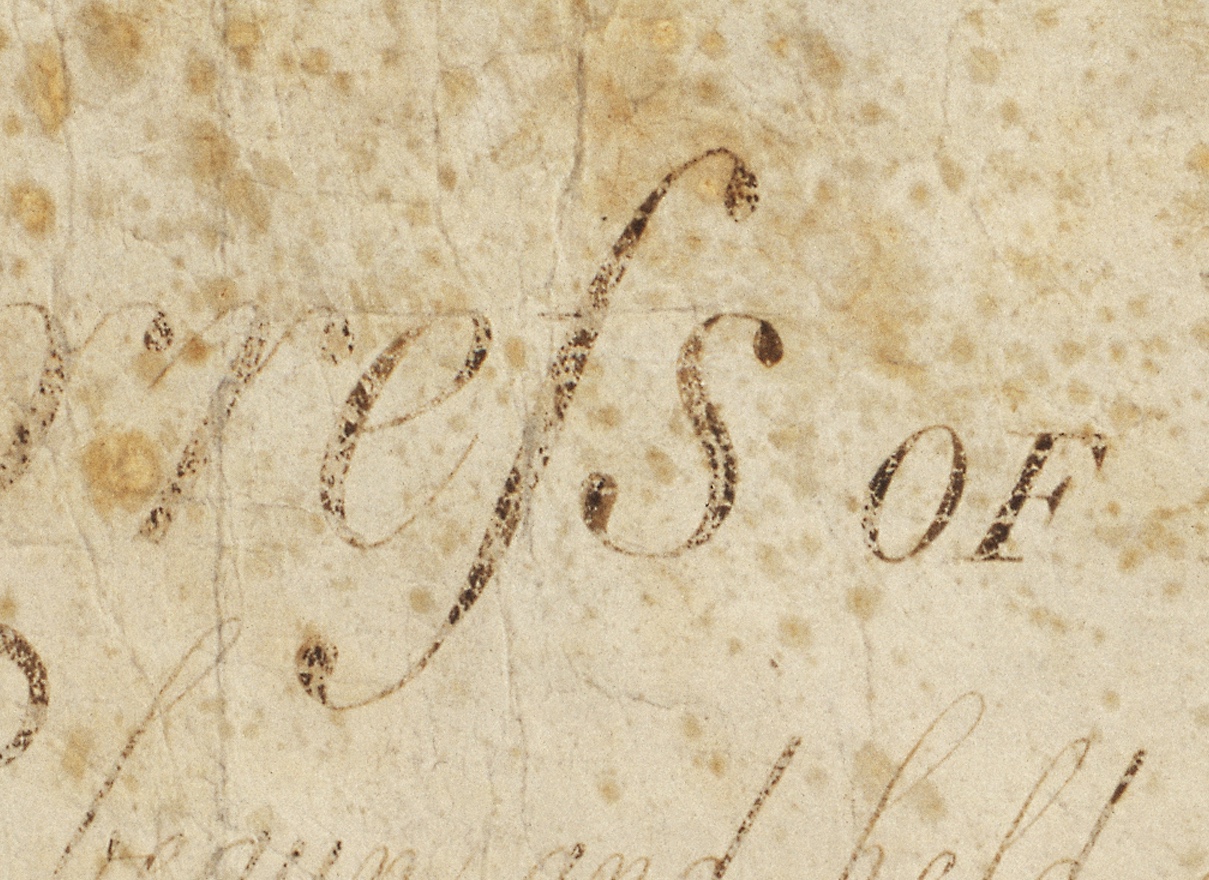|
Pangram
A pangram or holoalphabetic sentence is a sentence using every letter of a given alphabet at least once. Pangrams have been used to display typefaces, test equipment, and develop skills in handwriting, calligraphy, and keyboarding. Origins The best-known English pangram is " The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog". It has been used since at least the late 19th century, was used by Western Union to test Telex/ TWX data communication equipment for accuracy and reliability, and is now used by a number of computer programs to display computer fonts. Short pangrams Short pangrams in English are more difficult to devise and tend to use uncommon words and unnatural sentences. Longer pangrams afford more opportunity for humor, cleverness, or thoughtfulness. The following are examples of pangrams that are shorter than "The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog" (which has 33 letters) and use standard written English without abbreviations or proper nouns: *"Waltz, bad nymph, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portez Ce Vieux Whisky Au Juge Blond Qui Fume
"Portez ce vieux whisky au juge blond qui fume" ("Take this old whisky to the blond judge who is smoking") is a French language pangram, that is, a sentence that uses every letter of the alphabet (not including accents nor ligatures). It is also an alexandrine. The pangram contains 37 letters and does not repeat any consonants. Though not the oldest or shortest pangram, it is the best known. It is often used by people learning to type, is familiar to many French speakers, and is a standard piece of text to test typography and printing equipment, sometimes used as a placeholder. Some firmware in printers produced for the French market has the pangram stored in its internal code.. Sometimes an expanded version, "au juge blond qui fume ''la pipe''", which covers all lower-case letters, is used. The pangram became popular after being published in Albert Navarre's ''Manuel d’organisation du bureau'' in 1924. The first widespread commercial publication of the pangram has been attribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Quick Brown Fox Jumps Over The Lazy Dog
"The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" is an English-language pangram — a sentence that contains all the letters of the alphabet. The phrase is commonly used for touch-typing practice, testing typewriters and computer keyboards, displaying examples of fonts, and other applications involving text where the use of all letters in the alphabet is desired. History The earliest known appearance of the phrase was in '' The Boston Journal''. In an article titled "Current Notes" in the February 9, 1885, edition, the phrase is mentioned as a good practice sentence for writing students: "A favorite copy set by writing teachers for their pupils is the following, because it contains every letter of the alphabet: 'A quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.'" Dozens of other newspapers published the phrase over the next few months, all using the version of the sentence starting with "A" rather than "The". The earliest known use of the phrase starting with "The" is from the 1888 bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroha
The is a Japanese poem. Originally the poem was attributed to the founder of the Shingon Esoteric sect of Buddhism in Japan, Kūkai, but more modern research has found the date of composition to be later in the Heian period (794–1179). The first record of its existence dates from 1079. It is famous because it is a perfect pangram, containing each character of the Japanese syllabary exactly once. Because of this, it is also used as an ordering for the syllabary, in the same way as the ''A'', ''B'', ''C'', ''D''... sequence of the Latin alphabet. Text The first appearance of the Iroha, in was in seven lines: six with seven morae each, and one with five. It was also written in man'yōgana. 以呂波耳本部止 千利奴流乎和加 餘多連曽津祢那 良牟有為能於久 耶万計不己衣天 阿佐伎喩女美之 恵比毛勢須 Structurally, however, the poem follows the standard 7–5 pattern of Japanese poetry (with one hypometric line), and in modern times it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font. There are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly. The art and craft of designing typefaces is called '' type design''. Designers of typefaces are called '' type designers'' and are often employed by '' type foundries''. In desktop publishing, type designers are sometimes also called ''font developers'' or ''font designers''. Every typeface is a collection of glyphs, each of which represents an individual letter, number, punctuation mark, or other symbol. The same glyph may be used for characters from different scripts, e.g. Roman uppercase A looks the same as Cyrillic uppercase А and Greek uppercase alpha. There are typefaces tailored for special applications, such as cartography, astrology or mathematics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylt
Sylt (; da, Sild; Söl'ring North Frisian: ) is an island in northern Germany, part of Nordfriesland district, Schleswig-Holstein, and well known for the distinctive shape of its shoreline. It belongs to the North Frisian Islands and is the largest island in North Frisia. The northernmost island of Germany, it is known for its tourist resorts, notably Westerland, Kampen and Wenningstedt-Braderup, as well as for its sandy beach. It is frequently covered by the media in connection with its exposed situation in the North Sea and its ongoing loss of land during storm tides. Since 1927, Sylt has been connected to the mainland by the Hindenburgdamm causeway. In later years, it has been a resort for the German jet set and tourists in search of occasional celebrity sightings. Geography With , Sylt is the fourth-largest German island and the largest German island in the North Sea. Sylt is located from off the mainland, to which it is connected by the Hindenburgdamm. Southeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javanese Script
The Javanese script (natively known as ''Aksara Jawa'', ''Hanacaraka'', ''Carakan'', and ''Dentawyanjana'') is one of Indonesia's traditional scripts developed on the island of Java. The script is primarily used to write the Javanese language, but in the course of its development has also been used to write several other regional languages such as Sundanese, Madurese, and Sasak; the lingua franca of the region, Malay; as well as the historical languages Kawi and Sanskrit. Javanese script was actively used by the Javanese people for writing day-to-day and literary texts from at least the mid-15th century CE until the mid-20th century CE, before its function was gradually supplanted by the Latin alphabet. Today the script is taught in DI Yogyakarta, Central Java, and the East Java Province as part of the local curriculum, but with very limited function in everyday use. The Javanese script is an abugida writing system which consists of 20 to 33 basic letters, dependi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syllable, and logographic systems use characters to represent words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first fully phonemic script, the Proto-Sinaitic script, later known as the Phoenician alphabet, is considered to be the first alphabet and is the ancestor of most modern alphabets, including Arabic, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Latin, and possibly Brahmic. It was created by Semitic-speaking workers and slaves in the Sinai Peninsula (as the Proto-Sinaitic script), by selecting a small number of hieroglyphs commonly seen in their Egyptian surroundings to describe the sounds, as opposed to the semantic values of the Canaanite languages. However, Peter T. Daniels distinguishes an abugida, a set of graphemes that represent cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaeresis (diacritic)
The diaeresis ( ; is a diacritical mark used to indicate the separation of two distinct vowels in adjacent syllables when an instance of diaeresis (or hiatus) occurs, so as to distinguish from a digraph or diphthong. It consists of two dots placed over a letter, generally a vowel; when that letter is an , the diacritic replaces the tittle: . The diaeresis diacritic indicates that two adjoining letters that would normally form a digraph and be pronounced as one sound, are instead to be read as separate vowels in two syllables. For example, in the spelling "coöperate", the diaeresis reminds the reader that the word has four syllables ''co-op-er-ate'', not three, ''*coop-er-ate''. In British English this usage has been considered obsolete for many years, and in US English, although it persisted for longer, it is now considered archaic as well. Nevertheless, it is still used by the US magazine ''The New Yorker''. In English language texts it is perhaps most familiar in the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorn (letter)
Thorn or þorn (Þ, þ) is a letter in the Old English, Old Norse, Old Swedish, and modern Icelandic alphabets, as well as modern transliterations of the Gothic alphabet, Middle Scots, and some dialects of Middle English. It was also used in medieval Scandinavia, but was later replaced with the digraph '' th,'' except in Iceland, where it survives. The letter originated from the rune in the Elder Fuþark and was called ''thorn'' in the Anglo-Saxon and ''thorn'' or '' thurs'' in the Scandinavian rune poems. It is similar in appearance to the archaic Greek letter sho (ϸ), although the two are historically unrelated. The only language þ is still currently in use in is Icelandic. It is pronounced as either a voiceless dental fricative or its voiced counterpart . However, in modern Icelandic, it is pronounced as a laminal voiceless alveolar non-sibilant fricative ,, cited in similar to ''th'' as in the English word ''thick'', or a (usually apical) voiced alveolar non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s , also known as the medial s or initial s, is an archaic form of the lowercase letter . It replaced the single ''s'', or one or both of the letters ''s'' in a 'double ''s''' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess"—but never *"poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the 'short', 'terminal', or 'round' s. In typography, it is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash s". The long s is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet ligature letter , ('' eszett'' or harp s. Rules This list of rules for the long s is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th and 18th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar rules exist for other European languages. * A round s is always used at the end of a word ending with s: "his", "complains", "ſucceſs" ** However, long s is maintained in abbreviations such as "ſ." for "ſubſtantiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Alphabet
The Turkish alphabet ( tr, ) is a Latin-script alphabet used for writing the Turkish language, consisting of 29 letters, seven of which ( Ç, Ğ, I, İ, Ö, Ş and Ü) have been modified from their Latin originals for the phonetic requirements of the language. This alphabet represents modern Turkish pronunciation with a high degree of accuracy and specificity. Mandated in 1928 as part of Atatürk's Reforms, it is the current official alphabet and the latest in a series of distinct alphabets used in different eras. The alphabet was created by Agop Dilâçar (Martayan) ( hy, ) a linguist of Armenian origin. The Turkish alphabet has been the model for the official Latinization of several Turkic languages formerly written in the Arabic or Cyrillic script like Azerbaijani (1991), Turkmen (1993), and recently Kazakh (2021). History Early reform proposals and alternate scripts The earliest known Turkic alphabet is the Orkhon script, also known as the Old Turkic alphabet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logogram
In a written language, a logogram, logograph, or lexigraph is a written character that represents a word or morpheme. Chinese characters (pronounced ''hanzi'' in Mandarin, ''kanji'' in Japanese, ''hanja'' in Korean) are generally logograms, as are many hieroglyphic and cuneiform characters. The use of logograms in writing is called ''logography'', and a writing system that is based on logograms is called a ''logography'' or ''logographic system''. All known logographies have some phonetic component, generally based on the rebus principle. Alphabets and syllabaries are distinct from logographies in that they use individual written characters to represent sounds directly. Such characters are called ''phonograms'' in linguistics. Unlike logograms, phonograms do not have any inherent meaning. Writing language in this way is called ''phonemic writing'' or ''orthographic writing''. Etymology Doulgas Harper's Online Etymology Dictionary states that the term 'logogram' was derived from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)