|
Panel Fiducial
A fiducial marker or fiducial is an object placed in the field of view of an imaging system that appears in the image produced, for use as a point of reference or a measure. It may be either something placed into or on the imaging subject, or a mark or set of marks in the reticle of an optical instrument. Applications Microscopy In high-resolution optical microscopy, fiducials can be used to actively stabilize the field of view. Stabilization to better than 0.1 nm is achievable. Physics In physics, 3D computer graphics, and photography, fiducials are reference points: fixed points or lines within a scene to which other objects can be related or against which objects can be measured. Cameras outfitted with Réseau plates produce these reference marks (also called Réseau crosses) and are commonly used by NASA. Such marks are closely related to the timing marks used in optical mark recognition. Geographical survey Airborne geophysics, geophysical surveys also use the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
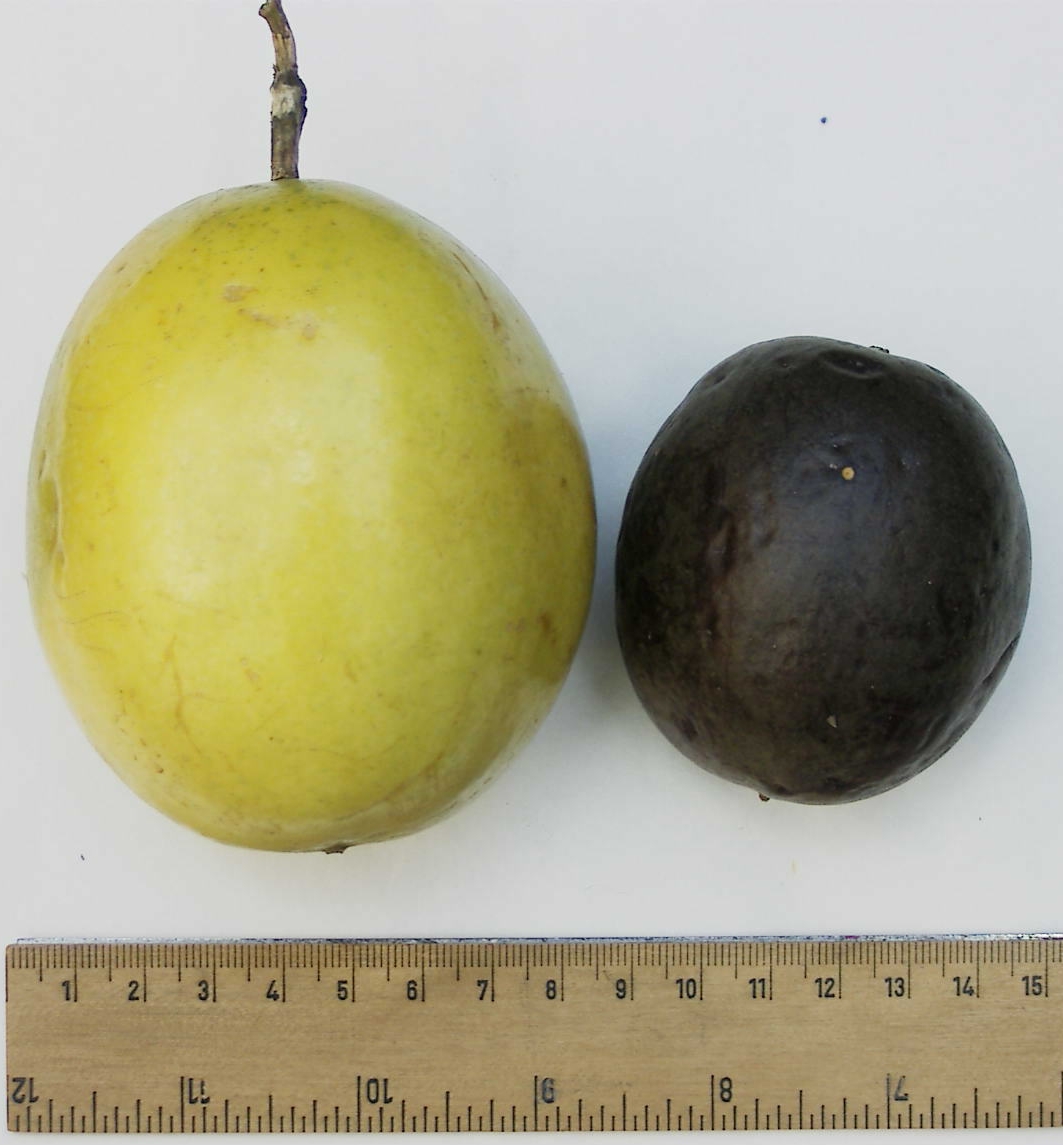
Passionfruit Comparison
''Passiflora edulis,'' commonly known as passion fruit, is a vine species of passion flower native to southern Brazil through Paraguay and northern Argentina. It is cultivated commercially in tropical and subtropical areas for its sweet, seedy fruit. The fruit is a pepo, a type of berry, round to oval, either yellow or dark purple at maturity, with a soft to firm, juicy interior filled with numerous seeds. The fruit is both eaten and juiced, the juice often added to other fruit juices to enhance aroma. Etymology The passion fruit is so called because it is one of the many species of passion flower, the English translation of the Latin genus name, ''Passiflora''. Around 1700, the name was given by missionaries in Brazil as an educational aid while trying to convert the indigenous inhabitants to Christianity; its name was ''flor das cinco chagas'' or "flower of the five wounds" to illustrate the crucifixion of Christ, with other plant components also named after an emblem in the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popup Book
The term pop-up book is often applied to any book with three-dimensional pages, although it is properly the umbrella term for movable book, pop-ups, tunnel books, transformations, volvelles, flaps, pull-tabs, pop-outs, pull-downs, and more, each of which performs in a different manner. Three-dimensional greeting cards use the same principles. Interactive and pop-up types Design and creation of such books in arts is sometimes called "paper engineering". This usage should not be confused with traditional paper engineering, the engineering of systems to mass-produce paper products. The artistic aspect of paper engineering is related to origami in that the two arts both employ folded paper. However, origami in its simplest form doesn't use scissors or glue and tends to be made with very foldable paper; by contrast, pop-ups rely more on glue, cutting, and stiff card stock. What they have in common is folding. Animated books Animated books combine three elements: story, colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
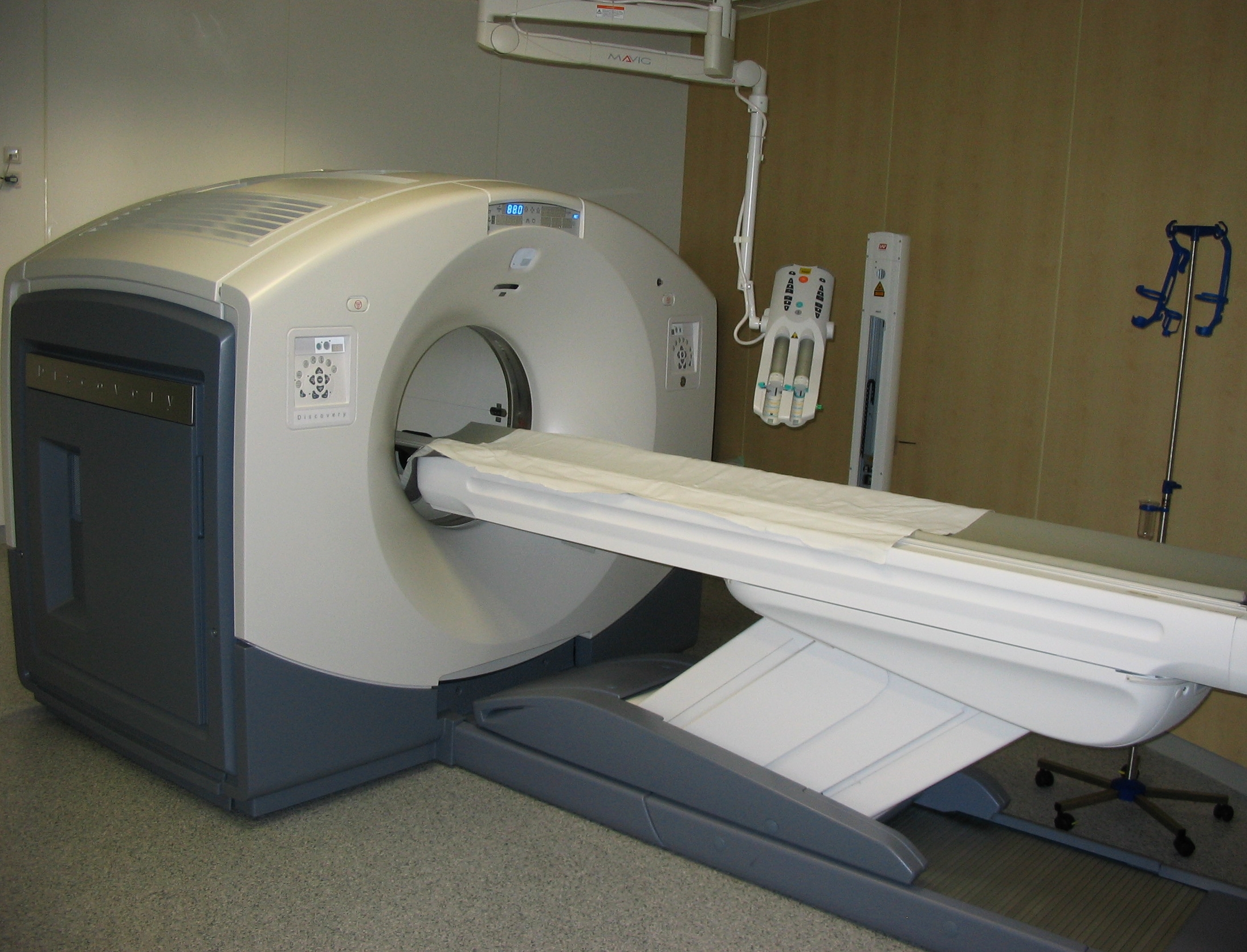
Computed Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetoencephalography
Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a functional neuroimaging technique for mapping brain activity by recording magnetic fields produced by electrical currents occurring naturally in the brain, using very sensitive magnetometers. Arrays of SQUIDs (superconducting quantum interference devices) are currently the most common magnetometer, while the SERF (spin exchange relaxation-free) magnetometer is being investigated for future machines. Applications of MEG include basic research into perceptual and cognitive brain processes, localizing regions affected by pathology before surgical removal, determining the function of various parts of the brain, and neurofeedback. This can be applied in a clinical setting to find locations of abnormalities as well as in an experimental setting to simply measure brain activity. History MEG signals were first measured by University of Illinois physicist David Cohen in 1968, before the availability of the SQUID, using a copper induction coil as the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18F-FDG, -FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, Sodium fluoride#Medical imaging, NaF is widely used for detecting bone formation, and Isotopes of oxygen#Oxygen-15, oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common medical imaging, imaging technique, a Scintigraphy#Process, medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical, radiopharmaceutical — a radioisotope attached to a drug — is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPECT
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, scintigraphy), but is able to provide true 3D information. This information is typically presented as cross-sectional slices through the patient, but can be freely reformatted or manipulated as required. The technique needs delivery of a gamma-emitting radioisotope (a radionuclide) into the patient, normally through injection into the bloodstream. On occasion, the radioisotope is a simple soluble dissolved ion, such as an isotope of gallium(III). Most of the time, though, a marker radioisotope is attached to a specific ligand to create a radioligand, whose properties bind it to certain types of tissues. This marriage allows the combination of ligand and radiopharmaceutical to be carried and bound to a place of interest in the body, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain data about the measurement loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers, of which there are several types. Later, two-dimensional (2D) variants were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons and other patterns, called ''matrix codes'' or ''2D barcodes'', although they do not use bars as such. 2D barcodes can be read using purpose-built 2D optical scanners, which exist in a few different forms. 2D barcodes can also be read by a digital camera connected to a microcomputer running software that takes a photographic image of the barcode and analyzes the image to deconstruct and decode the 2D barcode. A mobile device with an inbuilt camera, such as smartphone, can function as the latter type of 2D barcode reader using special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QR Code For Mobile English Wikipedia
QR may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Nippon Cultural Broadcasting (from call sign JOQR), a Tokyo radio station * Queen's Radio, a student radio station at Queen's University Belfast * Quiet Riot, an American rock band Businesses * Qatar Airways (IATA code) * Queensland Rail, a company responsible for the railway system in Queensland, Australia * Quintana Roo (company), a triathlon-specific wetsuit and bicycle company Places * Quintana Roo, a state of Mexico * Karakalpakstan (Qoraqalpog'iston Respublikasi), Uzbekistan (ISO 3166-2 subcode UZ-QR) Science and technology * QR code (Quick Response code), a two-dimensional code * ATCvet code QR ''Respiratory system'', a section of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System for veterinary medicinal products * DICOM Q/R, DICOM Query / Retrieve * Nissan QR engine Mathematics * QR decomposition, a decomposition of a matrix * QR algorithm, an eigenvalue algorithm using QR decomposition * Quadratic reciprocity, a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collimation
A collimated beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation has parallel rays, and therefore will spread minimally as it propagates. A perfectly collimated light beam, with no divergence, would not disperse with distance. However, diffraction prevents the creation of any such beam. Light can be approximately collimated by a number of processes, for instance by means of a collimator. Perfectly collimated light is sometimes said to be ''focused at infinity''. Thus, as the distance from a point source increases, the spherical wavefronts become flatter and closer to plane waves, which are perfectly collimated. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation can also be collimated. In radiology, X-rays are collimated to reduce the volume of the patient's tissue that is irradiated, and to remove stray photons that reduce the quality of the x-ray image ("film fog"). In scintigraphy, a gamma ray collimator is used in front of a detector to allow only photons perpendicular to the surface to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is the science and technology of obtaining reliable information about physical objects and the environment through the process of recording, measuring and interpreting photographic images and patterns of electromagnetic radiant imagery and other phenomena. The term photogrammetry was coined by the Prussian architect Albrecht Meydenbauer, which appeared in his 1867 article "Die Photometrographie." There are many variants of photogrammetry. One example is the extraction of three-dimensional measurements from two-dimensional data (i.e. images); for example, the distance between two points that lie on a plane parallel to the photographic image plane can be determined by measuring their distance on the image, if the scale (map), scale of the image is known. Another is the extraction of accurate color ranges and values representing such quantities as albedo, specular reflection, Metallicity#Photometric colors, metallicity, or ambient occlusion from photographs of mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)