|
Pandanus Tectorius
''Pandanus tectorius'' is a species of ''Pandanus'' (screwpine) that is native to Malesia, Papuasia, eastern Australia, and the Pacific Islands. It grows in the coastal lowlands typically near the edge of the ocean. Common names in English include thatch screwpine, Tahitian screwpine, hala tree ( in Hawaiian) and pandanus. The edible fruit is sometimes known as hala fruit. Description ''P. tectorius'' is a small tree that grows upright to reach in height. The single trunk is slender with brown ringed bark. It is spiny, grows to 4.5–11 m (15–35 ft) in width, and forks at a height of . It is supported by aerial roots (prop roots) that firmly anchors the tree to the ground. Roots sometimes grow along the branch, and they grow at wide angles in proportion to the trunk. 林投 20190525170309.jpg, Growth habit 林投 20190530190950.jpg, Aerial roots 林投帶刺氣生根與新葉 20190525170359.jpg, Spiny aerial roots and leaflets Pandanus tectorius fruit.jpg, Fruit showin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
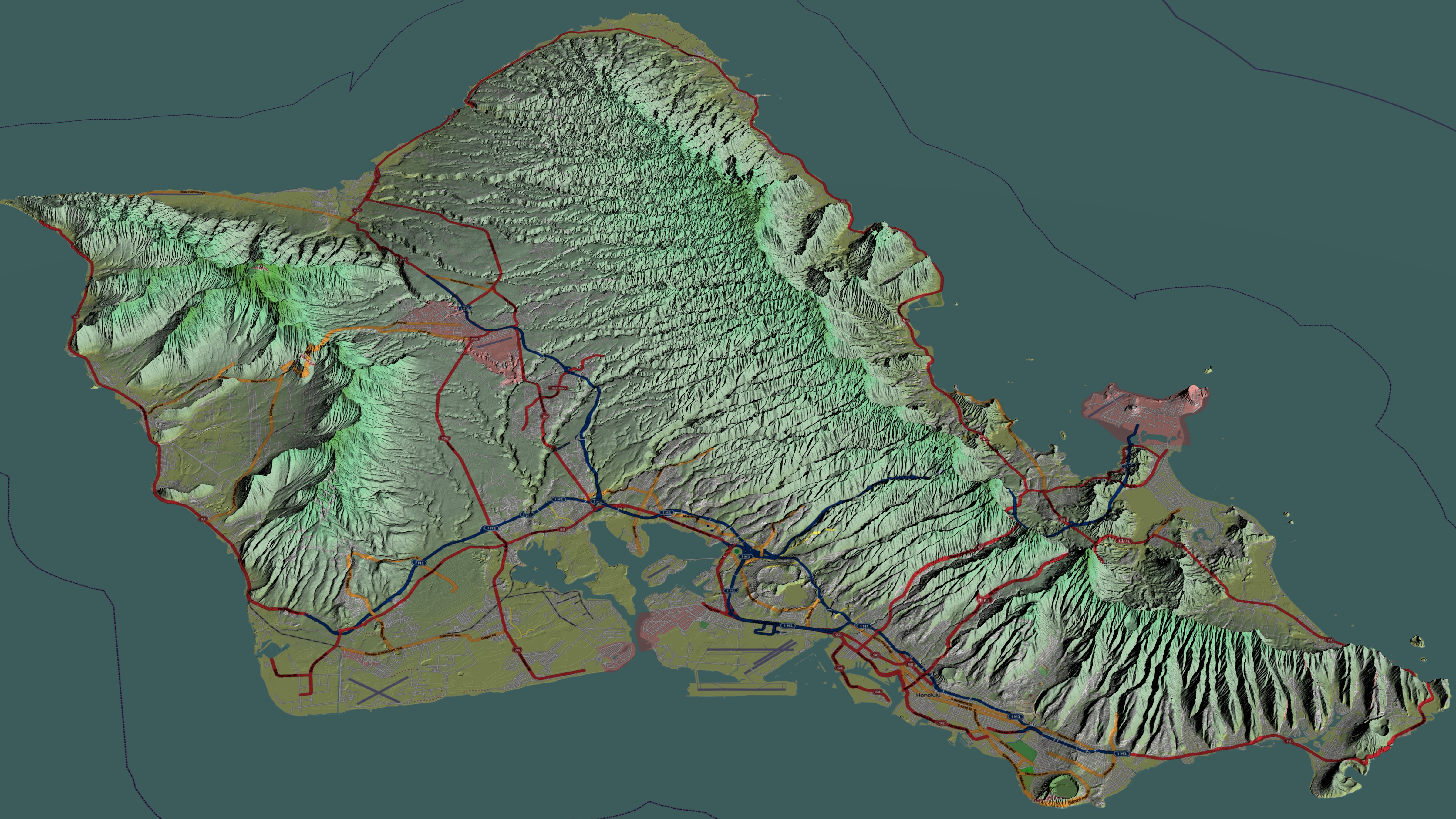
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian islands, Hawaiian Island, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aroma Compound
An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently volatile for transmission via the air to the olfactory system in the upper part of the nose. As examples, various fragrant fruits have diverse aroma compounds, particularly strawberries which are commercially cultivated to have appealing aromas, and contain several hundred aroma compounds. Generally, molecules meeting this specification have molecular weights of less than 310. Flavors affect both the sense of taste and smell, whereas fragrances affect only smell. Flavors tend to be naturally occurring, and the term ''fragrances'' may also apply to synthetic compounds, such as those used in cosmetics. Aroma compounds can naturally be found in various foods, such as fruits and their peels, wine, spices, floral scent, perfumes, fragrance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ancestor of all living gymnosperms before the end of the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. The closest fossil relatives of flowering plants are uncertain and contentious. The earliest angiosperm fossils ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (adaxial) and lower ( abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other areas at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Seed
__NOTOC__ Drift seeds (also sea beans) and drift fruits are seeds and fruits adapted for long-distance dispersal by water. Most are produced by tropical trees, and they can be found on distant beaches after drifting thousands of miles through ocean currents. This method of propagation has helped many species of plant such as the coconut colonize and establish themselves on previously barren islands. Consequently, drift seeds and fruits are of interest to scientists who study these currents. In botanical terminology, a drift fruit is a kind of diaspore, and drift seeds and fruits are disseminules. Sources of drift seeds * ''Caesalpinia bonduc'' – grey nickernut * ''Caesalpinia major'' – yellow nickernut * '' Carapa guianensis'' – crabwood (New World tropics) * '' Entada gigas'' – seaheart, (New World tropics) * ''Entada rheedii'' – snuff box sea bean, from the tropics of the Indian Ocean * ''Erythrina fusca'' – bucayo (pantropical) * ''Erythrina variegata'' – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
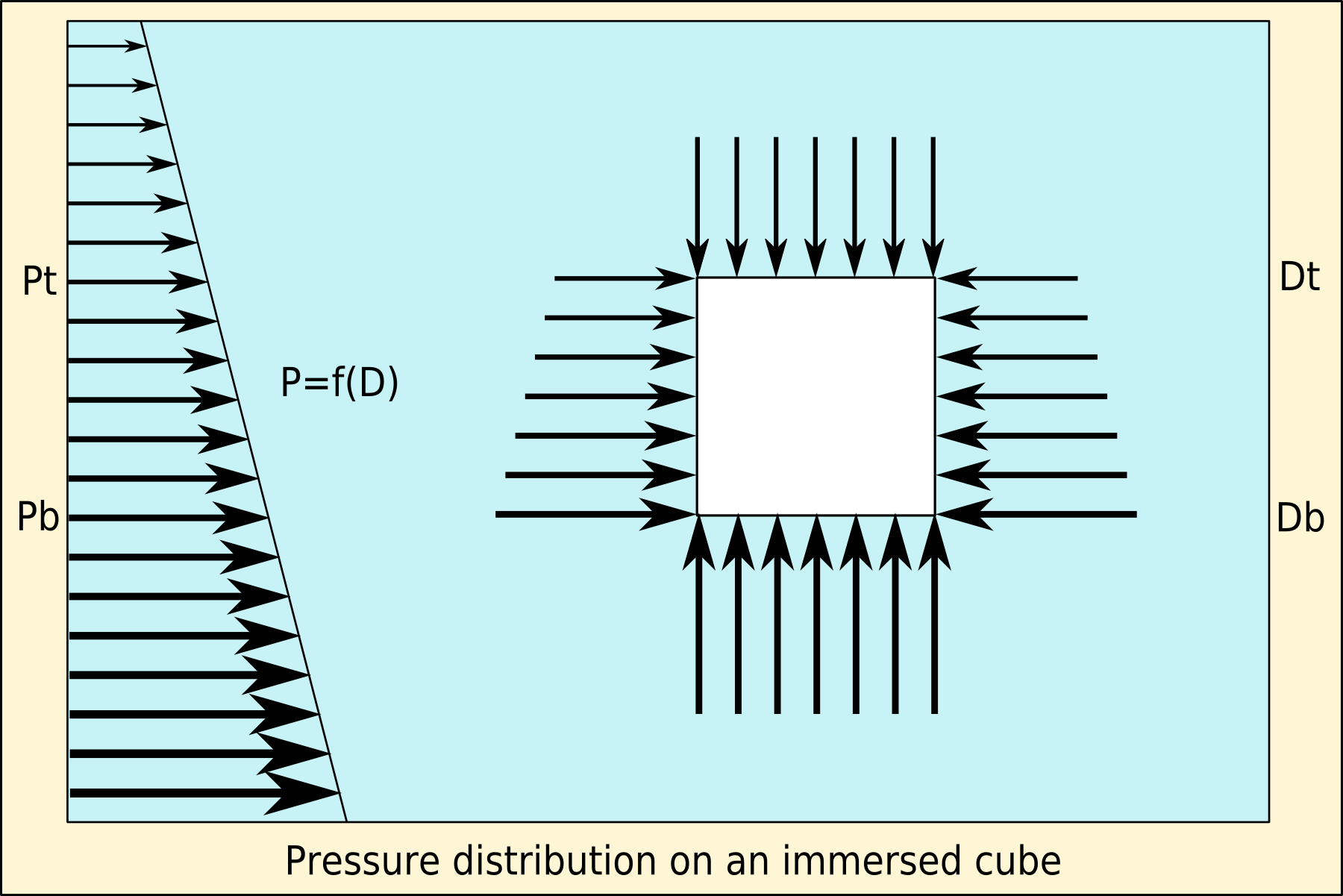
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote, and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The seed coat arises from the integuments of the ovule. Seeds have been an important development in the reproduction and success of vegetable gymnosperm and angiosperm plants, relative to more primitive plants such as ferns, mosses and liverworts, which do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. The term "seed" also has a general me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husk
Husk (or hull) in botany is the outer shell or coating of a seed. In the United States, the term husk often refers to the leafy outer covering of an ear of maize (corn) as it grows on the plant. Literally, a husk or hull includes the protective outer covering of a seed, fruit, or vegetable. It can also refer to the exuvia of insects or other small animals left behind after moulting. In cooking, hull can also refer to other waste parts of fruits and vegetables, notably the cap or sepal of a strawberry. The husk of a legume and some similar fruits is called a pod. Husking and dehulling Husking of corn is the process of removing its outer layers, leaving only the cob or seed rack of the corn. Dehulling is the process of removing the hulls (or chaff) from beans and other seeds. This is sometimes done using a machine known as a huller. To prepare the seeds to have oils extracted from them, they are cleaned to remove any foreign objects. Next, the seeds have their hulls, or oute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynoecium
Gynoecium (; ) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl of a flower; it consists of (one or more) ''pistils'' and is typically surrounded by the pollen-producing reproductive organs, the stamens, collectively called the androecium. The gynoecium is often referred to as the "female" portion of the flower, although rather than directly producing female gametes (i.e. egg cells), the gynoecium produces megaspores, each of which develops into a female gametophyte which then produces egg cells. The term gynoecium is also used by botanists to refer to a cluster of archegonia and any associated modified leaves or stems present on a gametophyte shoot in mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. The corresponding terms for the male parts of those plants are clusters of antheridia within the androecium. Flowers that bear a gynoecium but no stamens are called ''pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)