|
Pancreas Divisum
Pancreatic divisum is a congenital anomaly in the anatomy of the ducts of the pancreas in which a single pancreatic duct is not formed, but rather remains as two distinct dorsal and ventral ducts. Most individuals with pancreas divisum remain without symptoms or complications. A minority of people with pancreatic divisum may develop episodes of abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting due to acute or chronic pancreatitis. The presence of pancreas divisum is usually identified with cross sectional diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or computed tomography (CT) imaging. In some cases, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is performed, revealing the diagnosis of pancreas divisum. If no symptoms or complications are present, then treatment is not necessary. However, if there is recurrent pancreatitis, then a sphincterotomy of the minor papilla may be indicated. Causes The human embryo begins life with two ducts in the pancreas, the ventral duct and the dorsal duct. Normall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function (biology), function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic research, basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic scale, macroscopic and microscopic scale, microscopic. Gross anatomy, Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a medical imaging technique. It uses magnetic resonance imaging to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts non-invasively. This procedure can be used to determine whether gallstones are lodged in any of the ducts surrounding the gallbladder. Uses MRCP has been slowly replacing endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) as investigation of choice. MRCP is highly accurate in diagnosing the biliary system, pancreatic duct and accessing surrounding solid organs. Several advantages offered by MRCP is its non-invasive nature, less costly, requires less examination time when compared to ERCP (30 minutes), fewer staff required, and does not require any ionising radiation. MRCP is used to diagnose gallstones. It can also diagnose choledochal cysts very reliably. Besides providing information regarding the biliary system, MRCP also provides information regarding surrounding solid organs and blood vessels, thus useful for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the Human nose, nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like Food-poisoning, food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to Alcoholic drink, alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit, leading to suffocation. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia nervosa, bulimia, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word nausea is from Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ... associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy. In a third of cases the exact cause is unclear. Given that a variety of diseases can cause some form of abdominal pain, a systematic approach to the examination of a person and the formulation of a differential diagnosis remains important. Differential diagnosis The most frequent reasons for abdominal pain are gastroenteritis (13%), irritable bowel syndr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestive Enzyme
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals (including humans) and in the tracts of carnivorous plants, where they aid in the digestion of food, as well as inside cells, especially in their lysosomes, where they function to maintain cellular survival. Digestive enzymes of diverse specificities are found in the saliva secreted by the salivary glands, in the secretions of cells lining the stomach, in the pancreatic juice secreted by pancreatic exocrine cells, and in the secretions of cells lining the small and large intestines. Digestive enzymes are classified based on their target substrates: * Lipases split fatty acids into fats and oils. *Proteases and peptidases split proteins into small peptides and amino acids. *Amylases split carbohydrates such as starch and sugars into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphincterotomy
Anal sphincterotomy is a surgical procedure that involves treating mucosal fissures from the anal canal/sphincter. The word is formed from sphincter + otomy (to cut, to separate). Procedure # The surgery can be performed under any kind of anesthesia. # After anesthesia is administered, the area is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. # The sphincter is separated either by simply stretching or cutting. Cutting the muscle prevents spasm and temporarily weakens the muscles. Both methods help the underlying area to heal. # Remove the fissure and any underlying scar tissue. # Suture back the wound. See also * Lateral internal sphincterotomy * List of surgeries by type Many surgical procedure names can be broken into parts to indicate the meaning. For example, in gastrectomy, "ectomy" is a suffix meaning the removal of a part of the body. "Gastro-" means stomach. Thus, ''gastrectomy'' refers to the surgical remo ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Anal Sphincterotomy Digestive system su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skilled and specialty trained gastroenterologists. Through the endoscope, the physician can see the inside of the stomach and duodenum, and inject a contrast medium into the ducts in the biliary tree and pancreas so they can be seen on radiographs. ERCP is used primarily to diagnose and treat conditions of the bile ducts and main pancreatic duct, including gallstones, inflammatory strictures (scars), leaks (from trauma and surgery), and cancer. ERCP can be performed for diagnostic and therapeutic reasons, although the development of safer and relatively non-invasive investigations such as magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) and endoscopic ultrasound has meant that ERCP is now rarely performed without therapeutic intent. Medical u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
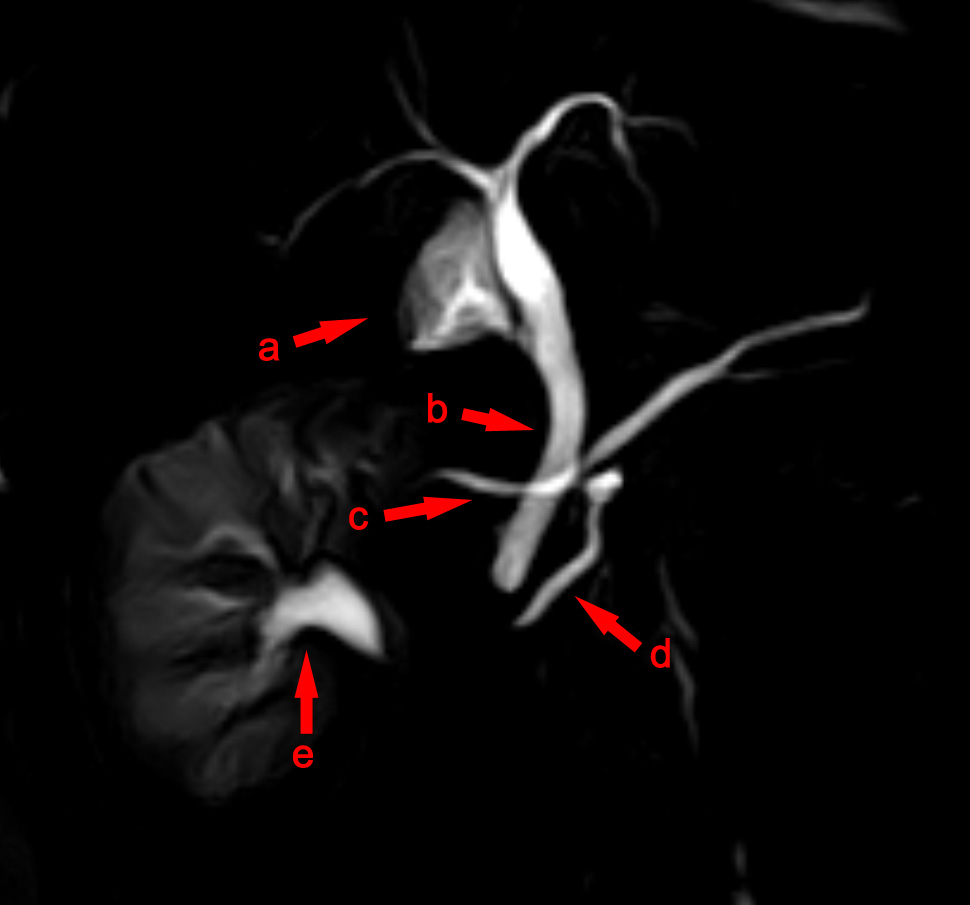
MRCP Pankreas Divisum
MRCP may be: * Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, in medical imaging, a technique to visualise the biliary tract and pancreatic ducts. * Membership of the Royal Colleges of Physicians of the United Kingdom, a postgraduate medical diploma run by the Federation of the Medical Royal Colleges of the United Kingdom * Media Resource Control Protocol, in computer systems, a communication protocol used by speech servers to provide various speech services * Master of Regional and City Planning, a variant of Master of Urban Planning * Movement Related Cortical Potentials - an activity in the motor cortex and supplementary motor area of the brain leading up to voluntary muscle movement {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Duodenal Papilla
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators, major is one rank above captain, and one rank below lieutenant colonel. It is considered the most junior of the field officer ranks. Background Majors are typically assigned as specialised executive or operations officers for battalion-sized units of 300 to 1,200 soldiers while in some nations, like Germany, majors are often in command of a company. When used in hyphenated or combined fashion, the term can also imply seniority at other levels of rank, including ''general-major'' or ''major general'', denoting a low-level general officer, and ''sergeant major'', denoting the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) of a military unit. The term ''major'' can also be used with a hyphen to denote the leader of a military band such as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |