|
Palladium On Carbon
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used as a catalyst. The metal is supported on activated carbon to maximize its surface area and activity. Uses Hydrogenation Palladium on carbon is used for catalytic hydrogenations in organic synthesis. Examples include reductive amination, carbonyl reduction, nitro compound reduction, the reduction of imines and Schiff bases and debenzylation reactions. Hydrogenolysis Palladium on carbon is a common catalyst for hydrogenolysis. Such reactions are helpful in deprotection strategies. Particularly common substrate for hydrogenolysis are benzyl ethers: *: Other labile substituents are also susceptible to cleavage by this reagent. Coupling reactions Palladium on carbon is also used for coupling reactions. Examples include the Suzuki reaction and Stille reaction. Preparation A solution of palladium chloride and hydrochloric acid is combined with aqueous suspension of activated carbon. The palladium(II) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urushibara Nickel
Urushibara nickel is a nickel based hydrogenation catalyst, named after Yoshiyuki Urushibara. History It was discovered by Yoshiyuki Urushibara in 1951, while doing research on the reduction of estrone to estradiol. Preparation First nickel is precipitated in metallic form by reacting a solution of a nickel salt with an excess of zinc. This precipitated nickel contains relatively large amounts of zinc and zinc oxide. Then the catalyst is activated by digesting with either base or acid. There are different designations for differently prepared Urushibara nickel catalysts. The most common is U-Ni-A and U-Ni-B. U-Ni-A is prepared by digesting the precipitated nickel with an acid such as acetic acid. U-Ni-B is prepared by digesting with a base such as sodium hydroxide. After the digestion with acid most of the zinc and zinc oxide is dissolved from the catalyst, while after digestion with base it still contains considerable amounts of zinc and zinc oxide. It is also possible to prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
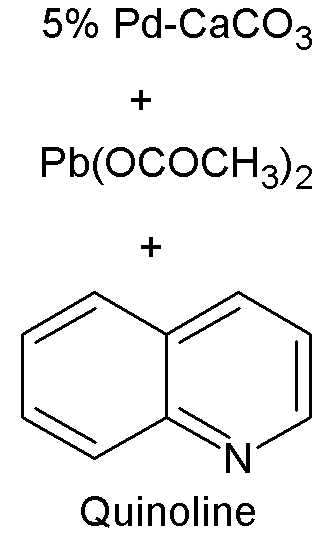
Lindlar Catalyst
A Lindlar catalyst is a heterogeneous catalyst that consists of palladium deposited on calcium carbonate or barium sulfate which is then poisoned with various forms of lead or sulfur. It is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes) and is named after its inventor Herbert Lindlar. Synthesis Lindlar catalyst is commercially available but may also be prepared by the reduction of palladium chloride in a slurry of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) followed by the addition of lead acetate. A variety of other "catalyst poisons" have been used, including lead oxide and quinoline. The palladium content of the supported catalyst is usually 5% by weight. Catalytic properties The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes to alkenes (i.e. without further reduction into alkanes). The lead serves to deactivate the palladium sites, further deactivation of the catalyst with quinoline or 3,6-dithia-1,8-octanediol enhances its selectivity, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodium-platinum Oxide
Rhodium-platinum oxide (Rh–Pt oxide), or Nishimura's catalyst, is an inorganic compound used as a hydrogenation catalyst. Uses Rh–Pt oxide is used to reduce various aromatic compounds to their respective cycloalkanes or saturated heterocycles under mild conditions (i.e. often at room temperature and atmospheric pressure). In this application, Rh–Pt oxide is superior to other group 10 catalysts such as platinum dioxide. Furthermore, the catalyst can be used to carryout the reaction with minimal losses of oxygen containing functional groups via hydrogenolysis. Preparation An aqueous solution of rhodium chloride, chloroplatinic acid, and sodium nitrate is evaporated and then fused in a porcelain dish between 460-480°C until the oxides of nitrogen cease (≈10 minutes). The resulting solidified mass is then washed with distilled water and dilute sodium nitrate followed by drying with calcium chloride to yield the catalyst. Typically the ratio of metals used for the cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum Dioxide
Adams' catalyst, also known as platinum dioxide, is usually represented as platinum(IV) oxide hydrate, PtO2•H2O. It is a catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis in organic synthesis. This dark brown powder is commercially available. The oxide itself is not an active catalyst, but it becomes active after exposure to hydrogen whereupon it converts to platinum black, which is responsible for reactions. Preparation Adams' catalyst is prepared from chloroplatinic acid H2PtCl6 or ammonium chloroplatinate, (NH4)2PtCl6, by fusion with sodium nitrate. The first published preparation was reported by V. Voorhees and Roger Adams. The procedure involves first preparing a platinum nitrate which is then heated to expel nitrogen oxides. :H2PtCl6 + 6 NaNO3 → Pt(NO3)4 + 6 NaCl (aq) + 2 HNO3 :Pt(NO3)4 → PtO2 + 4 NO2 + O2 The resulting brown cake is washed with water to free it from nitrates. The catalyst can either be used as is or dried and stored in a desiccator for later use. Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platinum On Carbon
Platinum on carbon, often referred to as Pt/C, is a form of platinum used as a catalyst. The metal is supported on activated carbon in order to maximize its surface area and activity. Uses Catalytic hydrogenation Platinum on carbon is used for catalytic hydrogenations in organic synthesis. Examples include carbonyl reduction, nitro compound reduction, secondary amine production via nitrile reduction, and the production of saturated heterocycles from their respective aromatic compound precursors. Preparation An aqueous solution of activated carbon and chloroplatinic acid is heated on a water bath for a few hours at 50°C, and after cooling, the solution is then made alkaline using sodium carbonate. The chloroplatinic acid is then reduced with hydrazine hydrate; however, this step is sometimes omitted in other preparations. After additional 2 hours of warming, the solution is filtered, washed with distilled water, and dried over calcium chloride to yield the catalyst. Platinum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium Black
Palladium black is a coarse, sponge-like form of elemental palladium which offers a large surface area for catalytic activity. It is used in organic synthesis as a catalyst for hydrogenation reactions. The term palladium black is also used colloquially to refer to a black precipitate of elemental palladium, which forms via decomposition of various palladium complexes. Preparation Palladium black is typically prepared from palladium(II) chloride or palladium(II)-ammonium chloride. The palladium chloride process entails the formation of palladium hydroxide using lithium hydroxide followed by reduction under hydrogen gas while the palladium(II)-ammonium chloride route employs a solution of formic acid followed by the precipitation of the catalyst using potassium hydroxide. See also *Platinum black *Platinum dioxide *Platinum on carbon *Palladium on carbon *Rhodium-platinum oxide Rhodium-platinum oxide (Rh–Pt oxide), or Nishimura's catalyst, is an inorganic compound used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, or sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. (See also Solvent and Inorganic nonaqueous solvent.) Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are ''hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium Chloride
Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures. Structure Two forms of PdCl2 are known, denoted α and β. In both forms, the palladium centres adopt a square-planar coordination geometry that is characteristic of Pd(II). Furthermore, in both forms, the Pd(II) centers are linked by μ2-chloride bridges. The α-form of PdCl2 is a polymer, consisting of "infinite" slabs or chains. The β-form of PdCl2 is molecular, consisting of an octahedral cluster of six Pd atoms. Each of the twelve edges of this octahedron is spanned by Cl−. PtCl2 adopts similar structures, whereas NiCl2 adopts the CdCl2 motif, featuring hexacoordinated Ni(II). Two further polymorphs, γ-PdCl2 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-chloride-xtal-3D-balls.png)