|
Palistin
Palistin (or Walistin), was an early Syro-Hittite kingdom located in what is now northwestern Syria and the southeastern Turkish province of Hatay. Its existence was confirmed by the discovery of several inscriptions mentioning Taita, king of Palistin. History Palistin was one of the Syro-Hittite states that emerged in Syria after the Late Bronze Age collapse. OUP Oxford, 2012 It dates to at least the 11th century BC and is known primarily through the inscriptions of its king Taita and his wife. The kingdom emerged some time soon after the collapse of the Hittite Empire, of which it is one of the successor states, and it encompassed a relatively extensive area, stretching at least from the Amouq Valley in the west, to Aleppo in the east, down to Mhardeh and Shaizar in the south. Prof. Itamar Singer proposes that it was the predecessor state that, once it disintegrated, gave birth to the kingdoms of Hamath, Bit Agusi and Pattin (shortened form of Palistin).''Before and After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.. The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called (accepted as cognate with Hebrew ); the parallel Assyrian term is , , or . Etymology The English term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Tayinat
Tell Ta'yinat is a low-lying ancient tell on the east bank at the bend of the Orontes River where it flows through the Amuq valley, in the Hatay province of southeastern Turkey about 25 kilometers south east of Antakya (ancient Antioch), and lies near Tell Atchana, the site of the ancient city of Alalakh. Tell Ta'yinat has been proposed as the site of Alalaḫu, inhabited in late 3rd millennium BC, mentioned in Ebla's Palace G archive; and in later times as Kinalua, the capital city of an Iron Age Neo-Hittite kingdom. Identification Archaeologist Timothy Harrison, the dig director for many years starting in 2004, supports the identification of the site with Kinalua, the capital of a Neo-Hittite/Aramean Iron Age kingdom. In the period of Neo-Assyrian control it was the center of the Unqi province. It is a possible site of the city of Calneh mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Archaeology The site consists of an upper mound of about 20 hectares and a lower mound (now under floodpla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black". , motto = , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Asia#Syria Aleppo , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_relief = yes , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Aleppo in Syria , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_type3 = Subdistrict , subdivision_name1 = Aleppo Governorate , subdivision_name2 = Mount Simeon (Jabal Semaan) , subdivision_name3 = Mount Simeon ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
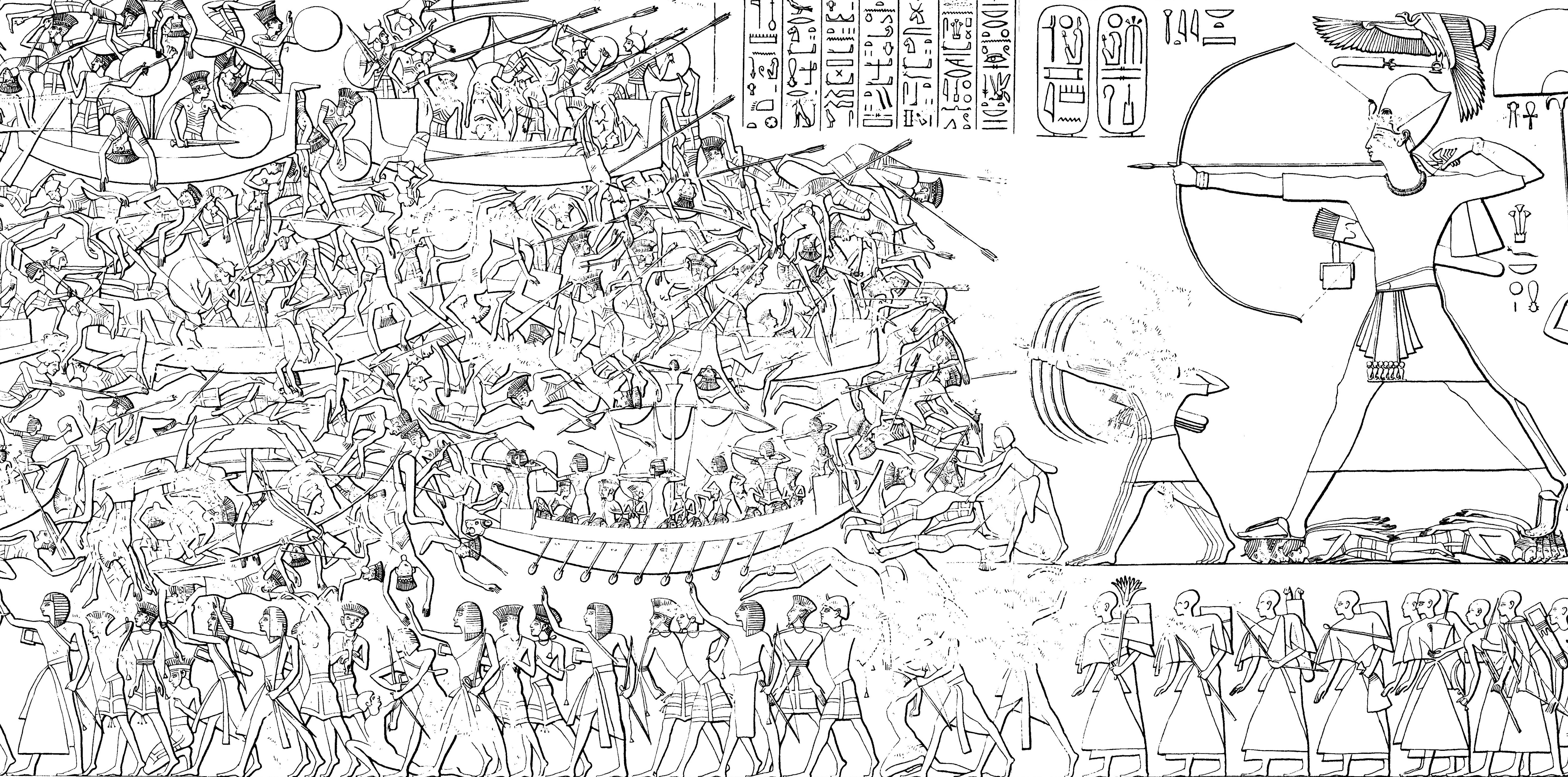
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syro-Hittite States
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwians, Luwian and Arameans, Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of modern Syria, known in ancient times as lands of Hatti (region), Hatti and Aram (region), Aram. They arose following the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom in the 12th century BCE, and lasted until they were subdued by the Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BCE. They are grouped together by scholars, on the basis of several cultural criteria, that are recognized as similar and mutually shared between both societies, northern (Luwian) and southern (Aramean). Cultural exchange between those societies is seen as a specific regional phenomena, particularly in light of significant linguistic distinctions between two main regional languages, with Luwian language, Luwian belonging to the Anatolian languages, Anatolian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatay
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province of Adana to the northwest, Osmaniye to the north, and Gaziantep to the northeast. It is partially in Çukurova, a large fertile plain along Cilicia. Its administrative capital is Antakya, making it the only Turkish province not named after its administrative capital or any settlement. Sovereignty over most of the province remains disputed with neighbouring Syria, which claims that the province had a demographic Arab majority, and was separated from itself against the stipulations of the French Mandate of Syria in the years following Syria's occupation by France after World War I. History Antiquity Settled since the early Bronze Age, Hatay was once part of the Akkadian Empire, then of the Amorite Kingdom of Yamhad. Later, it became par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taita I
Taita may refer to: * Taita people, a Bantu ethnic group in Kenya * Taita language, a Bantu language *Taitā, New Zealand, a suburb of Lower Hutt City * Taita Hills, a mountain range in Kenya * Taita Cushitic languages, an extinct pair of Afro-Asiatic languages spoken in the Taita Hills * Taita falcon, a small falcon found in central and eastern Africa * Taita Line, a railway line in Gifu prefecture, Japan * Taița, a tributary of Lake Babadag in Romania * Taița, a former village in Hamcearca Commune, Romania * Taita I, king of ancient Palistin * Taita, another name for the leavened flatbread injera popular in Ethiopia and Eritrea * Taita, a fictional character from The Egyptian Series, beginning with the novel '' River God'', by Wilbur Smith * Taita, another name for a yage shaman in Colombia. See also * * National Taiwan University National Taiwan University (NTU; ) is a public research university in Taipei, Taiwan. The university was founded in 1928 during Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattin
Pattin (also known as Pattina, Patina, Unqu and Unqi), was an ancient Luwian Syro-Hittite state at the beginning of the 1st millennium BC. It was known to the Assyrians as Unqi and Aramaeans as Unqu. It was located at the north-western coast of ancient Syria, associated with the modern-day Sanjak of Alexandretta. The capital of the state was Kinalua (Kunalua, Kalneh, or Kinaluwa), which has been tentatively associated with Tell Tayinat in modern-day Turkey. The state was formed in the 9th century BC towards the end of the Dark Age period, and shared a north-western border with the Syro-Hittite state of Quwê. Khazazu (modern-day Azaz) was one of Pattin's dependencies which was invaded by Assyria around 870 BC. The frontier fortress of ''Aribua'' (associated with the modern-day region of Idlib) within the land of Lukhuti to the immediate south of Pattin was also ravaged. References See also *Ancient regions of Anatolia The following is a list of regions of Ancient Anatol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia (around 1650 BC). This empire reached its height during the mid-14th century BC under Šuppiluliuma I, when it encompassed an area that included most of Anatolia as well as parts of the northern Levant and Upper Mesopotamia. Between the 15th and 13th centuries BC, the Empire of Hattusa—in modern times conventionally called the Hittite Empire—came into conflict with the New Kingdom of Egypt, the Middle Assyrian Empire and the empire of Mitanni for control of the Near East. The Middle Assyrian Empire eventually emerged as the dominant power and annexed much of the Hittite Empire, while the remainder was sacked by Phrygian newcomers to the region. After BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse, the Hittites splintered in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kubaba
Kubaba (in the ''Weidner'' or ''Esagila Chronicle''), sux, , , is the only queen on the ''Sumerian King List'', which states she reigned for 100 years – roughly in the Early Dynastic III period (ca. 2500–2330 BC) of Sumerian history. A connection between her and a goddess known from Hurro- Hittite and later Luwian sources cannot be established on the account of spatial and temporal differences.J. D. Hawkins, Kubaba A. Philologisch · Kubaba A. Philological' n:''Reallexikon der Assyriologie und vorderasiatischen Archäologie'' vol. 6, 1983, p. 257 History Kubaba is one of very few women to have ever ruled in their own right in Mesopotamian history. Most versions of the king list place her alone in her own dynasty, the 3rd Dynasty of Kish, following the defeat of Sharrumiter of Mari, but other versions combine her with the 4th dynasty, that followed the primacy of the king of Akshak. Before becoming monarch, the king list says she was an alewife. The ''Weidner Chronicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citadel Of Aleppo
The Citadel of Aleppo ( ar, قلعة حلب, Qalʿat Ḥalab) is a large medieval fortified palace in the centre of the old city of Aleppo, northern Syria. It is considered to be one of the oldest and largest castles in the world. Usage of the Citadel hill dates back at least to the middle of the 3rd millennium BC. Occupied by many civilizations over timeincluding the Armenians, Greeks, Byzantines, Ayyubids, Mamluks and Ottomans the majority of the construction as it stands today is thought to originate from the Ayyubid period. An extensive conservation work took place in the 2000s by the Aga Khan Trust for Culture, in collaboration with Aleppo Archeological Society. Dominating the city, the Citadel is part of the Ancient City of Aleppo, an UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1986. During the 2010s, the Citadel received significant damage during the lengthy Battle of Aleppo. It was reopened to the public in early 2018 with repairs to damaged parts underway. History The rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)