|
Palden Tenpai Nyima
Palden Tenpai Nyima (1782–1853) was the 7th Panchen Lama of Tibet. Early life and reign Lobsang Palden Yeshe, the previous Panchen Lama, died from smallpox in Beijing in 1780. His brother Shamarpa, who was acting as regent, wrote to the British Governor of India, Warren Hastings, in 1782 to say that a new incarnation had been found. Shamarpa had hoped to inherit some of the riches given to his brother in Beijing after his death. When this didn't happen, he conspired with the Nepalese, who sent a Gurkha army in 1788 and took control of Shigatse. Shamarpa, however, did not keep his side of the bargain and the Gurkha army returned three years later to claim their spoils, but a Chinese army drove them back to Nepal in 1792. The 7th Panchen Lama and successive Dalai Lamas The 7th Panchen Lama's life coincided with the "period of the short-lived Dalai Lamas". Tis made the Panchen Lama "the lama of the hour, filling the void left by the four Dalai Lamas who died in their youth." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Tibetan
Lhasa Tibetan (), or Standard Tibetan, is the Tibetan dialect spoken by educated people of Lhasa, the capital of the Tibetan Autonomous Region of China. It is an official language of the Tibet Autonomous Region. In the traditional "three-branched" classification of Tibetic languages, the Lhasa dialect belongs to the Central Tibetan branch (the other two being Khams Tibetan and Amdo Tibetan). In terms of mutual intelligibility, speakers of Khams Tibetan are able to communicate at a basic level with Lhasa Tibetan, while Amdo speakers cannot. Both Lhasa Tibetan and Khams Tibetan evolved to become Tone (linguistics), tonal and do not preserve the word-initial consonant clusters, which makes them very far from Classical Tibetan, especially when compared to the more Linguistic conservatism, conservative Amdo Tibetan. Registers Like many languages, Lhasa Tibetan has a variety of Register (sociolinguistics), language registers: * (Wylie transliteration, Wylie: , literally "wikt:demot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Urn
The Golden Urn refers to a method for selecting Tibetan reincarnations by drawing lots or tally sticks from a Golden Urn introduced by the Qing dynasty of China in 1793. After the Sino-Nepalese War, the Qianlong Emperor promulgated the 29-Article Ordinance for the More Effective Governing of Tibet, which included regulations on the selection of lamas including the Dalai Lama and Panchen Lama. The Golden Urn was introduced to prevent cheating and corruption in the selection process. In 1792, the Qianlong Emperor published article The Discourse of Lama to explain the history of lamas and the cases of cheating and corruption in the reincarnation system, while also explaining why he thought it would be a fair system of choosing reincarnated rinpoches, lamas, as opposed to choosing reincarnated rinpoches, lamas based on private designation, or based on one person's decision. Also, it's to eliminate greedy family with multiple reincarnated rinpoches, lamas. History Qing dynasty The G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1853 Deaths
Events January–March * January 6 – Florida Governor Thomas Brown signs legislation that provides public support for the new East Florida Seminary, leading to the establishment of the University of Florida. * January 8 – Taiping Rebellion: Zeng Guofan is ordered to assist the governor of Hunan in organising a militia force to search for local bandits. * January 12 – Taiping Rebellion: The Taiping army occupies Wuchang. * January 19 – Giuseppe Verdi's opera ''Il Trovatore'' premieres in performance at Teatro Apollo in Rome. * February 10 – Taiping Rebellion: Taiping forces assemble at Hanyang, Hankou, and Wuchang, for the march on Nanjing. * February 12 – The city of Puerto Montt is founded in the Reloncaví Sound, Chile. * February 22 – Washington University in St. Louis is founded as Eliot Seminary. * March – The clothing company Levi Strauss & Co. is founded in the United States. * March 4 – Inauguration of Franklin Pierce as 14th President of the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1782 Births
Year 178 ( CLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 931 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 178 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Bruttia Crispina marries Commodus, and receives the title of '' Augusta''. * Emperor Marcus Aurelius and his son Commodus arrive at Carnuntum in Pannonia, and travel to the Danube to fight against the Marcomanni. Asia * Last (7th) year of ''Xiping'' era and start of ''Guanghe'' era of the Chinese Han Dynasty. * In India, the decline of the Kushan Empire begins. The Sassanides take over Central Asia. Religion * The Montanist heresy is condemned for the first time. Births * Lü Meng, Chinese general (d. 220) * P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panchen Lamas
The Panchen Lama () is a tulku of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. Panchen Lama is one of the most important figures in the Gelug tradition, with its spiritual authority second only to Dalai Lama. Along with the council of high lamas, he is in charge of seeking out the next Dalai Lama. ''Panchen'' is a portmanteau of '' Pandita'' and ''Chenpo'', meaning "great scholar". The recognition of Panchen Lamas began with Lobsang Chökyi Gyaltsen, tutor of the 5th Dalai Lama, who received the title "Panchen Bogd" from Altan Khan and the Dalai Lama in 1645. ''Bogd'' is Mongolian, meaning "holy". Khedrup Gelek Pelzang, Sönam Choklang and Ensapa Lobsang Döndrup were subsequently recognized as the first to third Panchen Lamas posthumously. In 1713, the Kangxi Emperor of the Qing dynasty granted the title Panchen Erdeni to the 5th Panchen Lama. In 1792, the Qianlong Emperor issued a decree known as the 29-Article Ordinance for the More Effective Governing of Tibet, and Article O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenpai Wangchuk
Tenpai Wangchuk (1855–1882) was the eighth Panchen Lama of Tibet. 8th Panchen Lama, Tenpai Wangchuk, also known as Namgyal Wangdui Gyaltsen, was born in 1855 in Namling County (རྣམ་གླིང་རྫོང་། 南木林), Shigatse prefecture, western Tibet. He was born into an aristocratic family of Nyingma school. One member of his family was an incarnation of Nyingma school. The fact that the new Panchen Lama came from a different tradition created a discontent among the Tashilhunpo Monastery monks (who profess the Gelug tradition). His father's name was Tenzin Wangjia and his mother's name was Zhaxila (Chinese transcription). In 1857 Tenpai Wangchuk was identified as the eighth incarnation of the Panchen Lama. He was the first Panchen Lama to be identified by drawing a lot from the Golden Urn. In 1860 Tenpai Wangchuk (aged 5), in the presence of Reting Rinpoche Hutukthu, was finally enthroned as the 8th incarnation of Panchen Lama in the Tashilhunpo Monastery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashilhunpo Monastery
Tashi Lhunpo Monastery (), founded in 1447 by the 1st Dalai Lama, is the traditional monastic seat of the Panchen Lama, and an historically and culturally important monastery in Shigatse, the second-largest city in Tibet. The monastery was sacked when the Gorkha Kingdom invaded Tibet and captured Shigatse in 1791 before a combined Tibetan and Chinese army drove them back as far as the outskirts of Kathmandu, when they were forced to agree to keep the peace in the future, pay tribute every five years, and return what they had looted from Tashi Lhunpo. The monastery is the traditional seat of successive Panchen Lamas, the second highest ranking tulku lineage in the Gelug tradition of Tibetan Buddhism. The "Tashi" or Panchen Lama had temporal power over three small districts, though not over the town of Shigatse itself, which was administered by a ''dzongpön'' (prefect) appointed from Lhasa. Located on a hill in the center of the city, the full name in Tibetan of the monastery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
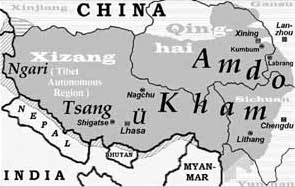
Ü-Tsang
Ü-Tsang is one of the three traditional provinces of Tibet, the others being Amdo in the north-east, and Kham in the east. Ngari (including former Guge kingdom) in the north-west was incorporated into Ü-Tsang. Geographically Ü-Tsang covered the south-central of the Tibetan cultural area, including the Brahmaputra River watershed. The western districts surrounding and extending past Mount Kailash are included in Ngari, and much of the vast Changtang plateau to the north. The Himalayas defined Ü-Tsang's southern border. The present Tibet Autonomous Region corresponds approximately to what was ancient Ü-Tsang and western Kham. Ü-Tsang was formed by the merging of two earlier power centers: Ü () in central Tibet, controlled by the Gelug lineage of Tibetan Buddhism under the early Dalai Lamas, and Tsang () which extended from Gyantse to points west, controlled by the rival Sakya lineage. Military victories by the powerful Khoshut Mongol Güshi Khan that backed 5th Dalai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sera Monastery
Sera Monastery ( "Wild Roses Monastery"; ) is one of the "great three" Gelug university monasteries of Tibet, located north of Lhasa and about north of the Jokhang. The other two are Ganden Monastery and Drepung Monastery. The origin of its name is attributed to a fact that during construction, the hill behind the monastery was covered with blooming wild roses (or "sera" in Tibetan). The original Sera Monastery is responsible for some 19 hermitages, including four nunneries, which are all located in the foothills north of Lhasa. The Sera Monastery, as a complex of structures with the Great Assembly Hall and three colleges, was founded in 1419 by Jamchen Chojey of Sakya Yeshe of Zel Gungtang (1355–1435), a disciple of Je Tsongkhapa. During the 1959 revolt in Lhasa, Sera monastery suffered severe damage, with its colleges destroyed and hundreds of monks killed. After the Dalai Lama took asylum in India, many of the monks of Sera who survived the attack moved to Bylakuppe in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobsang Trinley Lhündrub Chökyi Gyaltsen
Lobsang Trinley Lhündrub Chökyi Gyaltsen (born Gönbo Cêdän; 19 February 1938 – 28 January 1989) was the tenth Panchen Lama, officially the 10th Panchen Erdeni (), of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism. According to Tibetan Buddhism, Panchen Lamas are living emanations of the buddha Amitabha. He was often referred to simply as Choekyi Gyaltsen. Recognition The Paṇchen Lama incarnation line began in the seventeenth century after the 5th Dalai Lama gave Chokyi Gyeltsen the title, and declared him to be an emanation of Buddha Amitaba. Officially, he became the first Panchen Lama in the lineage, while he had also been the sixteenth abbot of Tashilhunpo Monastery. The 10th Panchen Lama was born as Gonpo Tseten on 19 February 1938, in Bido, today's Xunhua Salar Autonomous County of Qinghai, known as Amdo. His father was also called Gonpo Tseten and his mother was Sonam Drolma. After the Ninth Panchen Lama died in 1937, two simultaneous searches for the tenth Panche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Secondly, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes non-denominational, that is part of a building or complex with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, cemetery, airport, or a military or commercial ship. Thirdly, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy were permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. Finally, for historical reasons, ''chapel'' is also often the term used by independent or nonconformist denominations for their places of wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tashilhunpo
Tashi Lhunpo Monastery (), founded in 1447 by the 1st Dalai Lama, is the traditional monastic seat of the Panchen Lama, and an historically and culturally important monastery in Shigatse, the second-largest city in Tibet. The monastery was sacked when the Gorkha Kingdom invaded Tibet and captured Shigatse in 1791 before a combined Tibetan and Chinese army drove them back as far as the outskirts of Kathmandu, when they were forced to agree to keep the peace in the future, pay tribute every five years, and return what they had looted from Tashi Lhunpo. The monastery is the traditional seat of successive Panchen Lamas, the second highest ranking tulku lineage in the Gelug tradition of Tibetan Buddhism. The "Tashi" or Panchen Lama had temporal power over three small districts, though not over the town of Shigatse itself, which was administered by a ''dzongpön'' (prefect) appointed from Lhasa. Located on a hill in the center of the city, the full name in Tibetan of the monastery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |