|
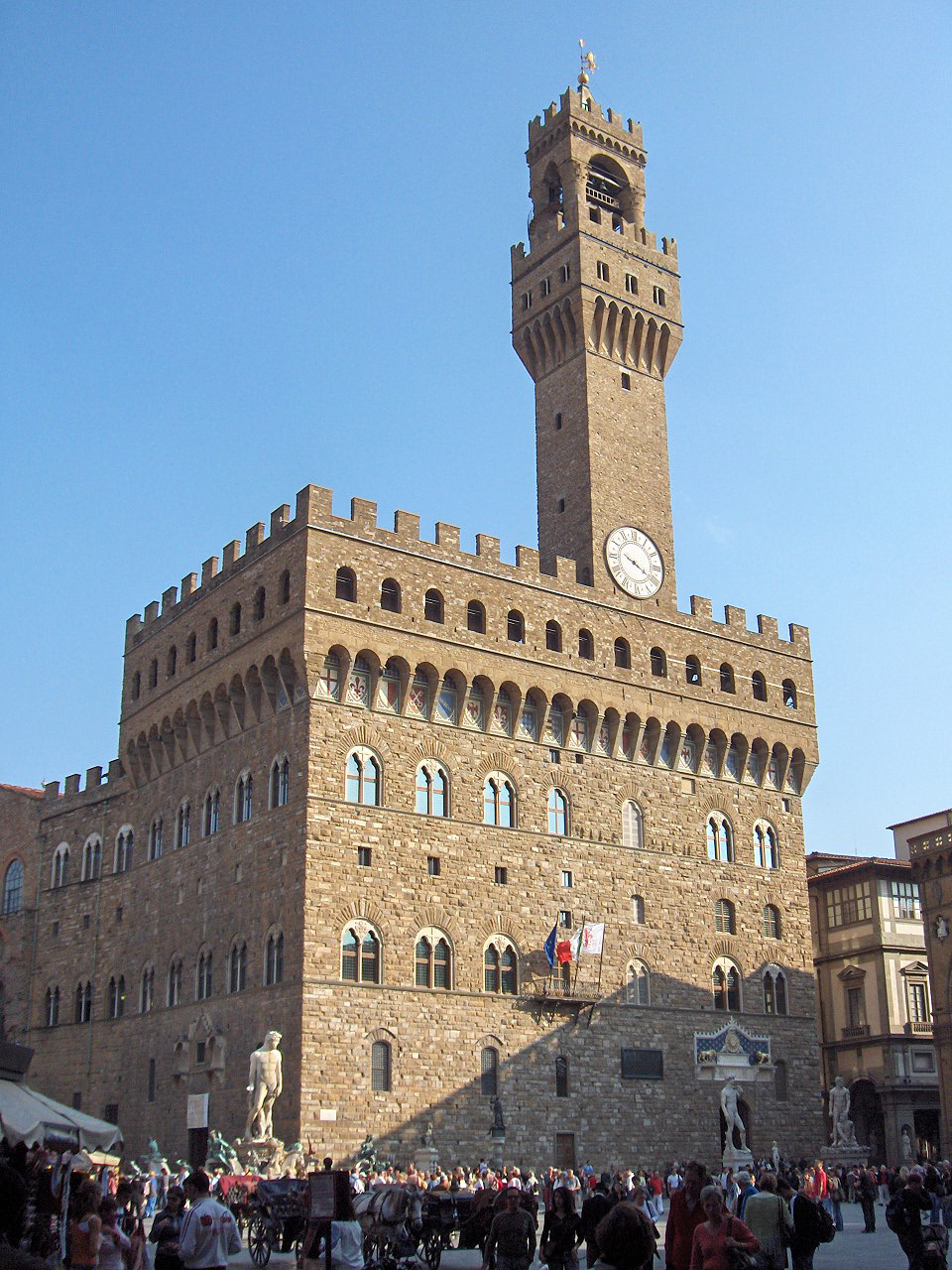
Palazzo Vecchio
The Palazzo Vecchio ( "Old Palace") is the town hall of Florence, Italy. It overlooks the Piazza della Signoria, which holds a copy of Michelangelo's ''David'' statue, and the gallery of statues in the adjacent Loggia dei Lanzi. Originally called the ''Palazzo della Signoria'', after the Signoria of Florence, the ruling body of the Republic of Florence, this building was also known by several other names: ''Palazzo del Popolo'', ''Palazzo dei Priori'', and ''Palazzo Ducale'', in accordance with the varying use of the palace during its long history. The building acquired its current name when the Medici duke's residence was moved across the Arno River to the Palazzo Pitti. History In 1299, the commune and people of Florence decided to build a palace that would be worthy of the city's importance, and that would be more secure and defensible in times of turbulence for the magistrates of the commune.Bartlett, 37. Arnolfo di Cambio, the architect of the Duomo and the Santa Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piazza Della Signoria
Piazza della Signoria () is a w-shaped square in front of the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence, Italy. It was named after the Palazzo della Signoria, also called Palazzo Vecchio. It is the main point of the origin and history of the Florentine Republic and still maintains its reputation as the political focus of the city. It is the meeting place of Florentines as well as the numerous tourists, located near Palazzo Vecchio and Piazza del Duomo and gateway to Uffizi Gallery. Buildings The impressive 14th-century Palazzo Vecchio is still preeminent with its crenellated tower. The square is also shared with the Loggia della Signoria, the Uffizi Gallery, the Palace of the Tribunale della Mercanzia (1359) (now the Bureau of Agriculture), and the Palazzo Uguccioni (1550, with a facade attributed to Raphael, who however died thirty years before its construction). Located in front of the Palazzo Vecchio is the Palace of the Assicurazioni Generali (1871, built in Renaissance style). Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guelphs And Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy. During the 12th and 13th centuries, rivalry between these two parties formed a particularly important aspect of the internal politics of medieval Italy. The struggle for power between the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire arose with the Investiture Controversy, which began in 1075, and ended with the Concordat of Worms in 1122. History Origins The Guelph vs Ghibelline conflict initially arose from the division caused by the Investiture Controversy, about whether secular rulers or the pope had the authority to appoint bishops and abbots. Upon the death of Emperor Henry V, of the Salian dynasty, the dukes elected an opponent of his dynasty, Lothair III, as the new emperor. This displeased the Hohenstaufen, who were allied with and related to the old dynasty. Out of fear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolò Bernardo
Nicolò () is an Italian male given name. Another variation is Niccolò, most common in Tuscany. It may refer to: * Nicolò Albertini, statesman * Nicolò Amati, luthier * Nicolò Barella, Italian footballer * Nicolò Barattieri, Italian engineer * Nicolò Brancaleon, artist * Nicolò Egidi, chemist * Nicolò Fagioli, Italian footballer * Nicolò Gabrielli, composer * Nicolò Gagliano, violin-maker * Nicolò Isouard (1773-1818), French composer * Nicolò Melli, Italian basketball player * Nicolò Minato, poet * Nicolò Pacassi, architect * Nicolò Pollari, general * Nicolo Rizzuto (1924–2010), Italian-Canadian mobster * Nicolo Schiro, mobster * Nicolò Zanon, judge * Nicolò Zaniolo, italian footballer See also *Niccolò (other) *Nicolao Nicolao is an Italian given name and a surname. It may refer to the following: Given name * Nicolao Civitali (1482 - after 1560), Italian sculptor and architect * Nicolao Colletti (18th century), Italian mathematician * Nicolao D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girolamo Savonarola
Girolamo Savonarola, OP (, , ; 21 September 1452 – 23 May 1498) or Jerome Savonarola was an Italian Dominican friar from Ferrara and preacher active in Renaissance Florence. He was known for his prophecies of civic glory, the destruction of secular art and culture, and his calls for Christian renewal. He denounced clerical corruption, despotic rule, and the exploitation of the poor. In September 1494, when Charles VIII of France invaded Italy and threatened Florence, such prophecies seemed on the verge of fulfilment. While Savonarola intervened with the French king, the Florentines expelled the ruling Medicis and, at the friar's urging, established a "popular" republic. Declaring that Florence would be the New Jerusalem, the world centre of Christianity and "richer, more powerful, more glorious than ever", he instituted an extreme puritanical campaign, enlisting the active help of Florentine youth. In 1495 when Florence refused to join Pope Alexander VI's Holy League ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosimo De' Medici
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 – 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the Medici family as effective rulers of Florence during much of the Italian Renaissance. His power derived from his wealth as a banker, and inter-marriage with other powerful and rich families. He was a patron of arts, learning and architecture. He spent over 600,000 gold florins (approx. $500 million inflation adjusted) on art and culture, including Donatello's David, the first freestanding nude male sculpture since antiquity. Despite his influence, his power was not absolute; Florence's legislative councils at times resisted his proposals throughout his life, and he was viewed as first among equals, rather than an autocrat.Martines, Lauro (2011). ''The Social World of the Florentine Humanists, 1390–1460''. University of Toronto Press. p. 8. Biography Early life and family business Cosimo de' Medici was born in Florence to Giovanni di Bicci de' M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pianta Del Buonsignori, Dettaglio 155 Palazzo Del Gran Duca (palazzo Vecchio)
is a 2002 platform game developed and published by Nintendo for the GameCube. It is the second 3D game in the ''Super Mario'' series, following ''Super Mario 64'' (1996). The game was directed by Yoshiaki Koizumi and Kenta Usui, produced by series creators Shigeru Miyamoto and Takashi Tezuka, written by Makoto Wada, and scored by Koji Kondo and Shinobu Tanaka. The game takes place on the tropical Isle Delfino, where Mario, Toadsworth, Princess Peach, and five Toads are taking a vacation. A villain resembling Mario, known as Shadow Mario, vandalizes the island with graffiti and leaves Mario to be wrongfully convicted for the mess. Mario is ordered to clean up Isle Delfino, using a device called the Flash Liquidizer Ultra Dousing Device (F.L.U.D.D.), while saving Princess Peach from Shadow Mario. ''Super Mario Sunshine'' received critical acclaim, with reviewers praising the game's graphics, gameplay, story, soundtrack, and the addition of F.L.U.D.D. as a mechanic, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Thermal Weapons
Early thermal weapons, which used heat or burning action to destroy or damage enemy personnel, fortifications or territories, were employed in warfare during the classical and medieval periods (approximately the 8th century BC until the mid-16th century AD). Incendiary devices were frequently used as projectiles during warfare, particularly during sieges and naval battles: some substances were boiled or heated to inflict damage by scalding or burning; other substances relied on their chemical properties to inflict burns or damage. These weapons or devices could be used by individuals, thrown by siege engines, or utilised as army strategy. Incendiary mixtures, such as the petroleum-based Greek fire, could be launched by throwing machines or administered through a siphon. Sulfur- and oil-soaked materials were sometimes ignited and thrown at the enemy, or attached to spears, arrow and bolts and fired by hand or machine. The simplest and most common thermal projectiles were b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embrasure
An embrasure (or crenel or crenelle; sometimes called gunhole in the domain of gunpowder-era architecture) is the opening in a battlement between two raised solid portions ( merlons). Alternatively, an embrasure can be a space hollowed out throughout the thickness of a wall by the establishment of a bay. This term designates the internal part of this space, relative to the closing device, door or window. In fortification this refers to the outward splay of a window or of an arrowslit on the inside. In ancient military engineering, embrasures were constructed in towers and walls, in particular between the merlons and the battle. A loophole, arrow loop or arrowslit passes through a solid wall, and thus forms an embrasure of shooting, allowing archer or gunner weapons to be fired out from the fortification while the firer remains under cover. This type of opening was flared inward - that is: the opening was very narrow on the outside, but wide on the inside, so that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbel
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the structure. A piece of timber projecting in the same way was called a "tassel" or a "bragger" in England. The technique of corbelling, where rows of corbels deeply keyed inside a wall support a projecting wall or parapet, has been used since Neolithic (New Stone Age) times. It is common in medieval architecture and in the Scottish baronial style as well as in the vocabulary of classical architecture, such as the modillions of a Corinthian cornice. The corbel arch and corbel vault use the technique systematically to make openings in walls and to form ceilings. These are found in the early architecture of most cultures, from Eurasia to Pre-Columbian architecture. A console is more specifically an "S"-shaped scroll bracket in the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battlement
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals to allow for the launch of arrows or other projectiles from within the defences. These gaps are termed " crenels" (also known as ''carnels'', or '' embrasures''), and a wall or building with them is called crenellated; alternative (older) terms are castellated and embattled. The act of adding crenels to a previously unbroken parapet is termed crenellation. The function of battlements in war is to protect the defenders by giving them something to hide behind, from which they can pop out to launch their own missiles. A defensive building might be designed and built with battlements, or a manor house might be fortified by adding battlements, where no parapet previously existed, or cutting crenellations into its existing parapet wall. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
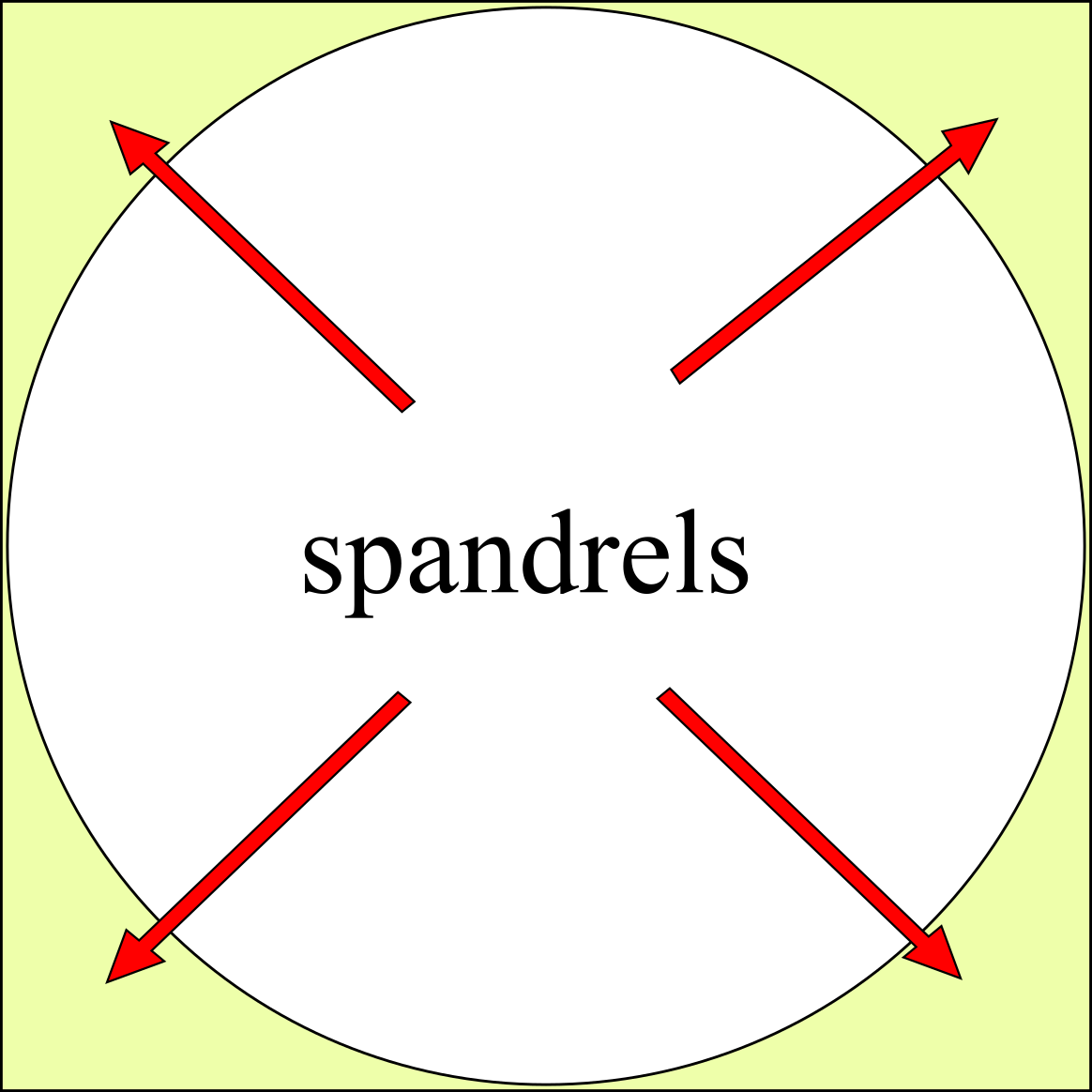
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florentine Lily
The fleur-de-lis, also spelled fleur-de-lys (plural ''fleurs-de-lis'' or ''fleurs-de-lys''), is a lily (in French, and mean 'flower' and 'lily' respectively) that is used as a decorative design or symbol. The fleur-de-lis has been used in the heraldry of numerous European nations, but is particularly associated with France, notably during its monarchical period. The fleur-de-lis became "at one and the same time, religious, political, dynastic, artistic, emblematic, and symbolic," especially in French heraldry. The fleur-de-lis has been used by French royalty and throughout history to represent saints of France. In particular, the Virgin Mary and Saint Joseph are often depicted with a lily. The fleur-de-lis is represented in Unicode at in the Miscellaneous Symbols block. Origin The ''fleur de lis'' is widely thought to be a stylized version of the species ''Iris pseudacorus'', or ''Iris florentina''.Stefan Buczacki However, the lily (genus lilium, family Liliaceae) and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)