|
Palace Of The Dukes Of Burgundy
The Palace of the Dukes and Estates of Burgundy or ''Palais des ducs et des États de Bourgogne'' is a remarkably well-preserved architectural assemblage in Dijon. The oldest part is the 14th and 15th century Gothic ducal palace and seat of the Dukes of Burgundy, made up of a logis still visible on place de la Liberation, the ducal kitchens on cour de Bar, the tour de Philippe le Bon, a "guette" overlooking the whole city, and tour de Bar. Most of what can be seen today, however, was built in the 17th and especially the 18th centuries, in a classical style, when the palace was a royal residence building and housed the estates of Burgundy. Finally, the 19th façade of the musée on place de la Sainte-Chapelle was added on the site of the palace's Sainte-Chapelle, demolished in 1802. The Palace houses the city's town hall and the musée des Beaux-Arts. History of the Palace of the Dukes The Duchy of Burgundy was founded in the 9th century, around the year 880, from the Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard, Duke Of Burgundy
Richard, Duke of Burgundy (858–921), also known as Richard of Autun or Richard the Justiciar, was Count of Autun from 880 and the first Margrave and Duke of Burgundy. He eventually attained suzerainty over all the counties of Burgundy save Mâcon and by 890 he was referred to as ''dux'' (duke) and by 900 as ''marchio'' (margrave). By 918 he was being called ''dux Burgundionem'' or ''dux Burgundiae'', which probably signified less the existence of a unified Burgundian dukedom than feudal suzerainty over a multiplicity of counties in a specific region. Life Richard was a Bosonid, the son of Bivin of Gorze and Richildis. His elder brother was Boso of Provence and his younger sister was Richildis, second wife of Charles the Bald. In 875, after the death of the Emperor Louis II, Richard and Boso accompanied Charles to Italy for his imperial coronation. In February 876, in Pavia, while preparing for his return journey, Charles nominated Boso "Duke and Viceroy of Italy and Duke o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine, Duke Of Lorraine
Antoine (4 June 148914 June 1544), known as the Good, was Duke of Lorraine from 1508 until his death in 1544. Raised at the French court, Antoine would campaign in Italy twice: once under Louis XII and the other with Francis I. During the German Peasants' War, he would defeat two armies while retaking Saverne and Sélestat. Antoine succeeded in freeing Lorraine from the Holy Roman Empire with the Treaty of Nuremberg of 1542. In 1544, while Antoine suffered from an illness, the Duchy of Lorraine was invaded by Emperor Charles V's army on their way to attack France. Fleeing the Imperial armies, Antoine was taken to Bar-le-Duc where he died. Biography Antoine was born, 4 June 1489, at Bar-le-Duc, the son of René II, Duke of Lorraine and Philippa of Guelders. He spent seven years at the court of King Louis XII together with his brother Claude, and became friends with the Duke of Angoulême, the future King Francis I. After the death of his father, Antoine succeeded him as duke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe De Chabot
Philippe de Chabot, Seigneur De Brion, Count of Charny and Buzançois (c. 1492 – 1 June 1543), also known as Admiral De Brion, was an admiral of France. Biography The Chabot family was one of the oldest and most powerful in Poitou. Philippe was a cadet of the Jarnac branch. He was a companion of Francis I as a child, and on that king's accession was loaded with honors and estates. After the battle of Pavia he was made Admiral of France and governor of Burgundy (1526), and shared with Anne de Montmorency the direction of affairs. He served as ambassador to England in 1533 and 1534. He was at the height of his power in 1535, and commanded the army for the invasion of the states of the duke of Savoy; but in the campaigns of 1536 and 1537 he was eclipsed by Montmorency, and from that moment his influence began to wane. He was accused by his enemies of peculation, and condemned on 10 February 1541 to a fine of 1,500,000 livres, to banishment, and to the confiscation of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis II De La Trémoille
Louis II de la Trémoille (29 September 1460 – 24 February 1525), also known as La Trimouille, was a French general. He served under three kings: Charles VIII, Louis XII and Francis I. He was killed in combat at the Battle of Pavia. Military career Louis was born in Thouars, the eldest son of Louis I de la Trémoille. He commanded an army that attempted to secure Brittany for the French crown after internal revolts had weakened Francis II, Duke of Brittany during the so-called "Mad War" (''La Guerre Folle''). By March 1488, Louis had been appointed lieutenant-general of Brittany by Charles VIII. His decisive victory at the Battle of Saint-Aubin-du-Cormier on 28 July 1488 ended effective Breton independence. Louis took part in several battles in the Italian Wars, notably the Battle of Fornovo in 1495 and the Battle of Agnadello of 1509. He suffered a severe defeat at the Battle of Novara (1513), in which his 10,000-strong army was ambushed by 13,000 Swiss mercenaries. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundy (region)
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former Regions of France, administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Duke of Burgundy, Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The capital of Dijon was one of the great European centres of art and science, a place of tremendous wealth and power, and Western Monasticism. In early Modern Europe, Burgundy was a focal point of courtly culture that set the fashion for European royal houses and their court. The Duchy of Burgundy was a key in the transformation of the Middle Ages toward early modern Europe. Upon the 9th-century partitions of the Kingdom of Burgundy, the lands and remnants partitioned to the Kingdom of France were reduced to a ducal rank by King Robert II of France in 1004. The House of Burgundy, a cadet branch of the House of Capet, ruled over a territory that roughly conformed to the borders and territories of the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I (22 March 1459 – 12 January 1519) was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1508 until his death. He was never crowned by the pope, as the journey to Rome was blocked by the Venetians. He proclaimed himself Elected Emperor in 1508 (Pope Julius II later recognized this) at Trent, thus breaking the long tradition of requiring a Papal coronation for the adoption of the Imperial title. Maximilian was the son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor, and Eleanor of Portugal. Since his coronation as King of the Romans in 1486, he ran a double government, or ''Doppelregierung'' (with a separate court), with his father until Frederick's death in 1493. Maximilian expanded the influence of the House of Habsburg through war and his marriage in 1477 to Mary of Burgundy, the ruler of the Burgundian State, heir of Charles the Bold, though he also lost his family's original lands in today's Switzerland to the Swiss Confederacy. Through marriage of his son Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XI Of France
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (french: le Prudent), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII. Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revolt known as the Praguerie in 1440. The king forgave his rebellious vassals, including Louis, to whom he entrusted the management of the Dauphiné, then a province in southeastern France. Louis's ceaseless intrigues, however, led his father to banish him from court. From the Dauphiné, Louis led his own political establishment and married Charlotte of Savoy, daughter of Louis, Duke of Savoy, against the will of his father. Charles VII sent an army to compel his son to his will, but Louis fled to Burgundy, where he was hosted by Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy, Charles' greatest enemy. When Charles VII died in 1461, Louis left the Burgundian court to take possession of his kingdom. His taste for intrigue and his intense diplomatic ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Arras (1482)
The Treaty of Arras was signed at Arras on 23 December 1482 by King Louis XI of France and Archduke Maximilian I of Habsburg as heir of the Burgundian Netherlands in the course of the Burgundian succession crisis. The dukes from the House of Valois-Burgundy, a cadet branch of the French royal House of Valois, had ruled over a significant amount of territories on both sides of the border between the Kingdom of France and the Holy Roman Empire. When the last Burgundian duke Charles the Bold died at the Battle of Nancy on 5 January 1477, his territories in France including Burgundy proper, Flanders, Artois and the Picardy were seized as reverted fiefs by the French king. Before his death however, Charles had arranged with Emperor Frederick III of Habsburg the marriage of their children Mary the Rich and Archduke Maximilian, which took place on 19 August 1477. Maximilian did not hesitate to defend the heritage of his wife, culminating in the 1479 Battle of Guinegate, where he de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. France originated as West Francia (''Francia Occidentalis''), the western half of the Carolingian Empire, with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ''rex Francorum'' ("king of the Franks") well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ''rex Francie'' ("King of France") was Philip II, in 1190, and officially from 1204. From then, France was continuously ruled by the Capetians and their cadet lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
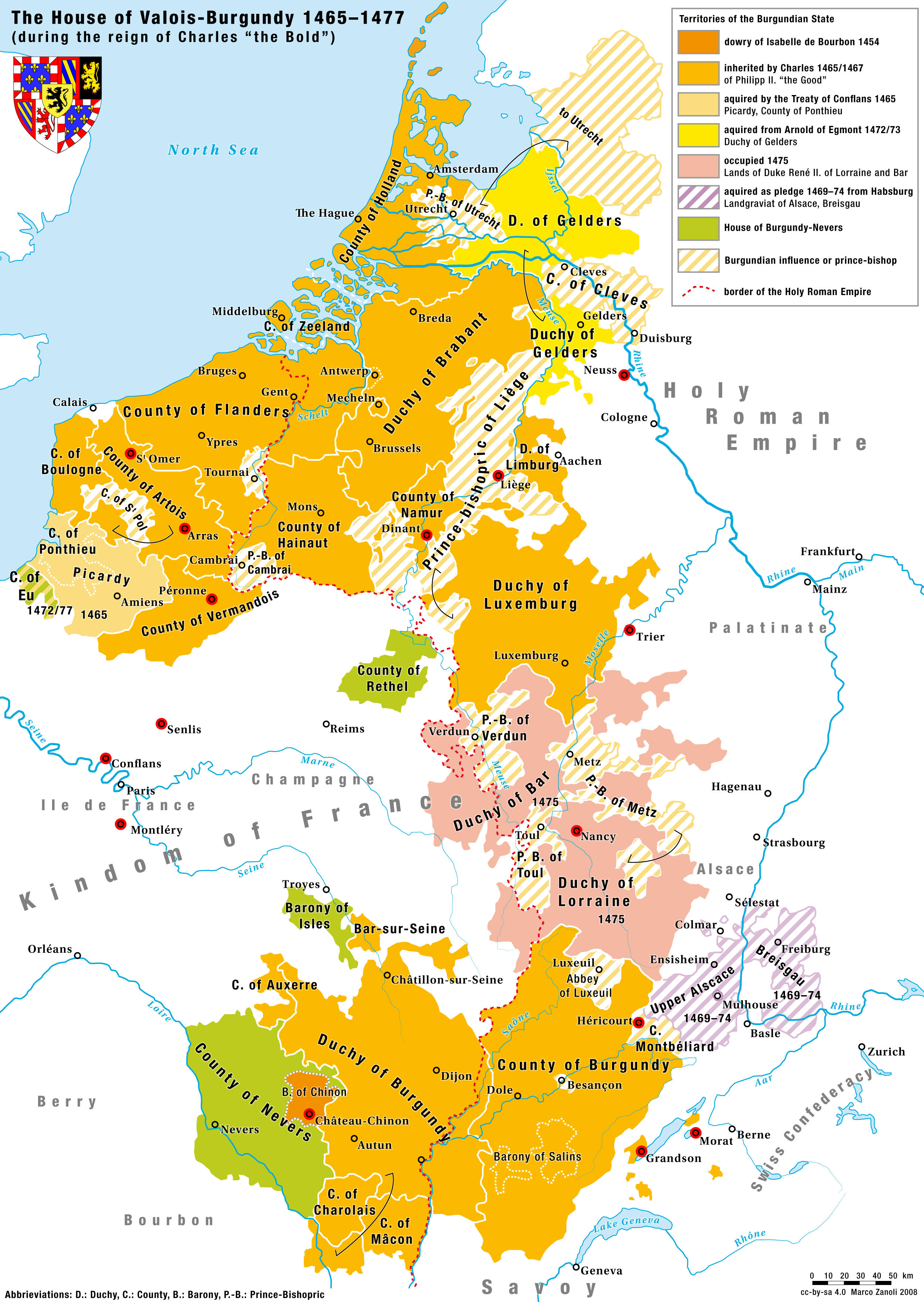
Charles The Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. Charles's main objective was to be crowned king by turning the growing Burgundian State into a territorially continuous kingdom. He declared himself and his lands independent, bought Upper Alsace and conquered Zutphen, Guelders and Lorraine, uniting at last Burgundian northern and southern possessions. This caused the enmity of several European powers and triggered the Burgundian Wars. Charles's early death at the Battle of Nancy at the hands of Swiss mercenaries fighting for René II, Duke of Lorraine, was of great consequence in European history. The Burgundian domains, long wedged between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire, were divided, but the precise disposition of the vast and disparate territorial possessions involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip The Good
Philip III (french: Philippe le Bon; nl, Filips de Goede; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonged. During his reign, the Burgundian State reached the apex of its prosperity and prestige, and became a leading centre of the arts. Philip is known historically for his administrative reforms, his patronage of Flemish artists such as van Eyck and Franco-Flemish composers such as Gilles Binchois, and perhaps most significantly the seizure of Joan of Arc, whom Philip ransomed to the English after his soldiers captured her, resulting in her trial and eventual execution. In political affairs, he alternated between alliances with the English and the French in an attempt to improve his dynasty's powerbase. Additionally, as ruler of Flanders, Brabant, Limburg, Artois, Hainaut, Holland, Luxembourg, Zeeland, Friesland and Namur, he played an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |