|
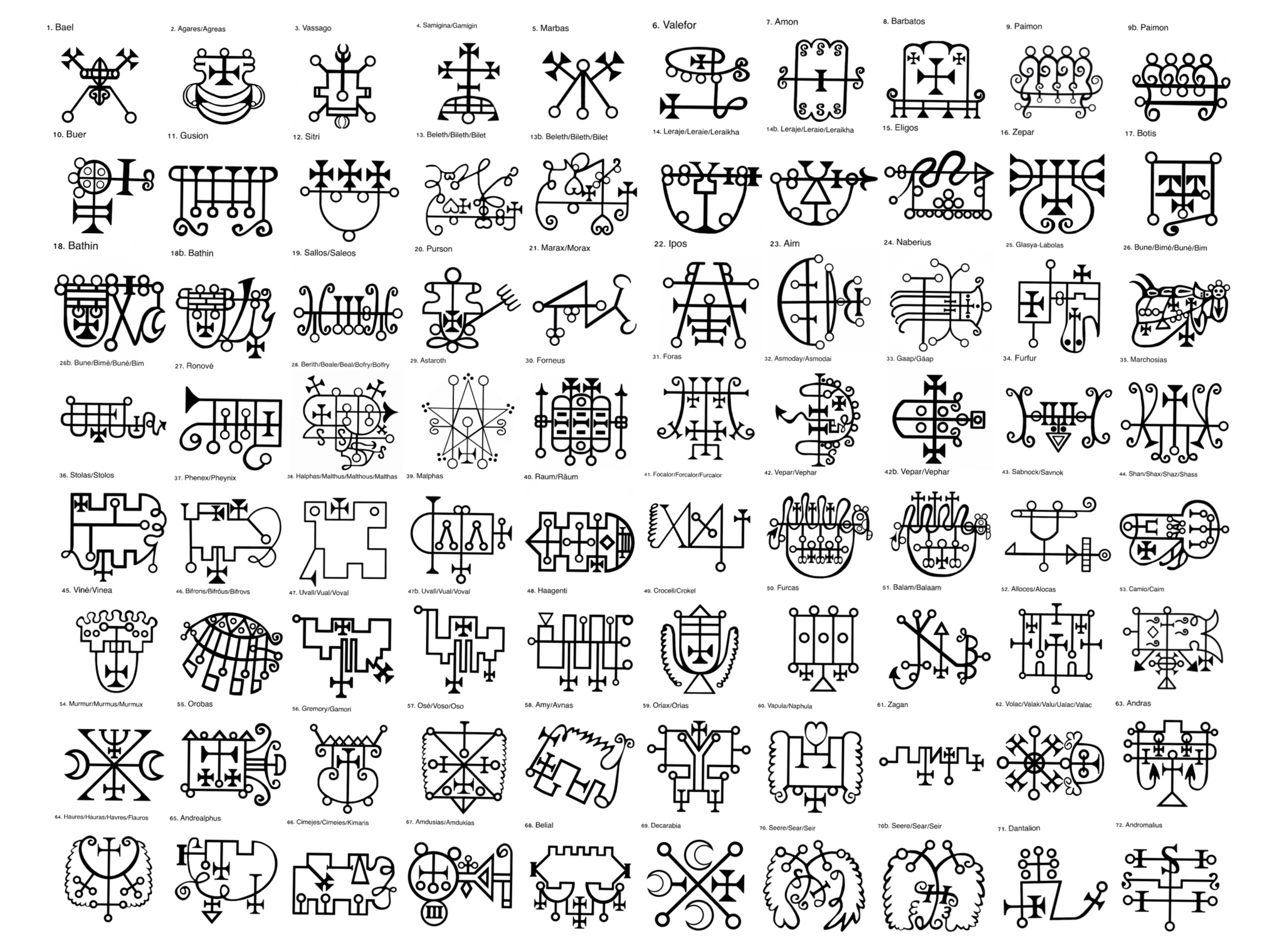
Paimon
The Goetic King known as Paimon, is a spirit named in various grimoires, prominently featured in the ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' (specifically in the ''Ars Goetia''). Other early grimoires and demonological texts where he is mentioned include Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'', Jacques Collin de Plancy's ''Dictionnaire Infernal'', the ''Livre des Esperitz'' (as "''Poymon''"), the ''Clavis Inferni'', the ''Liber Officiorum Spirituum'', ''The Book of Abramelin'', and certain French editions of ''The Grimoire of Pope Honorius'' (as Bayemon); as well as British Library, Sloane MS 3824. Status and rank The ''Goetia'', ''Liber Officiorum Spirituum'', and Weyer begin entries on King Paimon noting that he is quite obedient to Lucifer. Both the ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Liber Officiorum Spirituum'' note that he is more obedient to the will of Lucifer than any of the other kings be. King Paimon appears as the ninth spirit in the ''Ars Goetia'', the 22nd spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagan (demon)
In this article, the demons' names are taken from the goetic grimoire '' Ars Goetia'', which differs in terms of number and ranking from the ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' of Johann Weyer. As a result of multiple translations, there are multiple spellings for some of the names, explained in more detail in the articles concerning them. The sole demon which appears in ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' but not in the ''Ars Goetia'' is Pruflas. The 72 angels of the ''Shem HaMephorash'' are considered to be opposite and balancing forces against these fallen angels. Demons Kings # According to the Grand Grimoire, Baal (or Bael) is the head of the infernal powers. He is also the first demon listed in Wierus's ''Pseudomonarchia daemonum''. According to Wierus, Bael is the first king of Hell with estates in the east. He has three heads: a toad, a man, and a cat. He also speaks in a raucous, but well-formed voice, and commands 66 legions. Bael teaches the art of invisibility, and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purson
In this article, the demons' names are taken from the goetic grimoire ''Ars Goetia'', which differs in terms of number and ranking from the ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' of Johann Weyer. As a result of multiple translations, there are multiple spellings for some of the names, explained in more detail in the articles concerning them. The sole demon which appears in ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' but not in the ''Ars Goetia'' is Pruflas. The 72 angels of the ''Shem HaMephorash'' are considered to be opposite and balancing forces against these fallen angels. Demons Kings # According to the Grand Grimoire, Baal (demon), Baal (or Bael) is the head of the infernal powers. He is also the first demon listed in Wierus's ''Pseudomonarchia daemonum''. According to Wierus, Bael is the first king of Hell with estates in the east. He has three heads: a toad, a man, and a cat. He also speaks in a raucous, but well-formed voice, and commands 66 legions. Bael teaches the art of invisibili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liber Officiorum Spirituum
''Liber Officiorum Spirituum'' (English: ''The Book of the Office of Spirits'')A Book of the Office of Spirits; John Porter, Trans. Frederick Hockley, Ed. Colin D. Campbell; Teitan Press, 2011.''The Book of Oberon,'' eds. Daniel Harms and Joseph Peterson, Llewllyn Publications, 2015 was a goetic grimoire and a major source for Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Ars Goetia''. The original work (if it is a single work) has not been located, but some derived texts bearing the title have been found, some in the Sloane manuscripts, some in the Folger Shakespeare Library. Each version bears many similarities to each other and to the ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Ars Goetia'', though they are far from identical.Porter, Hockley, Campbell, p.vii-xvii''The Book of Oberon,'' eds. Daniel Harms and Joseph Peterson, Llewllyn Publications, 2015, p.1-30 History Johannes Trithemius mentions two separate works (''Liber'' quoque ''Officiorum'', and ''De Officiis Spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livre Des Esperitz
The ''Livre des Esperitz'' (''Book of Spirits'') is a 15th- or 16th-century French goetic grimoire that inspired later works including Johann Weyer's '' Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the '' Lesser Key of Solomon''."Les who's who démonologiques de la Renaissance et leurs ancêtres médiévaux" by Jean-Patrice Boudet, ''Médiévales'' 44, Spring 2003(online link) Twilit Grotto -- Esoteric Archives, 2000.''Forbidden Rites: A Necromancer's Manual of the Fifteenth Century''; Richard Kieckhefer; Pennsylvania State University Press, University Park, PA; 1997. P. 161The Goetia of Dr Rudd; Thomas Rudd, Ed. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p.32-33Entre science et nigromance: astrologie, divination et magie dans l'occident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known by its Latin title ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply the ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymously authored grimoire on Goetia, sorcery, mysticism and Magic (supernatural), magic. It was compiled in the mid-17th century from materials several centuries older... It is divided into five books: the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demon. Terminology The text is more properly called '', or, The little Key of Solomon''. The title most commonly used, ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A. E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the terms "so-called Greater Key" and "Lesser Key" to distinguish between the Clavicula Salomonis and Lemegeton, so he may have been the one to coin it. The Latin term refers to the evocati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Goetia
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known by its Latin title ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply the ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymously authored grimoire on sorcery, mysticism and magic. It was compiled in the mid-17th century from materials several centuries older... It is divided into five books: the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demon. Terminology The text is more properly called '', or, The little Key of Solomon''. The title most commonly used, ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A. E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the terms "so-called Greater Key" and "Lesser Key" to distinguish between the Clavicula Salomonis and Lemegeton, so he may have been the one to coin it. The Latin term refers to the evocation of demons or evil spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonarchia Daemonum
The ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' () first appears as an appendix to ''De praestigiis daemonum'' (1577) by Johann Weyer.Pseudomonarchia Daemonum (Liber officiorum spirituum); Johann Weyer, ed. Joseph Peterson; 2000. Available online aEsoteric Archives/ref> An abridgment of a grimoire similar in nature to the '' Ars Goetia'' (first book of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon''), it contains a list of demons, and the appropriate hours and rituals to conjure them. The ''Pseudomonarchia'' predates, and differs somewhat from, ''Ars Goetia''. The ''Pseudomonarchia'' lists sixty-nine demons (in contrast to the later seventy-two), and their sequence varies, along with some of their characteristics. The demon Pruflas appears only in ''Pseudomonarchia'',''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' add the demons Vassago, Seere, Dantalion, and Andromalius. and ''Pseudomonarchia'' does not attribute any sigils to the demons. Weyer referred to his source manuscript as ''Liber officiorum spirituum, seu Liber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionnaire Infernal
The ''Dictionnaire Infernal'' () is a book on demonology, describing demons organised in hierarchies. It was written by Jacques Collin de Plancy and first published in 1818. There were several editions of the book; perhaps the most famous is the 1863 edition, which included sixty-nine illustrations by Louis Le Breton depicting the appearances of several of the demons. Many but not all of these images were later used in S. L. MacGregor Mathers's edition of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon''. History ''Dictionnaire Infernal'' was first published in 1818 and then divided into two volumes, with six reprints—and many changes—between 1818 and 1863. This book attempts to provide an account of all the knowledge concerning superstitions and demonology. A review in 1822 read: The cover page for the 1826 edition reads: Influenced by Voltaire, Collin de Plancy initially did not believe in superstition. For example, the book reassures its contemporaries as to the torments of Hell: "To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uriel
Uriel , Auriel ( ''ʾŪrīʾēl'', " El/God is my Flame"; ''Oúriḗl''; ''Ouriēl''; ; Geʽez and Amharic: or ) or Oriel ( ''ʾÓrīʾēl'', "El/God is my Light") is the name of one of the archangels who is mentioned in Rabbinic tradition and in certain Christian traditions. He is well known in the Russian Orthodox tradition and in folk Catholicism (in both of which he is considered to be one of the seven major archangels) and recognised in Anglicanism as the fourth archangel. He is also well known in European esoteric medieval literature. Uriel is also known as a master of knowledge and the archangel of wisdom. In apocryphal, kabbalistic, and occult works, Uriel has been equated (or confused) with Urial, Nuriel, Uryan, Jeremiel, Vretil, Sariel, Suriel, Puruel, Phanuel, Jacob, Azrael, and Raphael. In the Secret Book of John, an early Gnostic work, Uriel is placed in control of the demons who help Yaldabaoth create Adam. Uriel, Auriel or Oriel (male) / Urielle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |