|
Pachycormidae Assortment
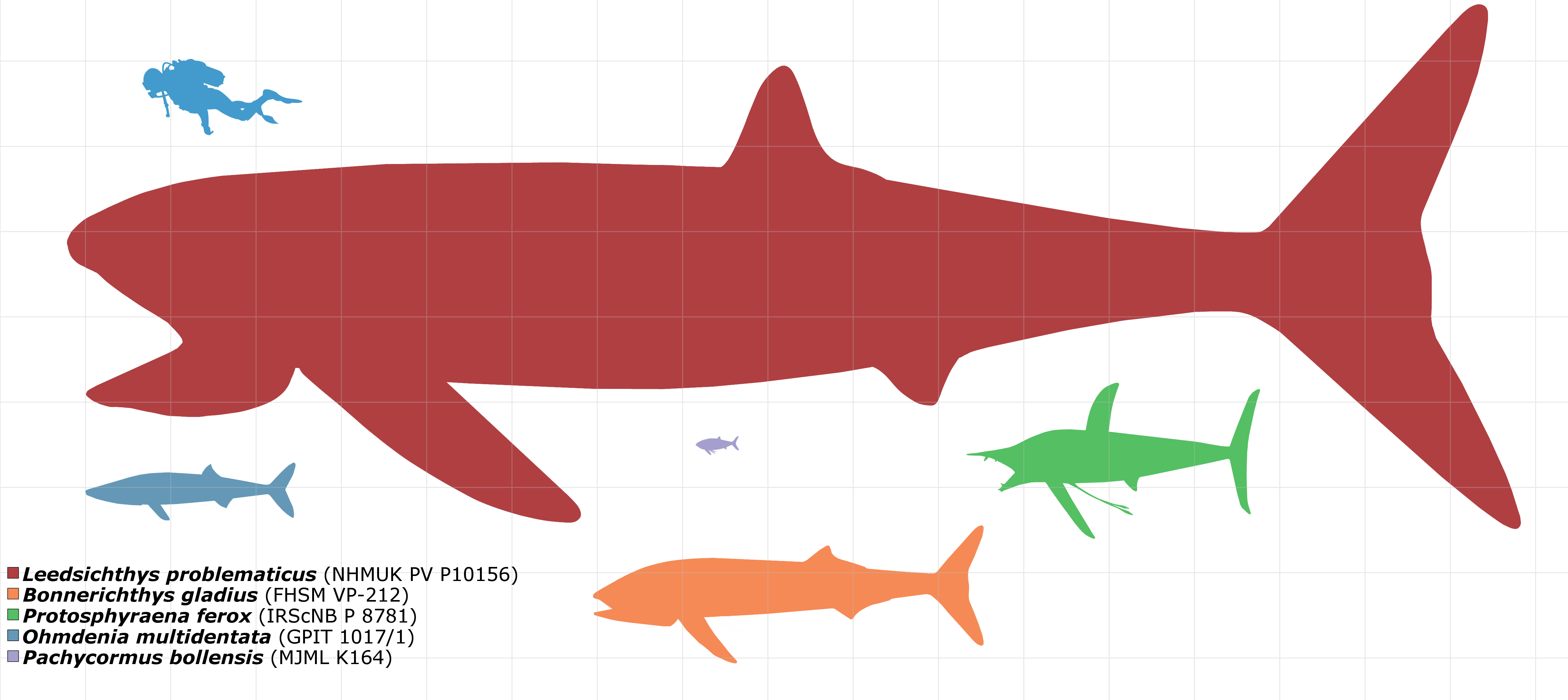
Pachycormiformes is an extinct order of marine ray-finned fish known from the Early Jurassic to the end of the Cretaceous. It only includes a single family, Pachycormidae. They were characterized by having serrated pectoral fins (though more recent studies demonstrated that fin shape diversity in this group was high), reduced pelvic fins and a bony rostrum. Their exact relations with other fish are unclear, but they are generally considered to be teleosteomorphs, more closely related to teleosts than to Holostei. Pachycormiformes are morphologically diverse, containing both tuna and swordfish-like carnivorous forms, as well as edentulous suspension-feeding forms, with the latter including the largest ray finned fish known to have existed, ''Leedsichthys,'' with an estimated maximum length of 16 metres. Synapomorphies Pachycormiformes are united by "a compound bone (rostrodermethmoid) forming the anterodorsal border of the mouth; a reduced coronoid process of the mandible; a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma (million years ago), and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.1 Ma. Certain rocks of marine origin of this age in Europe are called "Lias Group, Lias" and that name was used for the period, as well, in 19th-century geology. In southern Germany rocks of this age are called Black Jurassic. Origin of the name Lias There are two possible origins for the name Lias: the first reason is it was taken by a geologist from an England, English quarryman's dialect pronunciation of the word "layers"; secondly, sloops from north Cornwall, Cornish ports such as Bude would sail across the Bristol Channel to the Vale of Glamorgan to load up with rock from coastal limestone quarries (lias limestone from S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronoid Process Of The Mandible
In human anatomy, the mandible's coronoid process (from Greek ''korōnē'', denoting something hooked) is a thin, triangular eminence, which is flattened from side to side and varies in shape and size. Its anterior border is convex and is continuous below with the anterior border of the ramus. Its ''posterior border'' is concave and forms the anterior boundary of the mandibular notch. The ''lateral surface'' is smooth, and affords insertion to the temporalis and masseter muscles. Its ''medial surface'' gives insertion to the temporalis, and presents a ridge which begins near the apex of the process and runs downward and forward to the inner side of the last molar tooth. Between this ridge and the anterior border is a grooved triangular area, the upper part of which gives attachment to the temporalis, the lower part to some fibers of the buccinator. Clinical significance Fractures of the mandible are common. However, coronoid process fractures are very rare. Isolated fractures of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoasthenocormus
''Pseudoasthenocormus'' is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Pachycormidae. It contains one species, ''P. retrodorsalis''. It lived during the upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian– Tithonian, about 152–148 million years ago) and its fossil remains have been found in Germany.Eastman, C. R. (1914). Catalog of the fossil fishes in the Carnegie Museum. Memoirs of the Carnegie Museum. Vol. VI. No. 7. Description Large in size, this fish easily exceeded one metre in length. Like many other similar genera, ''Pseudoasthenocormus'' possessed a robust and compact body, although generally more slender than '' Asthenocormus''. As indicated by the specific epithet, the dorsal fin is set back, originating just behind the anal, and is much shorter than the latter. The dorsal fin is composed of a few rays, which decrease in size posteriorly. The anal fin has become independent, with the rays (about 30) starting almost vertically from the haemal arches. The palate was equippe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthynotus
''Euthynotus'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the early Toarcian stage of the Early Jurassic epoch. It is generally considered the basalmost pachycormiform. Species ''Euthynotus'' has two species classified within it: * ''Euthynotus incognitus'' Blainville, 1818 * ''Euthynotus intermedius'' Agassiz, 1839 See also * Prehistoric fish The evolution of fish began about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian explosion. It was during this time that the early chordates developed the skull and the vertebral column, leading to the first craniates and vertebrates. The first fis ... * List of prehistoric bony fish References Early Jurassic fish Pachycormiformes Jurassic fish of Europe {{Jurassic-fish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonnerichthys
''Bonnerichthys'' is a genus of fossil fishes within the family Pachycormidae that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period Fossil remains of this taxon were first described from the Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk Formation of Kansas (Late Coniacian-Early Campanian, about 87-81 million years ago), and additional material was later reported from the Pierre Shale, Mooreville Chalk, Demopolis Chalk, Wenonah Formation, and Moreno Formation, among other localities. It grew to around 6 m (20 ft) in length, substantially less than the related ''Leedsichthys'' from the Jurassic which likely grew up to 17 m (56 ft). Feeding One of the most significant features of ''Bonnerichthys'' is the recognition that it was a filter feeder, living on plankton. This recognition that many large-bodied fish from the Mesozoic in the Pachycormidae were filter feeders shows that this niche was filled for at least 100 million years before previously known. The modern niche is filled by several s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohmdenia
''Ohmdenia'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived from the Toarcian stage of the Early Jurassic epoch. ''Ohmdenia'' was first described in 1953 by B. Hauff, based on a fossil found in the well-known Posidonia Shale in Holzmaden, Germany. For a long time this animal has been considered a close relative of '' Birgeria'', a great predator typical of the Triassic period with an uncertain systematic position. Further studies have shown similarities with the Pachycormiformes, a group considered close to the origin of teleosts and also including giant forms and planktives (e.g. ''Leedsichthys''). Some studies have erroneously indicated ''Ohmdenia'' as a synonym of ''Saurostomus'', other studies have instead placed ''Ohmdenia'' as an important evolutionary passage between the basal pachicormiforms and the more derived planktivore pachicormiformes.Romano, C. & Brinkmann, W. 2009 Reappraisal of the lower actinopterygian ''Birgeria stensioei'' Aldinger, 1931 (Osteichthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protosphyraena
''Protosphyraena'' is a fossil genus of swordfish-like marine fish, that thrived worldwide during the Upper Cretaceous Period (Coniacian-Maastrichtian). Though fossil remains of this taxon have been found in both Europe and Asia, it is perhaps best known from the Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk Formation of Kansas (Late Coniacian-Early Campanian). ''Protosphyraena'' was a large fish, averaging 2–3 metres in length. ''Protosphyraena'' shared the Cretaceous oceans with aquatic reptiles, such as mosasaurs and plesiosaurs, as well as with many other species of extinct predatory fish. The name ''Protosphyraena'' is a combination of the Greek word ''protos'' ("early") plus '' Sphyraena'', the genus name for barracuda, as paleontologists initially mistook ''Protosphyraena'' for an ancestral barracuda. Recent research shows that the genus ''Protosphyraena'' is not at all related to the true swordfish-family Xiphiidae, but belongs to the extinct family Pachycormidae. History a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspidorhynchiformes
Aspidorhynchiformes (from New Latin "shield-snout forms") is an extinct order of ray-finned fish. It contains only a single family, the Aspidorhynchidae. Members of the group are noted for their elongated, conical rostrums, of varying length, formed from fused premaxillae. They are generally interpreted as stem-group teleosts. The range of the group extends from the Middle Jurassic to the late Paleocene. Taxonomic history The order was described by Pieter Bleeker in 1859. Aspidorhynchiformes has one family, which is divided into at least two genera: * Order †Aspidorhynchiformes Bleeker 1859 spidorhynchida; Aspidorhynchoidei Bleeker 1859** Family †Aspidorhynchidae Bleeker 1859 inctiferidae Silva Santos 1990; Diphyodontidae Jordan 1923*** Genus †'' Jonoichthys'' Gouiric-Cavalli 2015 *** Genus ?†'' Ophirachis'' Costa 1854 *** Genus †'' Platycerhynchus'' Costa 1864 *** Genus †'' Pseudovinctifer'' Arratia 2015 *** Genus †'' Richmondichthys'' Bartholomai 2004 *** Genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxonomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
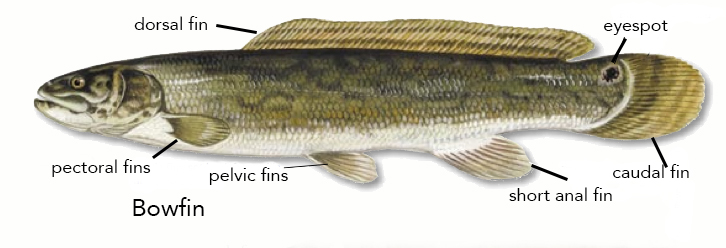
Bowfin
The bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a bony fish, native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being the sole surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "primitive fish" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Now, their range is limited to much of the eastern United States and adjacent southern Canada, including th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)