|
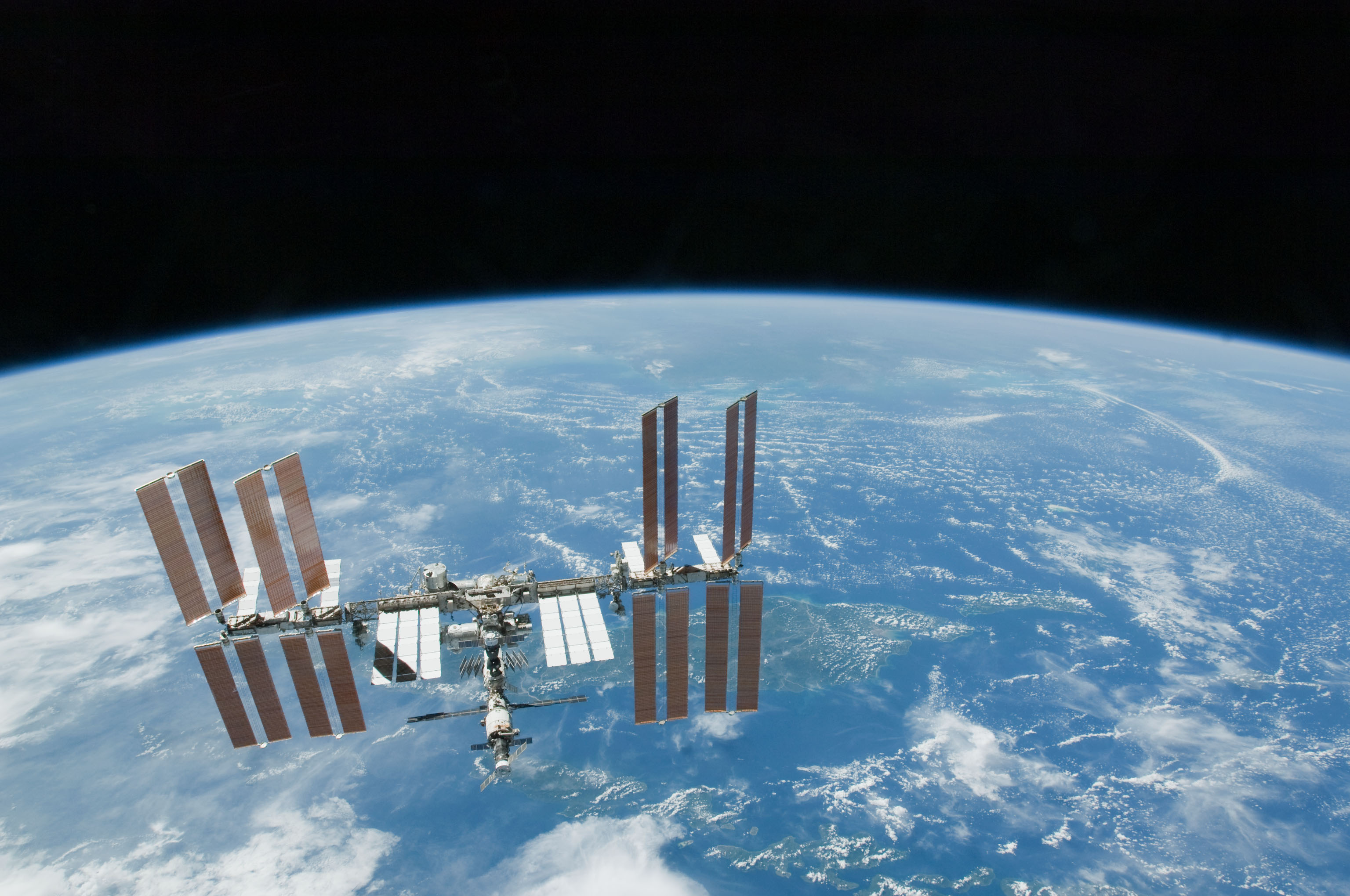
PSLV Orbital Experiment Module
---- PSLV Orbital Experiment Platform (POEM) also known as PSLV Stage 4 Orbital Platform (PS4-OP) is an orbital micro-gravity test bed based on spent fourth stage of PSLV. By adding modular subsystems for power generation, communication and stabilization like photovoltaic cells, Telemetry and Telecommand (TT&C) package, attitude control system, data storage etc to the PSLV fourth stage, it can function as a satellite bus. This augmented stage can then host payloads for up to six months while in orbit, making it useful for qualifying components, gaining space heritage and conduct experiments in micro-gravity conditions. Usually the fourth stage of PSLV is discarded after deployment of satellite and remains in orbit for a significant duration in a passive state as a piece of space debris. Objective POEM or PS4-OP was conceived by VSSC/ISRO to help Indian academia and start-ups by providing a low cost platform with essential subsystems to support their payloads hence lowering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro-gravity
The term micro-g environment (also μg, often referred to by the term microgravity) is more or less synonymous with the terms ''weightlessness'' and ''zero-g'', but emphasising that g-forces are never exactly zero—just very small (on the International Space Station (ISS), for example, the small g-forces come from tidal effects, gravity from objects other than the Earth, such as astronauts, the spacecraft, and the Sun, air resistance, and astronaut movements that impart momentum to the space station). The symbol for microgravity, ''μg'', was used on the insignias of Space Shuttle flights STS-87 and STS-107, because these flights were devoted to microgravity research in low Earth orbit. The most commonly known microgravity environment can be found aboard the ISS which is located in low-earth orbit at an altitude of around 400 km, orbiting Earth approximately 15 times per day in what is considered free fall. The effects of free fall also enable the creation of short-du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin-stabilisation
Spin stabilization is the method of stabilizing a satellite or launch vehicle by means of spin, i.e. rotation along the longitudinal axis. The concept originates from ballistics, where the spin is commonly obtain by means of rifling. For most satellite applications this approach has been superseded by three-axis stabilization. Despinning can be achieved by various techniques, including yo-yo de-spin. Use On rockets with a solid motor upper stage, spin stabilization is used to keep the motor from drifting off course as they don't have their own thrusters. Usually small rockets are used to spin up the spacecraft and rocket then fire the rocket and send the craft off. Some rockets, like the Jupiter-C, Delta II, Minotaur V and the satellite Aryabhata are spin-stabilised. The Pioneer 4 spacecraft, the second object sent on a lunar flyby in 1959, maintained its attitude using spin-stabilization. The Schiaparelli EDM lander was spun up to 2.5 RPM before being ejected from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preamble To The Constitution Of India
The Preamble of the Constitution of India presents the principles of the Constitution and indicates the sources of its authority It was adopted on 26 November 1949 by the Constituent Assembly and came into effect on 26 January 1950, celebrated as the Republic Day of India. It was amended during Indian emergency by Indira Gandhi where the words "socialist" and "secular" were added. Text Historical background The preamble is based on the Objectives Resolution, which was drafted and moved in the Constituent Assembly by Jawaharlal Nehru on 13 December 1946 accepted on 22 January 1947 and adopted by the Constituent Assembly on 26 November 1949, coming into force on 26 January 1950. B. R. Ambedkar said about the preamble: It was, indeed, a way of life, which recognizes liberty, equality, and fraternity as the principles of life and which cannot be divorced from each other: Liberty cannot be divorced from equality; equality cannot be divorced from liberty. Nor can liberty and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhruva Space
Dhruva Space Private Limited is an Indian private aerospace manufacturer headquartered in Hyderabad, India. Founded in 2012 by Sanjay Srikanth Nekkanti, the company is engaged in the development of small satellites in the commercial, governmental and academic markets. It provides full-stack space-engineering solutions across launch, space and ground segments. The founding team is composed of business and technology leaders who were formerly working with Exseed Space (now called Satellize), ams AG, Cisco and KPMG and all of whom are alumni of institutes such as BITS Pilani, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, EMLYON Business School, Luleå University of Technology and Arizona State University. History In 2014, Dhruva Space signed a deal with AMSAT India to develop HAMSAT-II. In December 2019, Dhruva Space raised ₹5 crore in funding led by Mumbai Angels Network. On 20 November 2020, Dhruva Space entered into an MoU with Skyroot Aerospace, an Indian private satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NewSpace India Limited
NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) is a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) of Government of India and commercial arm of Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was established on 6 March 2019 under the administrative control of Department of Space (DoS) and the Company Act 2013. The main objective of NSIL is to scale up private sector participation in Indian space programmes. Objectives NSIL was setup with the following objectives: * Transfer of Small Satellite technology to industry: NSIL will obtain license from DoS/ISRO and sub-license the same to industry * Manufacture of Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) in collaboration with private sector * Production of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) through Indian industry * Production and marketing of Space based products and services, including launch and application * Transfer of technology developed by ISRO Centres and constituent units of DoS * Marketing of spin-off technologies and products/services, both in India and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
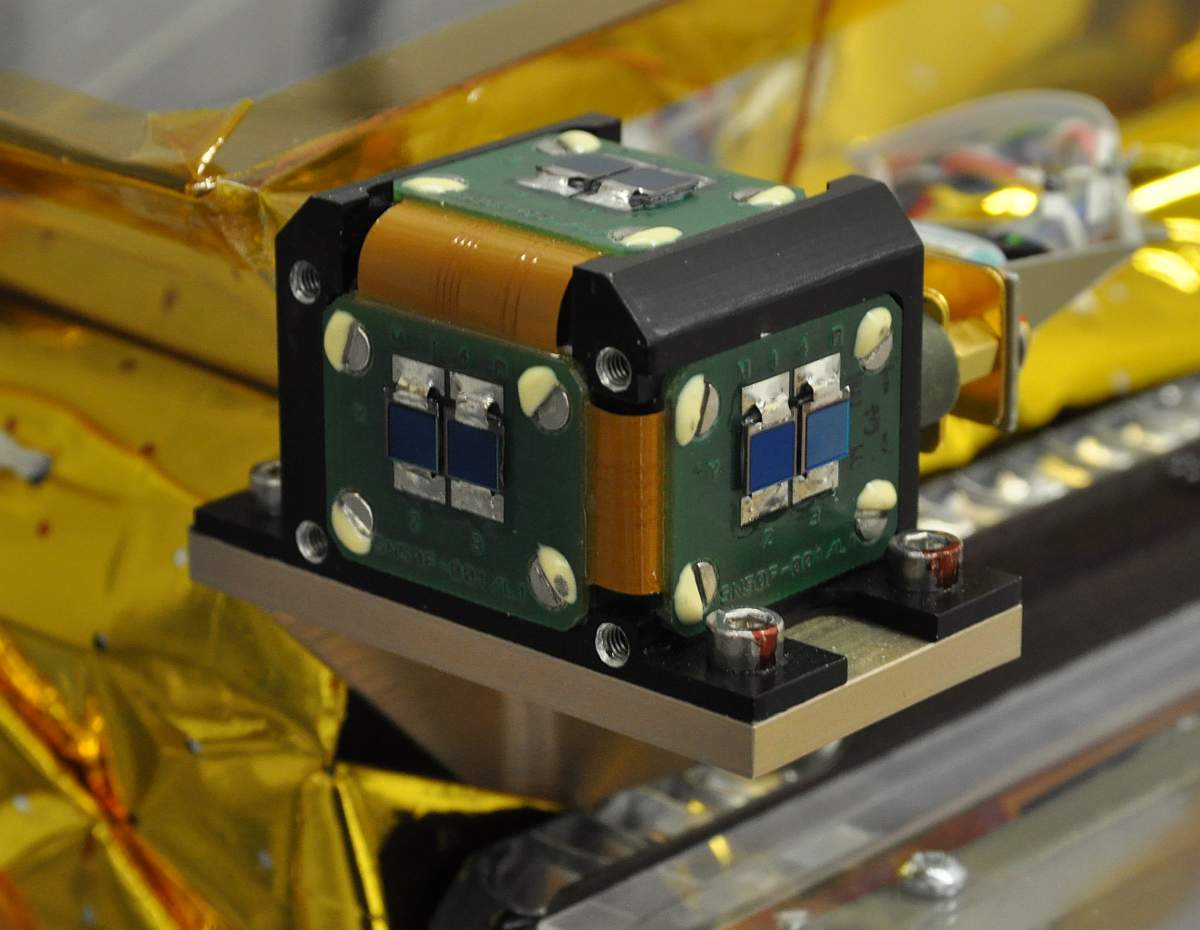
Sun Sensor
A sun sensor is a navigational instrument used by spacecraft to detect the position of the sun. Sun sensors are used for attitude control, solar array pointing, gyro updating, and fail-safe recovery. In addition to spacecraft, sun sensors find use in ground-based weather stations and sun-tracking systems, and aerial vehicles including balloons and UAVs. Mechanism There are various types of sun sensors, which differ in their technology and performance characteristics. Sun presence sensors provide a binary output, indicating when the sun is within the sensor's field of view. Analog and digital sun sensors, in contrast, indicate the angle of the sun by continuous and discrete signal outputs, respectively. In typical sun sensors, a thin slit at the top of a rectangular chamber allows a line of light to fall on an array of photodetector cells at the bottom of the chamber. A voltage is induced in these cells, which is registered electronically. By orienting two sensors perpendicul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number (SATCAT, also known as NORAD (North American Aerospace Defense) Catalog Number, NORAD ID, USSPACECOM object number or simply catalog number, among similar variants) is a sequential nine-digit number assigned by the United States Space Command (USSPACECOM) in the order of launch or discovery to all artificial objects in the orbits of Earth and those that left Earth's orbit. The first catalogued object, catalog number 1, is the Sputnik 1 launch vehicle, with the Sputnik 1 satellite having been assigned catalog number 2. __NOTOC__ Objects that fail to orbit or orbit for a short time are not catalogued. The minimum object size in the catalog is in diameter. , the catalog listed 54,200 objects, including 14,102 satellites that had been launched into orbit since 1957 of which 7,043 were still active. 24,146 of the objects were well tracked while 1,850 were lost. In addition USSPACECOM was also tracking 20,900 analyst objects. Analyst objects are variably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Designator
The International Designator, also known as COSPAR ID, is an international identifier assigned to artificial objects in space. It consists of the launch year, a three-digit incrementing launch number of that year and up to a three-letter code representing the sequential identifier of a piece in a launch. In TLE format the first two digits of the year and the dash are dropped. For example1990-037Ais the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' on mission STS-31, which carried the Hubble Space Telescope1990-037B into space. This launch was the 37th known successful launch worldwide in 1990. The designation system has been generally known as the COSPAR system, named for the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) of the International Council for Science. COSPAR subsumed the first designation system, devised at Harvard University. That system used letters of the Greek alphabet to designate artificial satellites. This was based on the scientific naming convention for natural satellites. For example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSLV-C58
The PSLV C-58 was the 60th flight of the Indian Space Research Organisation's Polar Satellite launch Vehicle. It carried the XPoSAT mission along with rideshare payloads. Payload Besides XPoSat, the rocket carried 10 other payloads on PSLV Orbital Experiment Module (POEM) - 3. Along side them, two payloads by Indian Space Research Organisation's (ISRO) Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) and one by the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) were manifested for the flight. On PSLV-C58/XPoSat campaign, POEM-3 hosted ten payloads weighing ~145 kg cumulatively. PSLV fourth stage was lowered to 350 km orbit at 9.6° inclination after deploying XPoSat to reach the POEM-3 operational orbit. For power generation and storage it will again have flexible solar panels in conjunction with 50Ah Li-Ion battery and will be three-axis stabilized. Payloads hosted on POEM-3 are following, seven of them facilitated by IN-SPACe and three are by ISRO, # Radiation Shielding Experimental Module (RSEM) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XPoSat
The X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) is an ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) manufactured space observatory to study Polarization (waves), polarisation of X-ray astronomy, cosmic X-rays. It was launched on 1 January 2024 on a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, PSLV rocket, and it has an expected operational lifespan of at least five years. The telescope was developed by the Raman Research Institute (RRI) in close collaboration with U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC). As per ISRO, this mission will complement the efforts of US space agency NASA, which launched its Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) in 2021 by observing space events across a broad energy range of 2-30 keV. Overview Studying how radiation is polarised gives away the nature of its source, including the strength and distribution of its magnetic fields and the nature of other radiation around it. XPoSat will study the 50 brightest known sources in the universe, including pulsars, X-ray binary, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_without_DLA_upper.png)


.jpg)
